Abstract
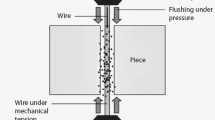
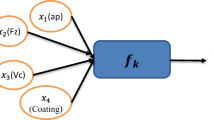
In this paper, an intelligent approach of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm-II (NSGA-II) was delineated to establish model and optimize the wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) process. The WEDM experiments were designed utilizing Taguchi L18 mixed orthogonal array for machining of Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy. The ANFIS model was delineated to explain the influence of input machining characteristics, viz. peak current (IP), pulse on-time (Ton), pulse off-time (Toff) and wire feed (WF) on output response of material removal rate (MRR) and wire wear ratio (WWR). The proximity of results with confirmation experimental results revealed the effectiveness of the developed ANFIS model in prediction of output quality characteristics for the chosen input machining factors. The artificial neural network (ANN) and NSGA-II were integrated and applied for multi-objective optimization in determining optimal WEDM machining process conditions. The optimal results obtained with NSGA-II for multi-objective optimization of input control variables are within tolerance limits and realized an improvement in MRR and WWR (maximum absolute percentage errors as 6.784% and 7.589%) with optimal machining characteristics.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal V, Khangura SS, Garg RK (2015) Parametric modeling and optimization for wire electrical discharge machining of Inconel 718 using response surface methodology. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79(1–4):31–47
Magabe R, Sharma N, Gupta K, Davim JP (2019) Modeling and optimization of Wire-EDM parameters for machining of Ni 55.8 Ti shape memory alloy using hybrid approach of Taguchi and NSGA-II. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 102(5–8):1703–1717
Kanagarajan D, Karthikeyan R, Palanikumar K, Davim JP (2008) Optimization of electrical discharge machining characteristics of WC/Co composites using non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (NSGA-II). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 36(11–12):1124–1132
Eswaramoorthy SB, Shanmugham EP (2015) Optimal control parameters of machining in CNC wire-cut EDM for titanium. Int J Appl Sci Eng Res 4(1):102–121
Dambatta YS, Sayuti M, Sarhan AA, Ab Shukor HB, Binti Derahman NA, Manladan SM (2019) Prediction of specific grinding forces and surface roughness in machining of AL6061-T6 alloy using ANFIS technique. Ind Lubr Tribol 71:309–317
Sharma N, Khanna R, Gupta RD (2015) WEDM process variables investigation for HSLA by response surface methodology and genetic algorithm. Eng Sci Technol Int J 18(2):171–177
Mahapatra SS, Patnaik A (2006) Parametric optimization of wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) process using Taguchi method. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 28(4):422–429
Goyal A (2017) Investigation of material removal rate and surface roughness during wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) of Inconel 625 super alloy by cryogenic treated tool electrode. J King Saud Univ Sci 29(4):528–535
Gauri SK, Chakraborty S (2010) A study on the performance of some multi-response optimisation methods for WEDM processes. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 49(1–4):155–166
Kuriachen B, Somashekhar KP, Mathew J (2015) Multiresponse optimization of micro-wire electrical discharge machining process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 76(1–4):91–104
Manna A, Bhattacharyya B (2006) Taguchi and Gauss elimination method: a dual response approach for parametric optimization of CNC wire cut EDM of PRAlSiCMMC. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 28(1–2):67–75
Bobbili R, Madhu V, Gogia AK (2015) Modelling and analysis of material removal rate and surface roughness in wire-cut EDM of armour materials. Eng Sci Technol Int J 18(4):664–668
Majumder A (2013) Process parameter optimization during EDM of AISI 316 LN stainless steel by using fuzzy based multi-objective PSO. J Mech Sci Technol 27(7):2143–2151
Maji K, Pratihar DK (2011) Modeling of electrical discharge machining process using conventional regression analysis and genetic algorithms. J Mater Eng Perform 20(7):1121–1127
Pasam VK, Battula SB, Madar Valli P, Swapna M (2010) Optimizing surface finish in WEDM using the Taguchi parameter design method. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 32(2):107–113
Goswami A, Kumar J (2014) Investigation of surface integrity, material removal rate and wire wear ratio for WEDM of Nimonic 80A alloy using GRA and Taguchi method. Eng Sci Technol Int J 17(4):173–184
Torres A, Puertas I, Luis CJ (2016) EDM machinability and surface roughness analysis of INCONEL 600 using graphite electrodes. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 84(9–12):2671–2688
Singh V, Bhandari R, Yadav VK (2017) An experimental investigation on machining parameters of AISI D2 steel using WEDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93(1–4):203–214
Kumar SS, Uthayakumar M, Kumaran ST, Parameswaran P, Mohandas E, Kempulraj G, Babu BR, Natarajan SA (2015) Parametric optimization of wire electrical discharge machining on aluminium based composites through grey relational analysis. J Manuf Process 20:33–39
Yang RT, Tzeng CJ, Yang YK, Hsieh MH (2012) Optimization of wire electrical discharge machining process parameters for cutting tungsten. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 60(1–4):135–147
Yadav RN, Yadava V (2013) Multiobjective optimization of slotted electrical discharge abrasive grinding of metal matrix composite using artificial neural network and nondominated sorting genetic algorithm. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 227(10):1442–1452
Conde A, Arriandiaga A, Sanchez JA, Portillo E, Plaza S, Cabanes I (2018) High accuracy wire electrical discharge machining using artificial neural networks and optimization techniques. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 49:24–38
Mukhopadhyay A, Barman TK, Sahoo P, Davim JP (2019) Modeling and optimization of fractal dimension in wire electrical discharge machining of EN 31 steel using the ANN-GA approach. Materials 12(3):454
Shakeri S, Ghassemi A, Hassani M, Hajian A (2016) Investigation of material removal rate and surface roughness in wire electrical discharge machining process for cementation alloy steel using artificial neural network. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82(1–4):549–557
Goyal A, Rahman HU, Ghani SAC (2020) Experimental investigation and optimisation of wire electrical discharge machining process parameters for Ni49Ti51 shape memory alloy. J King Saud Univ Eng Sci 33:129–135
Das PP, Diyaley S, Chakraborty S, Ghadai RK (2019) Multi-objective optimization of wire electro discharge machining (WEDM) process parameters using grey-fuzzy approach. Period Polytech Mech Eng 63(1):16–25
Vates UK, Singh NK, Singh RV (2016) Modelling and optimisation of wire electrical discharge machining process on D2 steel using ANN and RMSE approach. Int J Comput Mater Sci Surf Eng 6(3–4):161–185
Hasçalık A, Çaydaş U (2007) Electrical discharge machining of titanium alloy (Ti–6Al–4V). Appl Surf Sci 253(22):9007–9016
Javadi Y, Sadeghi S, Najafabadi MA (2014) Taguchi optimization and ultrasonic measurement of residual stresses in the friction stir welding. Mater Des 55:27–34
Ramamurthy A, Sivaramakrishnan R, Muthuramalingam T (2015) Taguchi-Grey computation methodology for optimum multiple performance measures on machining titanium alloy in WEDM process. Indian J Eng Mater Sci (IJEMS) 22:181–186
Sai T, Pathak VK, Srivastava AK (2020) Modeling and optimization of fused deposition modeling (FDM) process through printing PLA implants using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) model and whale optimization algorithm. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42(12):1–19
Unune DR, Nirala CK, Mali HS (2018) ANN-NSGA-II dual approach for modeling and optimization in abrasive mixed electro discharge diamond grinding of Monel K-500. Eng Sci Technol Int J 21(3):322–329
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan TAMT (2002) A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6(2):182–197
Huu PN, Tien LB, Duc QT, Van DP, Xuan CN, Van TN, Duc LN, Jamil M, Khan AM (2019) Multi-objective optimization of process parameter in EDM using low-frequency vibration of workpiece assigned for SKD61. Sādhanā 44(10):1–11
Funding
This research work does not receive any external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goyal, A., Gautam, N. & Pathak, V.K. An adaptive neuro-fuzzy and NSGA-II-based hybrid approach for modelling and multi-objective optimization of WEDM quality characteristics during machining titanium alloy. Neural Comput & Applic 33, 16659–16674 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06261-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06261-7