Abstract
Purpose
Cumulative sensory neurotoxicity induced by oxaliplatin impairs patients’ quality of life and treatment continuation. This study investigated the relationship between physician-assessed and patient-reported oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy (OIPN) during treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) over time.
Methods
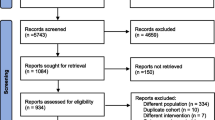
A post hoc analysis was conducted for 191 patients with mCRC who received mFOLFOX6 plus bevacizumab in the WJOG4407G trial. Physician-assessed OIPN was graded by CTCAE every 2 weeks. Patient-reported OIPN was assessed with the FACT/GOG-Ntx (11 items, best score 44) at baseline and at 3, 6, and 9 months. Physician underestimation was defined as when the highest scores of the NTX1–4 sensory subscale/CTCAE grade were 2/0, 3/0–1, or 4/0–1, and overestimation as 0/2–3, 1/2–3, or 2/3.
Results
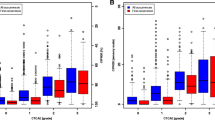
The median total dose (range) of oxaliplatin was 762 (85–5950) mg/m2. Overall, the least squares mean of FACT/GOG-Ntx scores (standard error), estimated by a linear mixed model, were 36 (0.8), 34 (0.9), 29 (1.0), and 27 (1.1) for CTCAE grades 0, 1, 2, and 3, respectively. FACT/GOG-Ntx scores were weakly-to-moderately correlated with CTCAE grade (Spearman’s r = − 0.24 [p = 0.0026], − 0.46 [p < 0.0001], and − 0.56 [p < 0.0001] at 3, 6, and 9 months, respectively). OIPN was underestimated in 85/159 (54%), 43/109 (39%), and 18/69 (26%) patients at 3, 6, and 9 months, respectively. In contrast, OIPN was overestimated in less than 5% of the patients at any time.
Conclusion
During early treatment, physician underestimation of OIPN in patients with mCRC is likely.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hochster HS, Hart LL, Ramanathan RK, Childs BH, Hainsworth JD, Cohn AL, Wong L, Fehrenbacher L, Abubakr Y, Saif MW, Schwartzberg L, Hedrick E (2008) Safety and efficacy of oxaliplatin and fluoropyrimidine regimens with or without bevacizumab as first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: results of the TREE study. J Clin Oncol 26:3523–3529
Cassidy J, Tabernero J, Twelves C, Brunet R, Butts C, Conroy T, Debraud F, Figer A, Grossmann J, Sawada N, Schoffski P, Sobrero A, Van Cutsem E, Diaz-Rubio E (2004) XELOX (capecitabine plus oxaliplatin): active first-line therapy for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 22:2084–2091
Loupakis F, Cremolini C, Masi G, Lonardi S, Zagonel V, Salvatore L, Cortesi E, Tomasello G, Ronzoni M, Spadi R, Zaniboni A, Tonini G, Buonadonna A, Amoroso D, Chiara S, Carlomagno C, Boni C, Allegrini G, Boni L, Falcone A (2014) Initial therapy with FOLFOXIRI and bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 371:1609–1618
Yamada Y, Higuchi K, Nishikawa K, Gotoh M, Fuse N, Sugimoto N, Nishina T, Amagai K, Chin K, Niwa Y, Tsuji A, Imamura H, Tsuda M, Yasui H, Fujii H, Yamaguchi K, Yasui H, Hironaka S, Shimada K, Miwa H, Hamada C, Hyodo I (2015) Phase III study comparing oxaliplatin plus S-1 with cisplatin plus S-1 in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced gastric cancer. Ann Oncol 26:141–148
Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouche O, Guimbaud R, Becouarn Y, Adenis A, Raoul JL, Gourgou-Bourgade S, de la Fouchardiere C, Bennouna J, Bachet JB, Khemissa-Akouz F, Pere-Verge D, Delbaldo C, Assenat E, Chauffert B, Michel P, Montoto-Grillot C, Ducreux M, Groupe Tumeurs Digestives of U, Intergroup P (2011) FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med 364: 1817–1825
Argyriou AA, Cavaletti G, Briani C, Velasco R, Bruna J, Campagnolo M, Alberti P, Bergamo F, Cortinovis D, Cazzaniga M, Santos C, Papadimitriou K, Kalofonos HP (2013) Clinical pattern and associations of oxaliplatin acute neurotoxicity: a prospective study in 170 patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer 119:438–444
Jordan B, Margulies A, Cardoso F, Cavaletti G, Haugnes HS, Jahn P, Le Rhun E, Preusser M, Scotte F, Taphoorn MJB, Jordan K, clinicalguidelines@esmo.org EGCEa, eons.secretariat@cancernurse.eu EEWGEa, office@eano.eu EGCEa (2020) Systemic anticancer therapy-induced peripheral and central neurotoxicity: ESMO-EONS-EANO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, prevention, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 31:1306–1319
Loprinzi CL, Lacchetti C, Bleeker J, Cavaletti G, Chauhan C, Hertz DL, Kelley MR, Lavino A, Lustberg MB, Paice JA, Schneider BP, Lavoie Smith EM, Smith ML, Smith TJ, Wagner-Johnston N, Hershman DL (2020) Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: ASCO guideline update. J Clin Oncol 38:3325–3348
Frigeni B, Piatti M, Lanzani F, Alberti P, Villa P, Zanna C, Ceracchi M, Ildebrando M, Cavaletti G (2011) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity can be misdiagnosed by the National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity scale. J Peripher Nerv Syst 16:228–236
Postma TJ, Heimans JJ, Muller MJ, Ossenkoppele GJ, Vermorken JB, Aaronson NK (1998) Pitfalls in grading severity of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Ann Oncol 9:739–744
Nyrop KA, Deal AM, Reeder-Hayes KE, Shachar SS, Reeve BB, Basch E, Choi SK, Lee JT, Wood WA, Anders CK, Carey LA, Dees EC, Jolly TA, Kimmick GG, Karuturi MS, Reinbolt RE, Speca JC, Muss HB (2019) Patient-reported and clinician-reported chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients with early breast cancer: current clinical practice. Cancer 125:2945–2954
Shimozuma K, Ohashi Y, Takeuchi A, Aranishi T, Morita S, Kuroi K, Ohsumi S, Makino H, Mukai H, Katsumata N, Sunada Y, Watanabe T, Hausheer FH (2009) Feasibility and validity of the Patient Neurotoxicity Questionnaire during taxane chemotherapy in a phase III randomized trial in patients with breast cancer: N-SAS BC 02 support. Care Cancer 17:1483–1491
Cavaletti G, Frigeni B, Lanzani F, Mattavelli L, Susani E, Alberti P, Cortinovis D, Bidoli P (2010) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity assessment: a critical revision of the currently available tools. Eur J Cancer 46:479–494
de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, Homerin M, Hmissi A, Cassidy J, Boni C, Cortes-Funes H, Cervantes A, Freyer G, Papamichael D, Le Bail N, Louvet C, Hendler D, de Braud F, Wilson C, Morvan F, Bonetti A (2000) Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 18:2938–2947
Cassidy J, Misset JL (2002) Oxaliplatin-related side effects: characteristics and management. Semin Oncol 29:11–20
Yamazaki K, Nagase M, Tamagawa H, Ueda S, Tamura T, Murata K, Eguchi Nakajima T, Baba E, Tsuda M, Moriwaki T, Esaki T, Tsuji Y, Muro K, Taira K, Denda T, Funai S, Shinozaki K, Yamashita H, Sugimoto N, Okuno T, Nishina T, Umeki M, Kurimoto T, Takayama T, Tsuji A, Yoshida M, Hosokawa A, Shibata Y, Suyama K, Okabe M, Suzuki K, Seki N, Kawakami K, Sato M, Fujikawa K, Hirashima T, Shimura T, Taku K, Otsuji T, Tamura F, Shinozaki E, Nakashima K, Hara H, Tsushima T, Ando M, Morita S, Boku N, Hyodo I (2016) Randomized phase III study of bevacizumab plus FOLFIRI and bevacizumab plus mFOLFOX6 as first-line treatment for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (WJOG4407G). Ann Oncol 27:1539–1546
Cella D, Peterman A, Hudgens S, Webster K, Socinski MA (2003) Measuring the side effects of taxane therapy in oncology: the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-taxane (FACT-taxane). Cancer 98:822–831
Alberti P, Rossi E, Cornblath DR, Merkies IS, Postma TJ, Frigeni B, Bruna J, Velasco R, Argyriou AA, Kalofonos HP, Psimaras D, Ricard D, Pace A, Galie E, Briani C, Dalla Torre C, Faber CG, Lalisang RI, Boogerd W, Brandsma D, Koeppen S, Hense J, Storey D, Kerrigan S, Schenone A, Fabbri S, Valsecchi MG, Cavaletti G, Group CI-P (2014) Physician-assessed and patient-reported outcome measures in chemotherapy-induced sensory peripheral neurotoxicity: two sides of the same coin. Ann Oncol 25:257–264
Cavaletti G, Cornblath DR, Merkies ISJ, Postma TJ, Rossi E, Frigeni B, Alberti P, Bruna J, Velasco R, Argyriou AA, Kalofonos HP, Psimaras D, Ricard D, Pace A, Galie E, Briani C, Dalla Torre C, Faber CG, Lalisang RI, Boogerd W, Brandsma D, Koeppen S, Hense J, Storey D, Kerrigan S, Schenone A, Fabbri S, Valsecchi MG, Group CI-P, Mazzeo A, Pace A, Pessino A, Schenone A, Toscano A, Argyriou AA, Brouwer B, Frigeni B, Piras B, Briani C, Dalla Torre C, Dominguez Gonzalez C, Faber CG, Tomasello C, Binda D, Brandsma D, Cortinovis D, Psimaras D, Ricard D, Storey D, Cornblath DR, Galie E, Lindeck Pozza E, Rossi E, Vanhoutte EK, Lanzani F, Pastorelli F, Altavilla G, Cavaletti G, Granata G, Kalofonos HP, Ghignotti I, Merkies ISJ, Bruna J, Hense J, Heimans JJ, Mattavelli L, Padua L, Reni L, Bakkers M, Boogerd M, Campagnolo M, Cazzaniga M, Eurelings M, Leandri M, Lucchetta M, Penas Prado M, Russo M, Valsecchi MG, Piatti ML, Alberti P, Bidoli P, Grant R, Plasmati R, Velasco R, Lalisang RI, Meijer RJ, Fabbri S, Dorsey SG, Galimberti S, Kerrigan S, Koeppen S, Postma TJ, Boogerd W, Grisold W (2013) The chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy outcome measures standardization study: from consensus to the first validity and reliability findings. Ann Oncol 24:454–462
Le-Rademacher J, Kanwar R, Seisler D, Pachman DR, Qin R, Abyzov A, Ruddy KJ, Banck MS, Lavoie Smith EM, Dorsey SG, Aaronson NK, Sloan J, Loprinzi CL, Beutler AS (2017) Patient-reported (EORTC QLQ-CIPN20) versus physician-reported (CTCAE) quantification of oxaliplatin- and paclitaxel/carboplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in NCCTG/Alliance clinical trials. Support Care Cancer 25:3537–3544
Kopec J, Land S, Cecchini R, Ganz P, Cella D, Costantino J, Wieand H, Smith R, Kuebler J, Wolmark N (2006) Validation of a self-reported neurotoxicity scale in patients with operable colon cancer receiving oxaliplatin. J Supp Oncol 4:W1–W8
Pachman DR, Qin R, Seisler DK, Smith EM, Beutler AS, Ta LE, Lafky JM, Wagner-Johnston ND, Ruddy KJ, Dakhil S, Staff NP, Grothey A, Loprinzi CL (2015) Clinical course of oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy: results from the randomized phase III trial N08CB (Alliance). J Clin Oncol 33:3416–3422
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by Asahi Kasei Pharma. We thank the West Japan Oncology Group (WJOG) Data Center (K Mori, S Nakamura, and K Takeda).
Funding
This study was funded by a grant from Asahi Kasei Pharma.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Yuji Miura, Masahiko Ando, and Kentaro Yamazaki; methodology: Yuji Miura and Masahiko Ando; formal analysis and investigation: Yuji Miura and Masahiko Ando; writing (original draft preparation): Yuji Miura; writing (review and editing): Ichinosuke Hyodo, Narikazu Boku, Masahiko Ando, Kentaro Yamazaki, Shuichi Hironaka, and Kei Muro; funding acquisition: Ichinosuke Hyodo and Kei Muro; supervision: Ichinosuke Hyodo and Kei Muro.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Y. Miura reports receiving personal fees from ONO Pharmaceutical, Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD, and Chugai separate to the submitted work. M. Ando reports receiving personal fees from Asahi Kasei Pharma Corp. and grants from Kyowa Kirin Co. Ltd. separate to the submitted work. K. Yamazaki reports receiving personal fees from Chugai Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo, Yakult Honsha, Takeda, Bayer, Merck Serono, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Lilly, Sanofi, Ono Pharmaceutical, MSD, and Bristol-Myers Squibb separate to the submitted work. S. Hironaka reports receiving grants and personal fees from Chugai Pharma and Yakult Honsha during the conduct of the study; grants and personal fees from Sanofi, Ono Pharma, Taiho Pharma and AstraZeneca; and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb Japan, Daiichi Sankyo, Lilly, Merck, Tsumura & Co., Nihonkayaku, and MSD. K.K., Shionogi, Astellas Pharma, Takeda, Boehinger Ingelheim, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Pfizer, and Toyama Chemical Co. separate to the submitted work. N. Boku reports receiving research grants from Ono, Taiho, and Takeda and honorarium from Ono, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Taiho separate to the submitted work. K. Muro reports receiving grants and personal fees from Ono and Sanofi; grants from Daiichi Sankyo, Parexel International, Shionogi Pharma, Sumitomo Dainippon, MSD, Pfizer, Mediscience Planning, and Solasia Pharma; and personal fees from Eli Lilly, Chugai, Takeda, Taiho, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Bayer separate to the submitted work. I. Hyodo reports receiving grants and personal fees from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Bristol-Myers Squibb Co., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., and Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.; personal fees from Eli Lilly Japan and Asahi Kasei Pharma Corp.; and grants from Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. separate to the submitted work.
Ethical approval
The WJOG4407G trial protocol was approved by the ethics committees of all participating centers.
Statement of informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all enrolled patients in the WJOG4407G trial.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miura, Y., Ando, M., Yamazaki, K. et al. Time-dependent discrepancies between physician-assessed and patient-reported oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer who received mFOLFOX6 plus bevacizumab: a post hoc analysis (WJOG4407GSS2). Support Care Cancer 29, 3715–3723 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-020-05891-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-020-05891-2