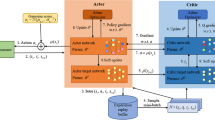
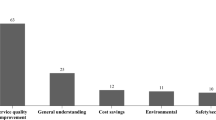
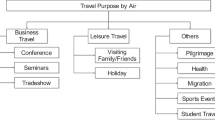
Abstract
Advances in artificial intelligence and data acquisition technology are growing, the research on deep learning algorithm has gone deep into various fields. At this stage, the demand supply matching model under the comprehensive passenger transport hub travel system is obtained by analyzing the travel mode data. This paper takes traffic time as the research direction, uses machine learning and complex network theory to conduct in-depth learning algorithm research, respectively, discusses, explores and forecasts the traffic supply and demand mode data, and explores the traffic mode supply and demand model under the comprehensive passenger transport hub travel service system. It is shown in traffic data that using the prediction form of deep learning to predict traffic conditions and travel pressure can enable traffic managers to master traffic dynamics and lead the direction for future traffic development. Finally, from the perspective of MaaS system, the paper uses big data and information processing methods to explore the supply and demand matching model in terms of transportation modes. The research shows that MaaS system can make overall planning in terms of traffic resources, provide reasonable travel modes for traffic travelers and match corresponding travel services. It not only makes overall planning and guarantee for travel services, but also promotes the sustainable development of the transportation supply and demand system.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Arias-Molinares D, García-Palomares JC (2020) Shared mobility development as key for prompting mobility as a service (MaaS) in urban areas: the case of Madrid. Case Stud Transport Policy 8(3):846–859
Chowdhury S, Van Wee B (2020) Examining women’s perception of safety during waiting times at public transport terminals. Transp Policy 94:102–108
de Abreu SJ, Bazrafshan H (2013) User satisfaction of intermodal transfer facilities in Lisbon, Portugal: analysis with structural equations modeling. Transp Res Record 2350(1):102–110
Ibrahim ANH, Borhan MN, Yazid MRM, Rahmat RA, Yukawa S (2021) Factors influencing passengers’ satisfaction with the light rail transit service in alpha cities: evidence from Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia using structural equation modelling. Mathematics 9:1954
Li D, Yang M, Jin CJ, Ren G, Liu X, Liu H (2020) Multi-modal combined route choice modeling in the MaaS age considering generalized path overlapping problem. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 22(4):2430–2441
Meurs H, Sharmeen F, Marchau V, van der Heijden R (2020) Organizing integrated services in mobility-as-a-service systems: Principles of alliance formation applied to a MaaS-pilot in the Netherlands. Transp Res Part a Policy Pract 131:178–195
Miri F, Javadpour A, Ja’fari F, Sangaiah AK, Pazzi R (2023) Improving resources in internet of vehicles transportation systems using markov transition and TDMA protocol. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2023.3244394
Rietveld P (2005) Six reasons why supply-oriented indicators systematically overestimate service quality in public transport. Transp Rev 25(3):319–328
Sadhukhan S, Banerjee UK, Maitra B (2015) Commuters’ perception towards transfer facility attributes in and around metro stations: experience in Kolkata. J Urban Plann Dev 141(4):04014038
Sangaiah AK, Javadpour A, Ja’fari F, Zhang W, Khaniabadi SM (2022) Hierarchical clustering based on dendrogram in sustainable transportation systems. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2022.3222789
Sangaiah AK, Ramamoorthi JS, Rodrigues JJ, Rahman MA, Muhammad G, Alrashoud M (2020) LACCVoV: linear adaptive congestion control with optimization of data dissemination model in vehicle-to-vehicle communication. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 22(8):5319–5328
Shah YU, Jain SS, Tiwari D, Jain MK (2013) Development of overall pavement condition index for urban road network. Proc Soc Behav Sci 104:332–341
Van Riel AC, Semeijn J, Pauwels P (2004) Online travel service quality: the role of pre-transaction services. Total Qual Manag Bus Excell 15(4):475–493
Wojuade CA, Badiora AI (2017) user’s satisfaction with public transport operations in Ibadan, Nigeria. J Social Sci Res 3(9):88–96
Wong YZ, Hensher DA, Mulley C (2020) Mobility as a service (MaaS): charting a future context. Transp Res Part a Policy Pract 131:5–19
Yang H, Lu J, Lu H, Gao Y, Liu X, Liu H (2022) Key technologies of low-carbon-oriented intelligent travel service for urban rail transit based on MaaS. Int Conf Intell Traffic Syst Smart City (ITSSC 2021) 12165:172–176
Yuan Y, Yang M, Feng T, Rasouli S, Li D, Ruan X (2021) Heterogeneity in passenger satisfaction with air-rail integration services: results of a finite mixture partial least squares model. Transp Res Part a Policy Pract 147:133–158
Zhang X, Liu H, Xu M, Mao C, Shi J, Meng G, Wu J (2020) Evaluation of passenger satisfaction of urban multi-mode public transport. PLoS ONE 15(10):e0241004
Funding
This study was supported by “Research on the Theory and Methodology of Mobility as a Service (MaaS) System Planning for Integrated Passenger Transport Hub, Sichuan Science and Technology Plan Project (Grant No. 2021YJ0076).”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Y., Lan, C., Dan, T. et al. Research on supply and demand matching model of transportation modes in MaaS system of integrated passenger transport hub based on deep learning. Soft Comput 27, 5973–5983 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08065-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08065-4