Abstract
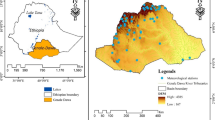
Drought is one of the most complex natural hazards. Therefore, precise drought monitoring and forecasting are the biggest tasks for hydrologists and environmentalists. Under grid data structure, this paper provides a new drought index—the adaptive standardized precipitation index (ASPI), for the evolution of drought, inferring its spatio-temporal patterns and detecting trends. The methodology of the proposed index is based mainly on dynamic time warping clustering algorithm and dynamic principal components. Historical simulated precipitation data from the Australian community climate and earth-system simulator model of coupled model intercomparison project 6 of 727 grid points scattered around the Tibet Plateau has been considered. Results show that as the time scale increases, the severe and extreme drought trends have increased significantly. Further, the significant decreasing magnitude in ASPI reveals the persistence of future drought in the Tibet Plateau region. From a data mining point of view, the outcomes associated with this research recommend the endorsement of ASPI for effective and precise drought monitoring under grid data structure.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data and code availability
All the data were analyzed using R software. The data and code used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Akdi Y, Ünlü KD (2020) Periodicity in precipitation and temperature for monthly data of Turkey. Theor Appl Climatol 143:1–12
Ali Z, Hussain I, Faisal M, Nazir HM, Abd-el Moemen M, Hussain T, Shamsuddin S (2017) A novel multi-scalar drought index for monitoring drought: the standardized precipitation temperature index. Water Resour Manag 31(15):4957–4969
Ali Z, Hussain I, Faisal M, Shoukry AM, Gani S, Ahmad I (2019) A framework to identify homogeneous drought characterization regions. Theor Appl Climatol 137(3–4):3161–3172
Ali Z, Hussain I, Faisal M, Grzegorczyk M, Qamar S, Shoukry AM, Sharkawy MA, Gani S (2020) On the more generalized non-parametric framework for the propagation of uncertainty in drought monitoring. Meteorol Appl 27(3):e1914
Allen M, Antwi-Agyei P, Aragon-Durand F, Babiker M, Bertoldi P, Bind M, Brown S, Buckeridge M, Camilloni I, Cartwright A, Cramer W (2019). Technical summary: global warming of 1.5°C.
An R, Shen J, Li Y, Bandaru S (2020) Projecting the influence of global warming on physical activity patterns: a systematic review. Curr Obes Rep 9:1–12
Bazrafshan J, Hejabi S, Rahimi J (2014) Drought monitoring using the multivariate standardized precipitation index (MSPI). Water Resour Manag 28(4):1045–1060
Brito TT, Oliveira-Júnior JF, Lyra GB, Gois G, Zeri M (2017) Multivariate analysis applied to monthly rainfall over Rio de Janeiro state, Brazil. Meteorol Atmos Phys 129(5):469–478
Brownlee J (2016) Machine learning mastery with python. Machine Learning Mastery Pty Ltd, Vermont, pp 100–120
Chen J, Li Y, Luo Y, Tu W, Wan T (2019) Drought differently affects growth properties, leaf ultrastructure, nitrogen absorption and metabolism of two dominant species of Hippophae in Tibet Plateau. Acta Physiol Plant 41(1):1
Chen N, Zhang Y, Zu J, Zhu J, Zhang T, Huang K, Cong N, Wang Z, Li J, Zheng Z, Tian Y (2020) The compensation effects of post-drought regrowth on earlier drought loss across the tibetan plateau grasslands. Agric for Meteorol 281:107822
Daim T, Lai KK, Yalcin H, Alsoubie F, Kumar V (2020) Forecasting technological positioning through technology knowledge redundancy: patent citation analysis of IoT, cybersecurity, and Blockchain. Technol Forecast Soc Change 161:120329
De Lucas DC (2010) Classification techniques for time series and functional data. Doctoral dissertation, Universidad Carlos III de Madrid
Ding J, Cuo L, Zhang Y, Zhu F (2018) Monthly and annual temperature extremes and their changes on the Tibetan Plateau and its surroundings during 1963–2015. Sci Rep 8(1):1–23
Erhardt TM, Czado C (2015) Standardized drought indices: a novel uni- and multivariate approach. J R Stat Soc Ser C Appl Stat 67(218):643–664
Fan Z, Xu Y, Zuo W, Yang J, Tang J, Lai Z, Zhang D (2014) Modified principal component analysis: an integration of multiple similarity subspace models. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 25(8):1538–1552
Feng W, Lu H, Yao T, Yu Q (2020) Drought characteristics and its elevation dependence in the Qinghai-Tibet plateau during the last half-century. Sci Rep 10(1):1–11
Frank A, Armenski T, Gocic M, Popov S, Popovic L, Trajkovic S (2017) Influence of mathematical and physical background of drought indices on their complementarity and drought recognition ability. Atmos Res 194:268–280
Gwelo AS (2019) Principal components to overcome multicollinearity problem. Oradea J Bus Econ 4(1):79–91
Hari V, Rakovec O, Markonis Y, Hanel M, Kumar R (2020) Increased future occurrences of the exceptional 2018–2019 Central European drought under global warming. Sci Rep 10(1):1–10
Hollins S, Dodson J (2013) Drought. In: Bobrowsky PT (ed) Encyclopedia of natural hazards. Encyclopedia of earth sciences series. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-4399-4_98
Horváth L, Kokoszka P (2012) Inference for functional data with applications, vol 200. Springer, Berlin
Jiang Y, Cooley D, Wehner MF (2020) Principal component analysis for extremes and application to US precipitation. J Clim 33(15):6441–6451
Jolliffe IT, Trendafilov NT, Uddin M (2003) A modified principal component technique based on the LASSO. J Comput Graph Stat 12(3):531–547
Kidziński Ł, Kokoszka P, Jouzdani NM (2018) Principal components analysis of periodically correlated functional time series. J Time Ser Anal 39(4):502–522
Krähenmann S, Walter A, Brienen S, Imbery F, Matzarakis A (2018) High-resolution grids of hourly meteorological variables for Germany. Theor Appl Climatol 131(3–4):899–926
Kuang X, Jiao JJ (2016) Review on climate change on the Tibetan Plateau during the last half century. J Geophys Res Atmos 121(8):3979–4007
Li H (2019) Multivariate time series clustering based on common principal component analysis. Neurocomputing 349:239–247
Li XY, Ma YJ, Xu HY, Wang JH, Zhang DS (2009) Impact of land use and land cover change on environmental degradation in Lake Qinghai watershed, northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Land Degrad Dev 20(1):69–83
Li Z, Chen Y, Fang G, Li Y (2017) Multivariate assessment and attribution of droughts in Central Asia. Sci Rep 7(1):1–12
Li X, Zhang L, Luo T (2020) Rainy season onset mainly drives the spatiotemporal variability of spring vegetation green-up across alpine dry ecosystems on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci Rep 10(1):1–10
Liu Y, Zhu Y, Ren L, Yong B, Singh VP, Yuan F, Jiang S, Yang X (2019) On the mechanisms of two composite methods for construction of multivariate drought indices. Sci Total Environ 647:981–991
McKee TB, Doesken NJ, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In: Proceedings of the 8th conference on applied climatology, vol 17, no. 22, pp 179–183
Mensah AC, Dadzie J (2020) Application of principal component analysis on perceived barriers to youth entrepreneurship. Am J Theor Appl Stat 9(5):201–209
Mikhaylov A, Moiseev N, Aleshin K, Burkhardt T (2020) Global climate change and greenhouse effect. Entrep Sustain Issues 7(4):2897
Pearson K (1901) LIII. On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Lond Edinb Dublin Philos Mag J Sci 2(11):559–572
Peña D, Yohai VJ (2016) Generalized dynamic principal components. J Am Stat Assoc 111(515):1121–1131
Raftery AE, Zimmer A, Frierson DM, Startz R, Liu P (2017) Less than 2 C warming by 2100 unlikely. Nat Clim Change 7(9):637
Reynolds JL (2021) Earth system interventions as technologies of the Anthropocene. Environ Innov Soc Transit 40:132–146
Staudenmann D, Stegeman DF, van Dieën JH (2013) Redundancy or heterogeneity in the electric activity of the biceps brachii muscle? Added value of PCA-processed multi-channel EMG muscle activation estimates in a parallel-fibered muscle. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 23(4):892–898
Tebaldi C, Debeire K, Eyring V, Fischer E, Fyfe J, Friedlingstein P, Knutti R, Lowe J, O’Neil B, Sanderson B, van Vuuren D (2020) Climate model projections from the Scenario Model Intercomparison Project (ScenarioMIP) of CMIP6. Earth Syst Dyn Discuss. https://doi.org/10.5194/esd-2020-68
Tseng KK, Li J, Tang YJ, Yang CW, Lin FY, Zhao Z (2020) Clustering analysis of aging diseases and chronic habits with multivariate time series electrocardiogram and medical records. Front Aging Neurosci 12:95
Vicente-Serrano SM, López-Moreno JI (2005) Hydrological response to different time scales of climatological drought: an evaluation of the Standardized Precipitation Index in a mountainous Mediterranean basin
Vicente-Serrano SM, Beguería S, López-Moreno JI (2010) A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J Clim 23(7):1696–1718
Wagemann J, Clements O, Marco Figuera R, Rossi AP, Mantovani S (2018) Geospatial web services pave new ways for server-based on-demand access and processing of Big Earth Data. Int J Digital Earth 11(1):7–25
Wang B, Bao Q, Hoskins B, Wu G, Liu Y (2008) Tibetan Plateau warming and precipitation changes in East Asia. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL034330
Wang W, Zhu Y, Xu R, Liu J (2015) Drought severity change in China during 1961–2012 indicated by SPI and SPEI. Nat Hazards 75(3):2437–2451
Wang H, Chen Y, Pan Y, Chen Z, Ren Z (2019) Assessment of candidate distributions for SPI/SPEI and sensitivity of drought to climatic variables in China. Int J Climatol 39(11):4392–4412
Wang J, Zhang L, Zhang D, Zhao F, Yang X (2020a) The application of principal component cluster analysis in environment classification for Chinese cities. In: IOP conference series: earth and environmental science, vol 569, no 1, p 012040. IOP Publishing
Wang Y, Wang L, Li X, Zhou J, Hu Z (2020b) An integration of gauge, satellite, and reanalysis precipitation datasets for the largest river basin of the Tibetan Plateau. Earth Syst Sci Data 12(3):1789–1803
Wei Y, Fang Y (2013) Spatio-temporal characteristics of global warming in the Tibetan Plateau during the last 50 years based on a generalized temperature zone-elevation model. PLoS ONE 8(4):e60044
Wu S, Yin Y, Zheng D, Yang Q (2007) Climatic trends over the Tibetan Plateau during 1971–2000. J Geograph Sci 17(2):141–151
Wu S, Guo C, Wang X (2020) Application of principal component analysis and adaptive median filter to improve real-time prostate capsula detection. J Med Imaging Health Inform 10(2):336–347
Xu X, Lu C, Shi X, Gao S (2008) World water tower: an atmospheric perspective. Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL035867
Yang K, Wu H, Qin J, Lin C, Tang W, Chen Y (2014) Recent climate changes over the Tibetan Plateau and their impacts on energy and water cycle: a review. Glob Planet Change 112:79–91
Yang Y, Zhang S, Roderick ML, McVicar TR, Yang D, Liu W, Li X (2020) Comparing Palmer Drought Severity Index drought assessments using the traditional offline approach with direct climate model outputs. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 24(6):2921–2930
Yihdego Y, Vaheddoost B, Al-Weshah RA (2019) Drought indices and indicators revisited. Arab J Geosci 12(3):69
Zargar A, Sadiq R, Naser B, Khan FI (2011) A review of drought indices. Environ Rev 19:333–349
Zhang A, Jia G (2013) Monitoring meteorological drought in semiarid regions using multi-sensor microwave remote sensing data. Remote Sens Environ 134:12–23
Zhou T, Zhang W (2021) Anthropogenic warming of Tibetan Plateau and constrained future projection. Environ Res Lett 16(4):044039
Zou H, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2006) Sparse principal component analysis. J Comput Graph Stat 15(2):265–286
Zuur AF, Ieno EN, Smith GM (2007) Principal component analysis and redundancy analysis. In: Analysing Ecological Data, pp 193–224
Funding
The authors are very grateful to the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (BK20210369).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have equal contribution.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The manuscript is prepared in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation and with the latest (2008) version of Helsinki Declaration of 1975.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Riaz, S., Qamar, S. et al. Development of adaptive standardized precipitation index and its application in the Tibet Plateau region. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 37, 557–575 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-022-02279-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-022-02279-y