Abstract
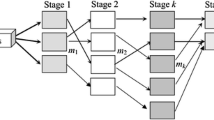
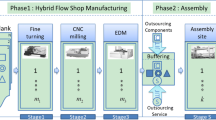
Proper scheduling of jobs is essential for modern production systems to work effectively. The hybrid flow shop scheduling problem is a scheduling problem with many applications in the industry. The problem has also attracted much attention from researchers due to its complexity. This study addresses the hybrid flow shop scheduling problem (HFSP), which considers unrelated parallel machines at each stage and the machine eligibility constraints. HFSP is a well-known NP-hard problem with the aim of minimizing the makespan. Owing to the complexity of the problem, this study develops constraint programming (CP) models for the HFSP and its extensions: the no-wait HFSP, the blocking HFSP, the HFSP with sequence-dependent setup times, the no-wait HFSP with sequence-dependent setup times, and the blocking HFSP with sequence-dependent setup times. We also propose two mixed-integer linear programming models (MILP) for no-wait and blocking HSFPs with sequence-dependent setup times. The performances of the CP models were tested against their MILP counterparts using randomly generated instances and benchmark instances from the literature. The computational results indicated that the proposed CP model outperformed the best MILP solutions for benchmark instances. It is also more effective for finding high-quality solutions for larger problem instances.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
All models, data sets, and solution results are available on Mendeley Data at http://dx.doi.org/10.17632/n4g8cfjg87.1.
References
Allahverdi A, Soroush HM (2008) The significance of reducing setup times/setup costs. Eur J Oper Res 187(3):978–984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2006.09.010
Allahverdi A, Ng CT, Cheng TCE, Kovalyov MY (2008) A survey of scheduling problems with setup times or costs. Eur J Oper Res 187(3):985–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2006.06.060
Aqil S, Allali K (2020) Local search metaheuristic for solving hybrid flow shop problem in slabs and beams manufacturing. Expert Syst Appl 162:113716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113716
Aqil S, Allali K (2021) Two efficient nature inspired meta-heuristics solving blocking hybrid flow shop manufacturing problem. Eng Appl Artif Intell 100:104196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104196
Arthanari TS, Ramamurthy KG (1971) An extension of two machines sequencing problem. Opsearch 8:10–22
Asefi H, Jolai F, Rabiee M, Tayebi Araghi ME (2014) A hybrid NSGA-II and VNS for solving a bi-objective no-wait flexible flowshop scheduling problem. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 75(5–8):1017–1033
Brah S, Hunsucker J, Shah J (1991) Mathematical modeling of scheduling problems. J Inf Optim Sci 12(1):113–137
Cao C, Zhang Y, Gu X, Li D, Li J (2020) An improved gravitational search algorithm to the hybrid flowshop with unrelated parallel machines scheduling problem. Int J Prod Res 59(18):5592–5608. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2020.1788732
Carlier J, Neron E (2000) An exact method for solving the multi-processor flow-shop. RAIRO Oper Res Recherche Opérationnelle 34(1):1–25
Carpov S, Carlier J, Nace D, Sirdey R (2012) Two-stage hybrid flow shop with precedence constraints and parallel machines at second stage. Comput Oper Res 39(3):736–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2011.05.020
Chang J, Ma G, Ma X (2006) A new heuristic for minimal makespan in no-wait hybrid flowshops. In: Chinese control conference, Harbin, China, pp 1352–1356. https://doi.org/10.1109/CHICC.2006.280673
Chen L, Xi LF, Cai JG, Bostel N, Dejax P (2006) Integrated approach for modeling and solving the scheduling problem of container handling systems. J Zhejiang Univ Sci 7(2):234–239
Chen L, Bostel N, Dejax P, Cai J, Xi L (2007) A tabu search algorithm for the integrated scheduling problem of container handling systems in a maritime terminal. Eur J Oper Res 181(1):40–58
Cheng TCE, Sriskandarajah C, Wang G (2000) Two- and three-stage flowshop scheduling with no-wait in process. Prod Oper Manag 9(4):367–378
Çolak M, Aydın Keskin G (2022) An extensive and systematic literature review for hybrid flowshop scheduling problems. Int J Ind Eng Comput 13:185–222. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ijiec.2021.12.001
Cui J, Li T, Zhang W (2005) Hybrid flowshop scheduling model and its genetic algorithm. [In Chinese]. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing 27(5):623–626. https://doi.org/10.13374/j.issn1001-053x.2005.05.058
Davoudpour H, Ashrafi M (2009) Solving multi-objective SDST flexible flow shop using GRASP algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 44(7–8):737–747
de Siqueira EC, Souza MJF, de Souza SR (2020) An MO-GVNS algorithm for solving a multiobjective hybrid flow shop scheduling problem. Int Trans Oper Res 27(1):614–650
Ebrahimi M, Fatemi Ghomi SMT, Karimi B (2014) Hybrid flow shop scheduling with sequence dependent family setup time and uncertain due dates. Appl Math Model 38(9–10):2490–2504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2013.10.061
Elmi A, Topaloglu S (2013) A scheduling problem in blocking hybrid flow shop robotic cells with multiple robots. Comput Oper Res 40(10):2543–2555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2013.01.024
Elmi A, Topaloglu S (2014) Scheduling multiple parts in hybrid flow shop robotic cells served by a single robot. Int J Comput Integr Manuf 27(12):1144–1159. https://doi.org/10.1080/0951192X.2013.874576
Fanjul-Peyro L, Ruiz R (2010) Iterated greedy local search methods for unrelated parallel machine scheduling. Eur J Oper Res 207(1):55–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2010.03.030
Fereidoonian F, Mirzazadeh A (2012) A genetic algorithm for the integrated scheduling model of a container-handling system in a maritime terminal. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part M J Eng Marit Environ 226(1):62–77
Fernandez-Viagas V, Costa A, Framinan JM (2020) Hybrid flow shop with multiple servers: a computational evaluation and efficient divide-and-conquer heuristics. Expert Syst Appl 153:113462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113462
Garavito-Hernández EA, Peña-Tibaduiza E, Perez-Figueredo LE, Moratto-Chimenty E (2019) A meta-heuristic based on the Imperialist Competitive Algorithm (ICA) for solving Hybrid Flow Shop (HFS) scheduling problem with unrelated parallel machines. J Ind Prod Eng 36(6):362–370. https://doi.org/10.1080/21681015.2019.1647299
Gedik R, Kirac E, Bennet Milburn A, Rainwater C (2017) A constraint programming approach for the team orienteering problem with time windows. Comput Ind Eng 107:178–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2017.03.017
Gheisariha E, Tavana M, Jolai F, Rabiee M (2021) A simulation–optimization model for solving flexible flow shop scheduling problems with rework and transportation. Math Comput Simul 180:152–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2020.08.019
Gholami M, Zandieh M, Alem-Tabriz A (2009) Scheduling hybrid flow shop with sequence-dependent setup times and machines with random breakdowns. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 42(1–2):189–201
Gil CB, Lee JH (2022) Deep reinforcement learning approach for material scheduling considering high-dimensional environment of hybrid flow-shop problem. Appl Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12189332
Gómez-Gasquet P, Andrés C, Lario FC (2012) An agent-based genetic algorithm for hybrid flowshops with sequence dependent setup times to minimise makespan. Expert Syst Appl 39(9):8095–8107
Grabowski J, Pempera J (2000) Sequencing of jobs in some production system. Eur J Oper Res 125(3):535–550
Gupta JND (1988) Two-stage, hybrid flowshop scheduling problem. J Oper Res Soc 39(4):359–3641
Ham AM, Cakici E (2016) Flexible job shop scheduling problem with parallel batch processing machines: MIP and CP approaches. Comput Ind Eng 102:160–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2016.11.001
Han W, Guo F, Su X (2019) A reinforcement learning method for a hybrid flow-shop scheduling problem. Algorithms 12(11):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/a12110222
Haouari M, Hidri L, Gharbi A (2006) Optimal scheduling of a two-stage hybrid flow shop. Math Methods Oper Res 64(1):107–124
Harbaoui H, Khalfallah S, Bellenguez-Morineau O (2017) A case study of a hybrid flow shop with no-wait and limited idle time to minimize material waste. In: IEEE 15th international symposium on intelligent systems and informatics (SISY), Subotica, Serbia, pp 207–212. https://doi.org/10.1109/SISY.2017.8080554
Huang RH, Yang CL, Huang YC (2009) No-wait two-stage multiprocessor flow shop scheduling with unit setup. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 44(9–10):921–927
IBM (2017) IBM ILOG CPLEX optimization studio CP optimizer user’s manual, 12th edn. IBM
Javadian N, Fattahi P, Farahmand-Mehr M, Amiri-Aref M, Kazemi M (2012) An immune algorithm for hybrid flow shop scheduling problem with time lags and sequence-dependent setup times. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 63(1–4):337–348
Jolai F, Sheikh S, Rabbani M, Karimi B (2009) A genetic algorithm for solving no-wait flexible flow lines with due window and job rejection. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 42(5–6):523–532
Jolai F, Rabiee M, Asefi H (2012) A novel hybrid meta-heuristic algorithm for a no-wait flexible flow shop scheduling problem with sequence dependent setup times. Int J Prod Res 50(24):7447–7466
Jungwattanakit J, Reodecha M, Chaovalitwongse P, Werner F (2008) Algorithms for flexible flow shop problems with unrelated parallel machines, setup times, and dual criteria. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 37(3–4):354–370
Jungwattanakit J, Reodecha M, Chaovalitwongse P, Werner F (2009) A comparison of scheduling algorithms for flexible flow shop problems with unrelated parallel machines, setup times, and dual criteria. Comput Oper Res 36(2):358–378
Kanet JJ, Ahire SL, Gorman MF (2004) Constraint programming for scheduling. In: Handbook of scheduling: algorithms, models, and performance analysis. University of Dayton MIS/OM/DS Faculty Publications Department, pp 1–22. http://ecommons.udayton.edu/mis_fac_pub/1
Karimi N, Zandieh M, Najafi AA (2011) Group scheduling in flexible flow shops: a hybridised approach of imperialist competitive algorithm and electromagnetic-like mechanism. Int J Prod Res 49(16):4965–4977
Kim HW, Lee DH (2009) Heuristic algorithms for re-entrant hybrid flow shop scheduling with unrelated parallel machines. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 223(4):433–442
Kreter S, Schutt A, Stuckey PJ, Zimmermann J (2018) Mixed-integer linear programming and constraint programming formulations for solving resource availability cost problems. Eur J Oper Res 266(2):472–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2017.10.014
Kurz ME, Askin RG (2004) Scheduling flexible flow lines with sequence-dependent setup times. Eur J Oper Res 159(1):66–82
Laborie P, Rogerie J, Shaw P, Vilím P (2018) IBM ILOG CP optimizer for scheduling: 20+ years of scheduling with constraints at IBM/ILOG. Constraints 23(2):210–250
Lei D, Zheng Y (2017) Hybrid flow shop scheduling with assembly operations and key objectives: a novel neighborhood search. Appl Soft Comput J 61:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2017.07.058
Lei D, Gao L, Zheng Y (2018) A novel teaching-learning-based optimization algorithm for energy-efficient scheduling in hybrid flow shop. IEEE Trans Eng Manag 65(2):330–340
Li JQ, Pan QK (2015) Solving the large-scale hybrid flow shop scheduling problem with limited buffers by a hybrid artificial bee colony algorithm. Inf Sci (NY) 316:487–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2014.10.009
Lin L, Gen M (2018) Hybrid evolutionary optimisation with learning for production scheduling: state-of-the-art survey on algorithms and applications. Int J Prod Res 56(1–2):193–223. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2018.1437288
Lin HT, Liao CJ (2003) A case study in a two-stage hybrid flow shop with setup time and dedicated machines. Int J Prod Econ 86(2):133–143
Lin CW, Lin YK, Hsieh HT (2013) Ant colony optimization for unrelated parallel machine scheduling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 67(1–4):35–45
Liu Z, Xie J, Li J, Dong J (2003) Heuristic for two-stage no-wait hybrid flowshop scheduling with a single machine in either stage. Tsinghua Sci Technol 8(1):43–48
Liu H, Zhao F, Wang L, Cao J, Tang J, Jonrinaldi J (2023) An estimation of distribution algorithm with multiple intensification strategies for two-stage hybrid flow-shop scheduling problem with sequence-dependent setup time. Appl Intell 53(5):5160–5178
Low C (2005) Simulated annealing heuristic for flow shop scheduling problems with unrelated parallel machines. Comput Oper Res 32(8):2013–2025
Lustig IJ, Puget J-F (2001) Program does not equal program: constraint programming and its relationship to mathematical programming. Interfaces (providence) 31(6):29–53. https://doi.org/10.1287/inte.31.7.29.9647
Maciel ISF, de Athayde Prata B, Nagano MS, de Abreu LR (2022) A hybrid genetic algorithm for the hybrid flow shop scheduling problem with machine blocking and sequence-dependent setup times. J Proj Manag 7(4):201–216. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.jpm.2022.5.002
Martello S, Soumis F, Toth P (1997) Exact and approximation algorithms for makespan minimization on unrelated parallel machines. Discret Appl Math 75(2):169–188
Meng L, Zhang C, Shao X, Ren Y, Ren C (2019) Mathematical modelling and optimisation of energy-conscious hybrid flow shop scheduling problem with unrelated parallel machines. Int J Prod Res 57(4):1119–1145
Meng L, Zhang C, Ren Y, Zhang B, Lv C (2020a) Mixed-integer linear programming and constraint programming formulations for solving distributed flexible job shop scheduling problem. Comput Ind Eng 142(2020):106347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020.106347
Meng L, Zhang C, Shao X, Zhang B, Ren Y, Lin W (2020b) More MILP models for hybrid flow shop scheduling problem and its extended problems. Int J Prod Res 58(13):3905–3930
Meng L, Lu C, Zhang B, Ren Y, Lv C, Sang H, Li J, Zhang C (2021) Constraint programming for solving four complex flexible shop scheduling problems. IET Collab Intell Manuf 3(2):147–160
Meng L, Gao K, Ren Y, Zhang B, Sang H, Chaoyong Z (2022) Novel MILP and CP models for distributed hybrid flowshop scheduling problem with sequence-dependent setup times. Swarm Evol Comput 71(2022):101058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2022.101058
Missaoui A, Ruiz R (2022) A parameter-Less iterated greedy method for the hybrid flowshop scheduling problem with setup times and due date windows. Eur J Oper Res 303(1):99–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2022.02.019
Missaoui A, Boujelbene Y (2021) An effective iterated greedy algorithm for blocking hybrid flow shop problem with due date window. RAIRO Oper Res 55(3):1603–1616
Moccellin JV, Nagano MS, Pitombeira Neto AR, de Athayde Prata B (2018) Heuristic algorithms for scheduling hybrid flow shops with machine blocking and setup times. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 40(2):1–11
Mollaei A, Mohammadi M, Naderi B (2019) A bi-objective MILP model for blocking hybrid flexible flow shop scheduling problem: robust possibilistic programming approach. Int J Manag Sci Eng Manag 14(2):137–146. https://doi.org/10.1080/17509653.2018.1505565
Moradinasab N, Shafaei R, Rabiee M, Ramezani P (2013) No-wait two stage hybrid flow shop scheduling with genetic and adaptive imperialist competitive algorithms. J Exp Theor Artif Intell 25(2):207–225
Mousavi SM, Zandieh M, Amiri M (2011) An efficient bi-objective heuristic for scheduling of hybrid flow shops. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 54(1–4):287–307
Naderi B, Yazdani M (2014) A model and imperialist competitive algorithm for hybrid flow shops with sublots and setup times. J Manuf Syst 33(4):647–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2014.06.002
Naderi B, Zandieh M, Khaleghi Ghoshe Balagh A, Roshanaei V (2009) An improved simulated annealing for hybrid flowshops with sequence-dependent setup and transportation times to minimize total completion time and total tardiness. Expert Syst Appl 36(6):9625–9633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.09.063
Naderi B, Gohari S, Yazdani M (2014) Hybrid flexible flowshop problems: models and solution methods. Appl Math Model 38(24):5767–5780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2014.04.012
Naderi B, Ruiz R, Roshanaei V (2023) Mixed-integer programming versus constraint programming for shop scheduling problems: new results and outlook. INFORMS J Comput. https://doi.org/10.1287/ijoc.2023.1287
Néron E, Baptiste P, Gupta JND (2001) Solving hybrid flow shop problem using energetic reasoning and global operations. Omega 29(6):501–511
Oujana S, Yalaoui F, Amodeo L (2021) A linear programming approach for hybrid flexible flow shop with sequence-dependent setup times to minimise total tardiness. IFAC-PapersOnLine 54(1):1162–1167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifacol.2021.08.207
Oujana S, Amodeo L, Yalaoui F, Brodart D (2023) Mixed-integer linear programming, constraint programming and a novel dedicated heuristic for production scheduling in a packaging plant. Appl Sci 13(10):1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106003
Oztop H, Fatih Tasgetiren M, Eliiyi DT, Pan QK (2019) Metaheuristic algorithms for the hybrid flowshop scheduling problem. Comput Oper Res 111:177–196
Pan QK, Wang L, Mao K, Zhao JH, Zhang M (2013) An effective artificial bee colony algorithm for a real-world hybrid flowshop problem in steelmaking process. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 10(2):307–322
Pan QK, Gao L, Li XY, Gao KZ (2017) Effective metaheuristics for scheduling a hybrid flowshop with sequence-dependent setup times. Appl Math Comput 303:89–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2017.01.004
Pargar F, Zandieh M (2012) Bi-criteria SDST hybrid flow shop scheduling with learning effect of setup times: water flow-like algorithm approach. Int J Prod Res 50(10):2609–2623
Pessoa R, Maciel I, Moccellin J, Pitombeira-Neto A, Prata B (2019) Hybrid flow shop scheduling problem with machine blocking, setup times and unrelated parallel machines per stage. Investig Oper
Piersma N, Van Dijk W (1996) A local search heuristic for unrelated parallel machine scheduling with efficient neighborhood search. Math Comput Model 24(9):11–19
Qin W, Zhang J, Song D (2018) An improved ant colony algorithm for dynamic hybrid flow shop scheduling with uncertain processing time. J Intell Manuf 29(4):891–904
Qin W, Zhuang Z, Liu Y, Tang O (2019) A two-stage ant colony algorithm for hybrid flow shop scheduling with lot sizing and calendar constraints in printed circuit board assembly. Comput Ind Eng 138:106115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2019.106115
Qin T, Du Y, Chen JH, Sha M (2020) Combining mixed integer programming and constraint programming to solve the integrated scheduling problem of container handling operations of a single vessel. Eur J Oper Res 285(3):884–901
Rabiee M, Sadeghi Rad R, Mazinani M, Shafaei R (2014) An intelligent hybrid meta-heuristic for solving a case of no-wait two-stage flexible flow shop scheduling problem with unrelated parallel machines. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71(5–8):1229–1245
Rabiee M, Jolai F, Asefi H, Fattahi P, Lim S (2016) A biogeography-based optimisation algorithm for a realistic no-wait hybrid flow shop with unrelated parallel machines to minimise mean tardiness. Int J Comput Integr Manuf 29(9):1007–1024. https://doi.org/10.1080/0951192X.2015.1130256
Ramezani P, Rabiee M, Jolai F (2015) No-wait flexible flowshop with uniform parallel machines and sequence-dependent setup time: a hybrid meta-heuristic approach. J Intell Manuf 26(4):731–744. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-013-0830-2
Rashidi E, Jahandar M, Zandieh M (2010) An improved hybrid multi-objective parallel genetic algorithm for hybrid flow shop scheduling with unrelated parallel machines. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 49(9–12):1129–1139
Rezaie N, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Torabi SA (2009) A new mathematical model for fuzzy flexible flow shop scheduling of unrelated parallel machines maximizing the weighted satisfaction level. IFAC 42(4):798–803. https://doi.org/10.3182/20090603-3-RU-2001.0239
Ribas I, Leisten R, Framiñan JM (2010) Review and classification of hybrid flow shop scheduling problems from a production system and a solutions procedure perspective. Comput Oper Res 37(8):1439–1454
Ruiz R, Maroto C (2006) A genetic algorithm for hybrid flowshops with sequence dependent setup times and machine eligibility. Eur J Oper Res 169(3):781–800
Ruiz R, Vázquez-Rodríguez JA (2010) The hybrid flow shop scheduling problem. Eur J Oper Res 205(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2009.09.024
Ruiz R, Şerifoǧlu FS, Urlings T (2008) Modeling realistic hybrid flexible flowshop scheduling problems. Comput Oper Res 35(4):1151–1175
Sawik T (2002) An exact approach for batch scheduling in flexible flow lines with limited intermediate buffers. Math Comput Model 36(4–5):461–471
Shahvari O, Logendran R (2016) Hybrid flow shop batching and scheduling with a bi-criteria objective. Int J Prod Econ 179:239–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2016.06.005
Shahvari O, Logendran R (2018) A comparison of two stage-based hybrid algorithms for a batch scheduling problem in hybrid flow shop with learning effect. Int J Prod Econ 195:227–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2017.10.015
Shao W, Shao Z, Pi D (2020) Modeling and multi-neighborhood iterated greedy algorithm for distributed hybrid flow shop scheduling problem. Knowl Based Syst 194:105527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.105527
Sherali HD, Sarin SC, Kodialam MS (1990) Models and algorithms for a two-stage production process. Prod Plan Control 1(1):2
Sriskandarajah C (1993) Performance of scheduling algorithms for no-wait flowshops with parallel machines. Eur J Oper Res 70(3):365–378
Tang L, Zhang Y (2005) Heuristic combined artificial neural networks to schedule hybrid flow shop with sequence dependent setup times. In: Wang J, Liao X, Yi Z (eds) Advances in neural networks—ISNN 2005. Lecture notes in computer science, vol 3496. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 788–793. https://doi.org/10.1007/11427391_126
Tang L, Xuan H (2006) Lagrangian relaxation algorithms for real-time hybrid flowshop scheduling with finite intermediate buffers. J Oper Res Soc 57(3):316–324
Tao Z, Zhou Q (2017) Study on MS-BHFSP with multi-objective. In: 13th international conference on natural computation, fuzzy systems and knowledge discovery (ICNC-FSKD), Guilin, China, pp 319–323. https://doi.org/10.1109/FSKD.2017.8393286
Tao Z, Liu X, Zeng P (2014) Study on hybrid flow shop scheduling problem with blocking based on GASA. Open Autom Control Syst J 6(1):593–600
Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Safaei N, Sassani F (2009) A memetic algorithm for the flexible flow line scheduling problem with processor blocking. Comput Oper Res 36(2):402–414
Topaloglu S, Ozkarahan I (2011) A constraint programming-based solution approach for medical resident scheduling problems. Comput Oper Res 38(1):246–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2010.04.018
Torabi SA, Sahebjamnia N, Mansouri SA, Bajestani MA (2013) A particle swarm optimization for a fuzzy multi-objective unrelated parallel machines scheduling problem. Appl Soft Comput J 13(12):4750–4762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2013.07.029
Tsubone H, Ohba M, Takamuki H, Miyake Y (1993) A production scheduling system for a hybrid flow shop-a case study. Omega 21(2):205–214
Ünal AT, Ağralı S, Taşkın ZC (2020) A strong integer programming formulation for hybrid flowshop scheduling. J Oper Res Soc 71(12):2042–2052. https://doi.org/10.1080/01605682.2019.1654414
Urlings T, Ruiz R, Stützle T (2010) Shifting representation search for hybrid flexible flowline problems. Eur J Oper Res 207(2):1086–1095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2010.05.041
Wang S, Liu M (2013) A genetic algorithm for two-stage no-wait hybrid flow shop scheduling problem. Comput Oper Res 40(4):1064–1075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2012.10.015
Wang X, Tang L (2009) A tabu search heuristic for the hybrid flowshop scheduling with finite intermediate buffers. Comput Oper Res 36(3):907–918
Wang L, Zhou G, Xu Y, Wang S (2012) An artificial bee colony algorithm for solving hybrid flow-shop scheduling problem with unrelated parallel machines. Control Theory Appl 29(12):1551–1556
Wang S, Liu M, Chu C (2015) A branch-and-bound algorithm for two-stage no-wait hybrid flow-shop scheduling. Int J Prod Res 53(4):1143–1167. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2014.949363
Wang S, Kurz M, Mason SJ, Rashidi E (2019) Two-stage hybrid flow shop batching and lot streaming with variable sublots and sequence-dependent setups. Int J Prod Res 57(22):6893–6907. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2019.1571251
Wang S, Wang X, Yu L (2020) Two-stage no-wait hybrid flow-shop scheduling with sequence-dependent setup times. Int J Syst Sci Oper Logist 7(3):291–307
Wang Y, Wang Y, Han Y (2023) A variant iterated greedy algorithm integrating multiple decoding rules for hybrid blocking flow shop scheduling problem. Mathematics. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11112453
Xie J, Xing W, Liu Z, Dong J (2004) Minimum deviation algorithm for two-stage no-wait flowshops with parallel machines. Comput Math Appl 47(12):1857–1863
Xu Y, Wang L (2011) Differential evolution algorithm for hybrid flow-shop scheduling problems. J Syst Eng Electron 22(5):794–798
Yang-Kuei L, Chi-Wei L (2013) Dispatching rules for unrelated parallel machine scheduling with release dates. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 67(1–4):269–279
Yaurima V, Burtseva L, Tchernykh A (2009) Hybrid flowshop with unrelated machines, sequence-dependent setup time, availability constraints and limited buffers. Comput Ind Eng 56(4):1452–1463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2008.09.004
Yong L, Zhantao L, Xiang L, Chenfeng P (2022) Heuristics for the hybrid flow shop scheduling problem with sequence-dependent setup times. Math Probl Eng 2022:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8682203
Yu C, Semeraro Q, Matta A (2018) A genetic algorithm for the hybrid flow shop scheduling with unrelated machines and machine eligibility. Comput Oper Res 100:211–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2018.07.025
Yunusoglu P, Topaloglu Yildiz S (2021) Constraint programming approach for multi-resource-constrained unrelated parallel machine scheduling problem with sequence-dependent setup times. Int J Prod Res 60(7):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2021.1885068
Zacharias M, Tonnius A, Gottschling J (2019) Machine learning in hybrid flow shop scheduling with unrelated machines. In: Proceedings of the 2019 international conference on industrial engineering and systems management IESM 2019, Shanghai, China, pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/IESM45758.2019.8948113
Zandieh M, Rashidi E (2009) An effective hybrid genetic algorithm for hybrid flow shops with sequence dependent setup times and processor blocking. J Ind Eng [Internet] 4(Issue 4):51–58. http://www.qjie.ir/article_32.html
Zandieh M, Fatemi Ghomi SMT, Moattar Husseini SM (2006) An immune algorithm approach to hybrid flow shops scheduling with sequence-dependent setup times. Appl Math Comput 180(1):111–127
Zandieh M, Dorri B, Khamseh AR (2009) Robust metaheuristics for group scheduling with sequence-dependent setup times in hybrid flexible flow shops. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 43(7–8):767–778
Zandieh M, Mozaffari E, Gholami M (2010) A robust genetic algorithm for scheduling realistic hybrid flexible flow line problems. J Intell Manuf 21(6):731–743
Zhang Q, Chen Y (2014) Hybrid PSO-NEH algorithm for solving no-wait flexible flow shop scheduling problem. Syst Eng | Theory Pract 34(3):802–809
Zhang XY, Chen L (2018) A re-entrant hybrid flow shop scheduling problem with machine eligibility constraints. Int J Prod Res 56(16):5293–5305. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2017.1408971
Zhang B, Pan Q, Gao L, Li X, Meng L, Peng K (2019) A multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition for hybrid flowshop green scheduling problem. Comput Ind Eng 136(2019):325–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2019.07.036
Zhang B, Pan QK, Gao L, Meng LL, Li XY, Peng KK (2020) A three-stage multiobjective approach based on decomposition for an energy-efficient hybrid flow shop scheduling problem. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 50(12):4984–4999
Zhang C, Tan J, Peng K, Gao L, Shen W, Lian K (2021) A discrete whale swarm algorithm for hybrid flow-shop scheduling problem with limited buffers. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 68:102081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rcim.2020.102081
Zhang B, Pan Q, Meng L, Lu C, Mou J, Li J (2022) An automatic multi-objective evolutionary algorithm for the hybrid flowshop scheduling problem with consistent sublots. Knowl Based Syst 238:107819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107819
Zheng X, Wang L (2016) A two-stage adaptive fruit fly optimization algorithm for unrelated parallel machine scheduling problem with additional resource constraints. Expert Syst Appl 65:28–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2016.08.039
Zhong W, Shi Y (2018) Two-stage no-wait hybrid flowshop scheduling with inter-stage flexibility. J Comb Optim 35(1):108–125
Zhou HR, Tang WS (2009) Optimise flexible flow-shop scheduling using genetic algorithm. [In Chinese]. Comput Eng Appl 45(30):224–227. https://doi.org/10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2009.30.066
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support were received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EEI: conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, data curation, writing—original draft. STY: supervision, methodology, validation, writing—review and editing. ÖŞA: methodology, software, validation, data curation, writing—original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix: MILP models taken from Meng et al. (2020a)
Appendix: MILP models taken from Meng et al. (2020a)
1.1 The HFSP
1.2 The HFSP-SDST
1.3 The HFSP-NW
1.4 The HFSP-B
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Işık, E.E., Topaloglu Yildiz, S. & Şatır Akpunar, Ö. Constraint programming models for the hybrid flow shop scheduling problem and its extensions. Soft Comput 27, 18623–18650 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09086-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-09086-9