Abstract
Key message
This study contributes to increasing the range of tree species studied as bioindicators. This research presents an analysis of 10 macro- and 39 microelements in Cedrus atlantica needles.
Abstract
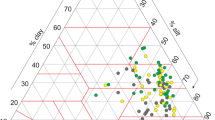
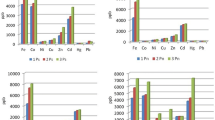
The main objective of this study was to analyze the capacity of Cedrus atlantica (Endl.) Manetti ex Carrière 1855 to accumulate macro- and microelements in order to assess the environmental status. The element concentrations were measured using X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) analysis. The obtained pH values in this study show that the urban soils are neutral to slightly alkaline with low OM content. Macroelements with the highest mean concentrations in soil are Si, Al, Fe, K, Mg, and Ca. The ratio > 2 was determined for mean concentrations of Ca in the soil and Mg in needles from the Zvezdara forest, and for mean concentrations of Cl, Ti, and Fe in needles from the Byford’s forest in relation to the reference site. The accumulation pattern of the macroelements based on the Biological Concentration Factor (BCF) values > 1 for needles is for P, S, Cl, and Ca. Microelements with the highest mean values in soil are Ba, Zr, Ce, Cr, Zn, Rb, Sr, V, and La. Microelements with the highest mean values in Atlas cedar needles are Ce, La, Ba, and Cs. The ratio > 2 was determined for Cr and V concentrations in the needles from the Byford’s and Zvezdara forests and for Cu concentrations in needles from the Byford’s forest in relation to the reference site. The accumulation pattern of the microelements based on the BCF for needles is higher for I, Cs, Mo, Ag, Cd, In, Sn, Sb, and Tl. Since differences in the concentrations of macro- and microelements in the urban areas and the reference site can be identified C. atlantica can be recommended for assessing the environmental status.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Al-Alawi MM, Mandiwana KL (2007) The use of Aleppo pine needles as a biomonitor of heavy metals in the atmosphere. J Hazard Mater 148:43–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.02.001
Alexandrino K, Viteri F, Rybarczyk Y, Guevara Andino JE, Zalakeviciute R (2020) Biomonitoring of metal levels in urban areas with different vehicular traffic intensity by using Araucaria heterophylla needles. Ecol Indic 117:106701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106701
Andersen MK, Raulund-Rasmussen K, Strobe BW, Hansen HCB (2004) The effects of tree species and site on the solubility of Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 154:357–370. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000022991.59456.01
Ashton WM (1972) Nickel pollution. Nature, London
Augusto L, Ranger J, Binkley D, Rothe A (2002) Impact of several common tree species of European temperate forests on soil fertility. Ann For Sci 59:233–253. https://doi.org/10.1051/forest:2002020
Bertolotti G, Gialanella S (2014) Review: use of conifer needles as passive samplers of inorganic pollutants in air quality monitoring. Anal Methods 6:6208–6222. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4AY00172A
Bowen JE (1979) Kinetics of boron, zinc and copper uptake by barley and sugarcane. In: International symposium trace element stress in plants, Los Angeles, November 6, p 24
Brown G, Luu I, O’Sullivan G (2017) Trace metal concentrations in pine needles at varying elevations in proximity to roadways in an urban environment. J Environ Prot 8:733–743. https://doi.org/10.4236/jep.2017.86047
Cansaran-Duman D, Atakol O, Aras S (2011) Assessment of air pollution genotoxicity by RAPD in Evernia prunastri L. Ach. from around iron-steel factory in Karabük. Turkey J Environ Sci 23:1171–1178. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(10)60505-0
Chen L, Liu C, Zhang L, Zou R, Zhang Z (2017) Variation in tree species ability to capture and retain airborne fine particulate matter (PM2.5). Nat Sci Rep 7:3206. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03360-1
De Kimpe CR, Morel JL (2000) Urban soil management: a growing concern. Soil Sci 165:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-200001000-00005
Dmuchowski W, Gozdowski D, Baczewska-Dąbrowska AH, Dąbrowski P, Gworek B, Suwara I (2018) Evaluation of the impact of reducing national emissions of SO2 and metals in Poland on background pollution using a bioindication method. PLoS ONE 13:0192711. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0192711
Dudley N (2008) Guidelines for applying protected area management categories. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland
Farjon A (2010) A handbook of the world’s conifers. Brill Academic Publishers, Leiden, Netherlands
Fellet G, Poscic F, Licen S, Marchiol L, Musetti R, Tolloi A, Berbieri P, Zerbi G (2016) PAHs accumulation on leaves of six evergreen urban shrubs: a field experiment. Atmos Pollut Res 7:915–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2016.05.007
Giampaoli P, Wannaz ED, Tavares AR, Domingos M (2016) Suitability of Tillandsia usneoides and Aechmea fasciata for biomonitoring toxic elements under tropical seasonal climate. Chemosphere 149:14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.01.080
Gough LP, Shacklette HT, Case AA (1979) Element concentrations toxic to plants, animals, and man. U.S. Geological Survey Publications 1466:80. https://doi.org/10.3133/b1466
Guardo AD, Zaccara S, Cerebolini B, Acciarri M, Terzaghi G, Calamari D (2003) Conifer needles as passive biomonitors of the spatial and temporal distribution of DDT from a point source. Chemosphere 52:789–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00256-X
Guidotti M, Stella D, Dominici C, Blasi G, Owczarek M, Vitali M, Protano C (2009) Monitoring of traffic-related pollution in a province of central Italy with transplanted lichen Pseudovernia furfuracea. Bull Environ Contam Tox 83:852–858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9792-7
Herceg Romanić S, Krauthacker B (2007) Are pine needles bioindicators of air pollution? Comparison of organochlorine compound levels in pine needles and ambient air. Arh Hig Rada Toksiko 58:195–199. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10004-007-0012-8
Jonczak J, Parzych A (2015) Comparing Empetronigri-Pinetum and Vaccinio uliginosi-Betuletum pubescentis soils in terms of organic matter stocks and ecochemical indices in the Słowiński National Park. For Res Pap 76:360–369. https://doi.org/10.1515/frp-2015-0035
JuranovićCindrić I, Zeiner M, Starčević A, Stingeder G (2019) Metals in pine needles: characterisation of bioindicators depending on species. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:4339–4346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-2096-x
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (1999) Biogeochemia pierwiastków śladowych. PWN, Warszawa
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (2001) Trace elements in soils and plants, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Koç İ (2021) Using Cedrus atlantica’s annual rings as a biomonitor in observing the changes of Ni and Co concentrations in the atmosphere. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 28:35880–35886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13272-3
Kord B, Mataji A, Babaie S (2010) Pine (Pinus Eldarica Medw.) needles as an indicator for heavy metals pollution. Int J Environ Sci Te 7:79–84. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326119
Lehndorff E, Schwark L (2010) Biomonitoring of air quality in the Cologne Conurbation using pine needles as a passive sampler—part III: major and trace elements. Atmos Environ 44:2822–2829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.04.052
Luo J, She J, Yang P, Sun S, Li W, Gong Y, Tang R (2014) Heavy metal concentrations in timberline trees of Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Ecotoxicology 23:1086–1098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1251-5
Maathuis FJM (2009) Physiological functions of mineral macronutrients. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:250–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2009.04.003
Mahendrappa MK, Foster NW, Weetman GF, Krause HH (1986) Nutrient cycling and availability in forest soils. Can J Soil Sci 66:547–572
Mankovská B (2001) A study of nutrition and toxic elements in the Carpathian Mountain forests using foliar analysis of white fir (Abies alba Mill.), Norway spruce (Picea abies Karst.), beech (Fagus sylvatica L.), and hummus. In: Horst WJ (ed) Plant nutrition: food security and sustainability of agro-ecosystems through basic and applied research. Springer, Dordrecht
Manninen S, Huttunen S, Kontio M (1997) Accumulation of sulphur in and on scots pine needles in the subarctic. Water Air Soil Pollut 95:147–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02406162
Minganti V, Drava G (2018) Tree bark as a bioindicator of the presence of scandium, yttrium and lanthanum in urban environments. Chemosphere 193:847–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.074
Miri M, Ehrampoush MH, Ghaffari HR, Aval HE, Rezai M, Najafpour F, AbaszadehFathabadi Z, Aval MY, Ebrahimi A (2016) Atmospheric heavy metals biomonitoring using a local Pinus eldarica tree. Health Scope 6:39241. https://doi.org/10.17795/jhealthscope-39241
Molina-Villalba I, Lacasaña M, Rodríguez-Barranco M, Hernández AF, Gonzalez-Alzaga B, Aguilar-Garduño C, Gil F (2015) Biomonitoring of arsenic, cadmium, lead, manganese and mercury in urine and hair of children living near mining and industrial areas. Chemosphere 124:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.11.016
Moreira TC, De Oliveira RC, Amato LF, Kang CM, Saldiva P, Saiki M (2016) Intra-urban biomonitoring: source apportionment using tree barks to identify air pollution sources. Environ Int 91:271–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.03.005
Mullins G, Haering KC, Hansen DJ (2011) Basic soil fertility. In: Goatley M Jr, Hensle K (eds) Urban nutrient management handbook. Virginia Cooperative Extension, Virginia
Nadgórska-Socha A, Kandziora-Ciupa M, Ciepał R, Barczyk G (2016) Robinia pseudoacacia and Melandrium album in trace elements biomonitoring and air pollution tolerance index study. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:1741–1752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-016-1010-7
Naidenov M, Travesi A (1977) Nondestructive neutron activation analysis of Bulgarian soils. Soil Sci 124:152
Parzych A (2018) Macro- and micronutrients accumulation in needles of Scots pine in coniferous forest habitats. Sylwan 162:127–137
Parzych A, Sobisz Z (2012) The macro- and microelement content of Pinus sylvestris L. and Pinus nigra J.F. Am. needles in Cladonio-Pinetum habitat of the Słowiński National Park. For Res Pap 73:295–303. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10111-012-0028-y
Petrova S, Yurukova L, Velcheva I (2016) Possibilities of using deciduous tree species in trace element biomonitoring in an urban area (Plovdiv, Bulgaria). Atmos Pollut Res 5:196–202. https://doi.org/10.5094/APR.2014.024
Pietrzykowski M, Socha J, Van Doorn NS (2014) Linking heavy metal bioavailability (Cd, Cu, Zn, and Pb) in Scots pine needles to soil properties in reclaimed mine areas. Sci Total Environ 470–471:501–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.10.008
Protasova NA, Kopayeva MT (1985) Trace and dispersed elements in soils of the Russian Plateau. Pochvovedenie 1:29
Rahman MA, Lee SH, Ji HC, Kabir AH, Jones CS, Lee KW (2018) Importance of mineral nutrition for mitigating aluminum toxicity in plants on acidic soils: current status and opportunities. Int J Mol Sci 19:3073. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103073
Romney EM, Wallace A, Alexander GV (1975) Responses of bush bean and barley to tin applied to soil and to solution culture. Plant Soil 42:585. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009944
Rühling A, Rasmussen L, Pilegaard K, Mäkinen A, Steinnes E (1987) Survey of atmospheric heavy metal deposition in nordic countries in 1985. Report for Nordic Council of Ministers, Kobenhavn
Sæbø A, Popek R, Nawrot B, Hanslin HM, Gawronska H, Gawronski SW (2012) Plant species differences in particulate matter accumulation on leaf surfaces. Sci Total Environ 15:427–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.03.084
Sardans J, Peñuelas J (2005) Trace element accumulation in the moss Hypnum cupressiforme Hedw. and the trees Quercus ilex L. and Pinus halepensis Mill. in Catalonia. Chemosphere 60:1293–1307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.01.059
Savas DS, Sevik H, Isinkaralar K, Türkyılmaz A (2021) The potential of using Cedrus atlantica as a biomonitor in the concentrations of Cr and Mn. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:55446–55453. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14826-1
Scalenghe R, Marsan FA (2009) The anthropogenic sealing of soils in urban areas. Landscape Urban Plan 90:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2008.10.011
Schroeder HA, Buckman J, Balassa JJ (1967) Abnormal trace elements in man: tellurium. J Chron Dis 20:147. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9681(67)90049-5
Serbula SM, Miljkovic DD, Kovacevic RM, Ilic AA (2012) Assessment of airborne heavy metal pollution using plant parts and topsoil. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 76:209–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.10.009
Sevik H, Ozel HB, Cetin M, Özel HU, Erdem T (2019a) Determination of changes in heavy metal accumulation depending on plant species, plant organism, and traffic density in some landscape plants. Air Qual Atmos Health 12:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-018-0641-x
Sevik H, Cetin M, Ozel HB, Akarsu H, Zeren Cetin I (2019b) Analyzing of usability of tree-rings as biomonitors for monitoring heavy metal accumulation in the atmosphere in urban area: a case study of cedar tree (Cedrus sp.). Environ Monit Assess 192:23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-8010-2
Shacklette HT, Erdman JA, Harms TF (1978) Trace elements in plant foodstuffs, in toxicity of heavy metals in the environments, Part I. Marcel Dekker, New York
Shacklette HT, Boerngen JG (1984) Element concentrations in soils and other surficial materials of the conterminous United States. U.S. Geological Survey professional paper 1270:105
Skonieczna J, Małek S, Polowy K, Węgiel A (2014) Element content of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) stands of different densities. Drewno 57:77–87. https://doi.org/10.12841/wood.1644-3985.S13.05
Solgi E, Keramaty M, Solgi M (2020) Biomonitoring of airborne Cu, Pb, and Zn in an urban area employing a broad leaved and a conifer tree species. J Geochem Explor 208:106400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2019.106400
Sun S-Q, Wu Y-H, Zhou J, Yu D, Luo J, Bing H-J (2011) Comparison of element concentrations in FIR and rhododendron leaves and twigs along an altitudinal gradient. Environ Toxicol Chem 30:2608–2619. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.661
Sundaramoorthy P, Chidambaram A, Ganesh KS, Unnikannan P, Baskaran L (2010) Chromium stress in paddy: (i) nutrient status of paddy under chromium stress; (ii) phytoremediation of chromium by aquatic and terrestrial weeds. C R Biol 333:597–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2010.03.002
Swan HSD (1972) Foliar nutrient concentrations in Norway spruce as indicators of tree nutrient status and fertilizer requirement. Woodlands Rep 40:1–20
Tausz M, Trummer W, Goessler W, Wonisch A, Grill D, Naumann S, Jimenez MS, Morales D (2005) Accumulating pollutants in conifer needles on an Atlantic Island: a case study with Pinus canariensis on Tenerife, Canary Islands. Environ Pollut 136:397–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.01.020
Thomas P (2013) Cedrus atlantica. IUCN Red List Threatened Species. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2013-1.RLTS.T42303A2970716.en
Tomašević M, Vukmirović Z, Rajšić S, Tasić M, Stevanović B (2008) Contribution to biomonitoring of some trace metals by deciduous tree leaves in urban areas. Environ Monit Assess 137:393–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9775-2
Tomašević M, Aničić M, Jovanović L, Perić-Grujić A, Ristić M (2011) Deciduous tree leaves in trace elements biomonitoring: a contribution to methodology. Ecol Indic 11:1689–1695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.04.017
Turkyilmaz A, Sevik H, Cetin M (2018) The use of perennial needles as biomonitors for recently accumulated heavy metals. Landscape Ecol Eng 14:115–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11355-017-0335-9
Watmough SA (2014) Calcium, strontium and barium biogeochemistry in a forested catchment and insight into elemental is crimination. Biogeochemistry 118:357–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-013-9938-x
Wyttenbach A, Tobler L (1988) The seasonal variation of 20 elements in 1st and 2nd year needles of Norway spruce, Picea abies (L.) Karst. Trees 2:52–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01196345
Wyttenbach A, Tobler L (2000) The concentrations of Fe, Zn and Co in successive needle age classes of Norway spruce [Picea abies (L.) Karst.]. Trees 14:198–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009763
Yilmaz S, Zengin M (2004) Monitoring environmental pollution in Erzurum by chemical analysis of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) needles. Environ Int 29:1041–1047. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00097-7
Zhang K, Xu XN, Wang Q (2010) Characteristics of N mineralization in urban soils of Hefei, East China. Pedosphere 20:236–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(10)60011-2
Acknowledgements
This research has been financially supported by the Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation of Republic of Serbia (Contract No: 451-03-47/2023-01/200026, 451-03-47/2023-01/200012, and 451-03-47/2023-01/200168).
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Communicated by Koike.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Štrbac, S., Veselinović, G., Antić, N. et al. The macro- and microelements content in Cedrus atlantica (Endl.) Manetti ex Carrière (Pinaceae) needles as an indicator for assessing the environmental status. Trees 37, 1013–1025 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-023-02401-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-023-02401-9