Abstract
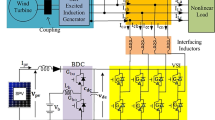
The issues related to the optimal control of large-scale storage systems in electric power systems such as pumped storage (PS) plant have turned into vital challenges in the way of integrating renewable energy sources into power systems to provide reliable and economical electric energy. In this regard, this paper uses the direct power control strategy to model and simulate a variable-speed PS plant, which includes a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG). The active and the reactive power of the stator would be able to be controlled, separately. This approach has a better dynamic performance compared to other methods, while it would be quite simple to implement. But there are some shortfalls with this method, such as high ripple relating to the active power as well as reactive power together with the current harmonics. In this respect, the space vector modulation (SVM) is applied to eliminate these shortfalls. In the proposed control technique, including SVM, the dynamic performance of the studied DFIG unit is controlled using the proportional–integral (PI) controller. It should be noted that the teaching–learning-based optimization (TLBO) method is employed to tune the PI controller for controlling the DFIG system in the PS plant. Finally, in order to validate the performance of the suggested framework, a comparison is made between the results obtained by the TLBO and the ones reported by other optimization methods. The obtained results using the TLBO algorithm indicate better performance of the PI controller to reduce the ripples of the active and reactive power of the stator as well as the harmonic power.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad G, Rodriguez MA, Poza J (2007) Predictive direct power control of the doubly fed induction machine with reduced power ripple at low constant switching frequency. In: IEEE international symposium on industrial electronics, ISIE, pp 1119–1124
Abido MA (2002) Optimal design of power-system stabilizer using particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 17(3):406–413
Atashpaz E, Lucas C (2007) Imperialistic competitive algorithm for optimization inspired by imperialistic competition. In: 2007 IEEE congress on evolutionary computation (CEC 2007), pp 4664–4667
Cai WW, Jia LX, Zhang YB (2010) Design and simulation of intelligent PID controller based on particle swarm optimization. In: E-Produce E-Service E-Entertainment (ICEEE), Henan
Chatterjee SH, Mukherjee V (2016) PID controller for automatic voltage regulator using teaching–learning based optimization technique. Electr Power Energy Syst 77:418–429
Dadfar S, Wakil K, Khaksar M, Rezvani A, Miveh MR, Gandomkar M (2019) Enhanced control strategies for a hybrid battery/photovoltaic system using FGS-PID in grid-connected mode. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44(29):14642–14660
Dendouga A, Abdessemed R, Bendas M, Chaiba A (2007) Decoupled active and reactive power control of a doubly fed induction generator (DFIG). In: Mediterranean conference on control and automation, Athens
Farajdadian S, Hosseini SMH (2019) Design of an optimal fuzzy controller to obtain maximum power in solar power generation system. Sol Energy 182:161–178
Hasanien HM, Muyeen SM (2012) Design optimization of controller parameters used in variable speed wind energy conversion system by genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans Sustain Energy 3(2):200–208
Hosseini SMH, Eslami S (2019) Modelling of PSPP control system by using vector control principle and VSI. In: 5th International conference on power generation systems and renewable energy technologies (PGSRET), 26–27 Aug 2019, Turkey
Hosseini SMH, Semsar MR (2016) A novel technology for control of variable speed pumped storage power plant. J Central South Univ 23(8):2008–2023
Ju P, Handschin E, Reyer F (1996) Genetic algorithm aided controller design with application to SVC. IEE Proc Gener Transm Distrib 143(3):258–262
Kennedy J, Eberhart R (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proc. IEEE. int. conf. neural networks, vol 4, pp 1942–1948
Lansberry JE, Wozniak L (1994) Adaptive hydrogenator governor tuning with a genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans Power Syst 9(1):179–183
Muller S, Deicke M, De Doncker RW (2002) Doubly fed induction generator system for wind turbines. IEEE Ind Appl Mag 8(3):26–33
Ou C, Lin W (2006) Comparison between PSO and GA for parameters optimization of PID controller. In: Proceeding of the 2006 IEEE international conference on mechatronics and automation
Pannatier Y, Kawkabani B, Nicolet C, Simond J, Schwery A, Allenbach P (2010) Investigation of control strategies for variable-speed pump-turbine units by using a simplified model of the converters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57:3039–3049
Pena R, Clare JC, Asher GM (1996) Doubly fed induction generator using back-to-back PWM converters and its application to variable speed wind-energy generation. IEE Proc Electr Power Appl 143(3):231–241
Qiao W, Venayagamoorthy GK, Harley RG (2006) Design of optimal PI controllers for doubly fed induction generators driven by wind turbines using particle swarm optimization. In: 2006 Int. joint conf. on neural networks, Vancouver, BC, pp 1982–1987
Rai D (2017) Comments on “A note on multi-objective improved teaching-learning based optimization algorithm (MO-ITLBO)”. Int J Ind Eng Comput 8(2):179–190
Rao RV, Savsani VJ, Vakharia DP (2011) Teaching–learning-based optimization: a novel method for constrained mechanical design optimization problems. Comput Aided Des 43(1):303–315
Rezvani A, Khalili A, Mazareie A, Gandomkar M (2016) Modeling, control, and simulation of grid connected intelligent hybrid battery/photovoltaic system using new hybrid fuzzy-neural method. ISA Trans 1(63):448–460
Rezvani A, Esmaeily A, Etaati H, Mohammadinodoushan M (2019) Intelligent hybrid power generation system using new hybrid fuzzy-neural for photovoltaic system and RBFNSM for wind turbine in the grid connected mode. Front Energy 13(1):131–148
Schmidt J, Kemmetmuller W, Kugi A (2017) Modeling and static optimization of a variable speed pumped storage power plant. Renew Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.03.055
Tang T, Xu L (1995) A flexible active reactive power control strategy for a variable speed constant frequency generating system. IEEE Trans Power Electron 10(4):472–477
Tapia A, Tapia G, Ostolaza JX, Saenz JR (2003) Modeling and control of a wind turbine driven doubly fed induction generator. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 18(2):194–204
Wu F, Zhang XP, Godfrey K, Ju P (2007) Small signal stability analysis and optimal control of a wind turbine with doubly fed induction generator. IET Gener Transm Distrib 1(5):751–760
Yamamoto M, Motoyoshi O (1991) Active and reactive power control for doubly-fed wound rotor induction generator. IEEE Trans Power Electron 6(4):624–629
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by V. Loia.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseini, S.M.H., Rezvani, A. Modeling and simulation to optimize direct power control of DFIG in variable-speed pumped-storage power plant using teaching–learning-based optimization technique. Soft Comput 24, 16895–16915 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04984-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04984-8