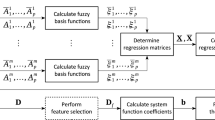
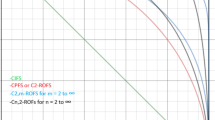
Abstract
Existing operational rules of interval grey numbers do not make full use of possible background information when determining the interval boundaries, and this may result in inconsistent results if applying different logical operations. This paper finds that multiplication and division rules of interval grey numbers do not meet the calculation rule of inverse operators. Direct solution and inverse solution of the same interval grey number object may differ not only in numerical ranges but also in greyness degrees. To improve the accuracy of grey number calculation, new operational rules for multiplication and division of interval grey numbers are proposed. Then the traditional prediction modelling method of grey heterogeneous data is refined and expanded by integrating a greyness reduction preprocessing, which is based on the proposed calculation rules. Application of the expanded heterogeneous interval grey number prediction model to a stock replenishment scheduling problem in emergency rescue scenarios is included to illustrate the new operational rules of grey numbers and their application in prediction algorithm, and the proposed approach is compared with other existing methods to demonstrate its effectiveness.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bezuglov A, Comert G (2016) Short-term freeway traffic parameter prediction: application of grey system theory models. Expert Syst Appl 62:284–292
Deschrijver G, Kerre EE (2003) On the relationship between some extensions of fuzzy set theory. Fuzzy Sets Syst 133(2):227–235
Evans M (2014) An alternative approach to estimating the parameters of a generalised Grey Verhulst model: an application to steel intensity of use in the UK. Expert Syst Appl 41(4):1236–1244
Fang ZG, Liu SF (2005) A study on the GM(1, 1)(GMBIGN(1, 1)) model based on interval grey sequences. Eng Sci China 7(2):57–61
Guo XJ, Liu SF, Wu LF, Gao YB, Yang YJ (2015) A multi-variable grey model with a self-memory component and its application on engineering prediction. Eng Appl Artif Intell 42:82–93
Guo S, Tang G, Chen X (2019) An approach of multi-attribute group decision making. In: Proceedings of the 2019 3rd international conference on cloud and big data computing, pp 21–25
Karmakar S, Mujumdar PP (2006) Grey fuzzy optimization model for water quality management of a river system. Adv Water Resour 29(7):1088–1105
Li QX, Liu SF (2009) Some results about grey mathematics. Kybernetes 38(3/4):297–305
Li GD, Yamaguchi D, Nagai M (2007) A GM (1, 1)–Markov chain combined model with an application to predict the number of Chinese international airlines. Technol Forecast Soc Change 74(8):1465–1481
Li QX, Liu SF, Lin Y (2012) Grey enterprise input–output analysis. J Comput Appl Math 236(7):1862–1875
Li D, Wang W, Ismail F (2015) A fuzzy-filtered grey network technique for system state forecasting. Soft Comput 19(12):3497–3505
Lin YH, Lee PC, Ting HI (2008) Dynamic multi-attribute decision making model with grey number evaluations. Expert Syst Appl 35(4):1638–1644
Liu SF, Fang ZG (2006) Study on algorithm of grey numbers and grey algebraic system. In: 2006 IEEE International conference on systems, man and cybernetics, pp 2272–2276. IEEE
Liu SF, Forrest JYL (2010) Grey systems: theory and applications. Springer, Berlin
Liu SF, Lin Y (2006) Grey information: theory and practical applications. Springer, Berlin
Liu SF, Xie NM (2011) New grey evaluation method based on reformative triangular whitenization weight function. J Syst Eng 26(2):244–250
Liu SF, Dang YG, Fang ZG (2004) Grey systems theory and its applications. The Science Press of China, Beijing
Liu SF, Forrest J, Yang YJ (2013) A summary of the progress in grey system research. In: Proceedings of 2013 IEEE international conference on grey systems and intelligent services. IEEE, pp 1–10
Luo D (2009) Decision-making methods with three-parameter interval grey number. Syst Eng Theory Pract 29(1):124–130
Luo D, Liu M (2018) Stochastic multiple criteria decision-making method with grey heterogeneous data information. Control Decis 33(12):2227–2233
Ogiela MR, Castiglione A, You I (2014) Soft computing for security services in smart and ubiquitous environments. Soft Comput 18:1655–1658
Oztaysi B (2014) A decision model for information technology selection using AHP integrated TOPSIS-Grey: the case of content management systems. Knowl Based Syst 70:44–54
Salmeron JL, Papageorgiou EI (2012) A fuzzy grey cognitive maps-based decision support system for radiotherapy treatment planning. Knowl Based Syst 30:151–160
Shih CS, Hsu YT, Yeh J, Lee PC (2011) Grey number prediction using the grey modification model with progression technique. Appl Math Model 35(3):1314–1321
Teng HC, Huang YF (2013) The use for the competition theory of the industrial investment decisions-a case study of the Taiwan IC assembly industry. Int J Prod Econ 141(1):335–338
Tsaur RC (2008) Forecasting analysis by using fuzzy grey regression model for solving limited time series data. Soft Comput 12(11):1105–1113
Tsaur RC (2009) Insight of the fuzzy grey autoregressive model. Soft Comput 13(10):919–931
Tseng ML (2009) A causal and effect decision making model of service quality expectation using grey-fuzzy DEMATEL approach. Expert Syst Appl 36(4):7738–7748
Wu Q, Liu Z (2009) Real formal concept analysis based on grey-rough set theory. Knowl Based Syst 22(1):38–45
Wu G, Du Z, Hu Y, Jung T, Fiore U, Yim K (2014) A dynamic trust model exploiting the time slice in WSNs. Soft Comput 18(9):1829–1840
Wu L, Liu S, Yao L, Xu R, Lei X (2015) Using fractional order accumulation to reduce errors from inverse accumulated generating operator of grey model. Soft Comput 19(2):483–488
Wu L, Liu S, Yang Y, Ma L, Liu H (2016) Multi-variable weakening buffer operator and its application. Inf Sci 339:98–107
Xiao Q, Shan M, Xiao X, Rao C (2020) Evaluation model of industrial operation quality under multi-source heterogeneous data information. Int J Fuzzy Syst 22(2):522–547
Xie NM, Liu SF (2005) Discrete GM (1, 1) and mechanism of grey forecasting model. Syst Eng Theory Pract 25(1):93–98
Xiong PP, Huang S, Peng M, Wu XH (2020) Examination and prediction of fog and haze pollution using a multi-variable grey model based on interval number sequences. Appl Math Model 77:1531–1544
Yamaguchi D, Li GD, Nagai M (2007) A grey-based rough approximation model for interval data processing. Inf Sci 177(21):4727–4744
Yang YJ, John R (2003) Grey systems and interval valued fuzzy sets. In: Proceedings of the 3rd conference of the european society for fuzzy logic and technology, pp 193–197
Yang YJ, John R (2012) Grey sets and greyness. Inf Sci 185(1):249–264
Yang YJ, Liu SF (2011) Reliability of operations of grey numbers using kernels. Grey Syst Theory Appl 1(1):57–71
Ye J, Dang Y, Yang Y (2019) Forecasting the multifactorial interval grey number sequences using grey relational model and GM (1, N) model based on effective information transformation. Soft Comput 24(7):5255–5269
Zeng B (2013) Research on prediction modeling method of double heterogeneous data sequence based on core and grey degree. In: Statistics and information forum, pp 3–7
Zeng B, Chen G, Liu SF (2013) A novel interval grey prediction model considering uncertain information. J Frankl Inst 350(10):3400–3416
Zeng B, Meng W, Liu SF, Li C, Cui J (2015) Prediction modeling method of grey isomerism data for calamity emergency material demand. Chin J Manag Sci 23(8):84–91
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Leverhulme Trust International Network project entitled “Grey Systems and Its Applications” (Grant Number IN-2014-020), the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 71401039), the China Scholarship Council Grant Number 2016 06655020), the Humanities and Social Sciences Youth Fund Project of Education Ministry of China (Grant Number 14YJC630060), and the Fujian Natural Science Foundation (Grant Number 2017J01517).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Yang, Y. & Liu, S. A greyness reduction framework for prediction of grey heterogeneous data. Soft Comput 24, 17913–17929 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05040-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-05040-1