Abstract
Background
Congenital obstructive uropathy (OU) is a leading cause of pediatric kidney failure, representing a unique mechanism of injury, in part from renal tubular stretch and ischemia. Tubular injury biomarkers have potential to improve OU-specific risk stratification.
Methods
Patients with OU were identified in the Chronic Kidney Disease in Children (CKiD) study. “Cases” were defined as individuals receiving any kidney replacement therapy (KRT), while “controls” were age- and time-on-study matched and KRT free at last study visit. Urine and plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), interleukin 18 (IL-18), and liver-type fatty acid-binding protein (L-FABP) levels were measured at enrollment and annually and compared between cases and controls. Urine values were normalized to urine creatinine.
Results
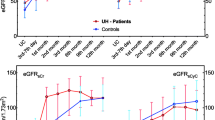
In total, 22 cases and 22 controls were identified, with median (interquartile range) ages of 10.5 (9.0–13.0) and 15.9 (13.9–16.9) years at baseline and outcome, respectively. At enrollment there were no differences noted between cases and controls for any urine (u) or plasma (p) biomarker measured. However, the mean pNGAL and uL-FABP/creatinine increased throughout the study period in cases (15.38 ng/ml per year and 0.20 ng/ml per mg/dl per year, respectively, p = 0.01 for both) but remained stable in controls. This remained constant after controlling for baseline glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
Conclusions
In children with OU, pNGAL and uL-FABP levels increased over the 5 years preceding KRT; independent of baseline GFR. Future studies are necessary to identify optimal cutoff values and to determine if these markers outperform current clinical predictors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roth KS, Koo HP, Spottswood SE, Chan JC (2002) Obstructive uropathy: an important cause of chronic renal failure in children. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 41:309–314. https://doi.org/10.1177/000992280204100503
Weaver DJ Jr, Somers MJG, Martz K, Mitsnefes MM (2017) Clinical outcomes and survival in pediatric patients initiating chronic dialysis: a report of the NAPRTCS registry. Pediatr Nephrol 32:2319–2330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3759-4
Benfield MR, McDonald RA, Bartosh S, Ho PL, Harmon W (2003) Changing trends in pediatric transplantation: 2001 annual report of the North American pediatric renal transplant cooperative study. Pediatr Transplant 7:321–335
McLeod DJ, Szymanski KM, Gong E, Granberg C, Reddy P, Sebastiao Y, Fuchs M, Gargollo P, Whittam B, VanderBrink BA, Pediatric Urology Midwest Alliance (PUMA) (2019) Renal replacement therapy and intermittent catheterization risk in posterior urethral valves. Pediatrics 143:e20182656. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2018-2656
McLeod DJ, Ching CB, Sebastiao YV, Greenberg JH, Furth SL, McHugh KM, Becknell B (2019) Common clinical markers predict end-stage renal disease in children with obstructive uropathy. Pediatr Nephrol 34:443–448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-018-4107-z
Winnicki E, McCulloch CE, Mitsnefes MM, Furth SL, Warady BA, Ku E (2018) Use of the kidney failure risk equation to determine the risk of progression to end-stage renal disease in children with chronic kidney disease. JAMA Pediatr 172:174–180. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2017.4083
Devarajan P (2008) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL): a new marker of kidney disease. Scand J Clin Lab Investig Suppl 241:89–94. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365510802150158
Mitsnefes MM, Kathman TS, Mishra J, Kartal J, Khoury PR, Nickolas TL, Barasch J, Devarajan P (2007) Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a marker of renal function in children with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 22:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-006-0244-x
Noyan A, Parmaksiz G, Dursun H, Ezer SS, Anarat R, Cengiz N (2015) Urinary NGAL, KIM-1 and L-FABP concentrations in antenatal hydronephrosis. J Pediatr Urol 11(249):e241–e246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpurol.2015.02.021
Dinarello CA (2007) Interleukin-18 and the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. Semin Nephrol 27:98–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semnephrol.2006.09.013
Awad AS, El-Sharif AA (2011) Curcumin immune-mediated and anti-apoptotic mechanisms protect against renal ischemia/reperfusion and distant organ induced injuries. Int Immunopharmacol 11:992–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2011.02.015
Wang S, Chen F, Yang S, Shi J (2018) Interleukin-18. Int Heart J 59:786–790. https://doi.org/10.1536/ihj.17-154
Mohamed Ali OS, Elshaer SS, Anwar HM, Zohni MSE (2017) Relevance of cystatin-C, N-acetylglucosaminidase, and Interleukin-18 with the diagnosis of acute kidney injury induced by cadmium in rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 31(11). https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.21968
Parikh CR, Jani A, Melnikov VY, Faubel S, Edelstein CL (2004) Urinary interleukin-18 is a marker of human acute tubular necrosis. Am J Kidney Dis 43:405–414
Kamijo-Ikemori A, Sugaya T, Matsui K, Yokoyama T, Kimura K (2011) Roles of human liver type fatty acid binding protein in kidney disease clarified using hL-FABP chromosomal transgenic mice. Nephrology 16:539–544. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1797.2011.01469.x
Kamijo A, Sugaya T, Hikawa A, Okada M, Okumura F, Yamanouchi M, Honda A, Okabe M, Fujino T, Hirata Y, Omata M, Kaneko R, Fujii H, Fukamizu A, Kimura K (2004) Urinary excretion of fatty acid-binding protein reflects stress overload on the proximal tubules. Am J Pathol 165:1243–1255. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63384-6
Furth SL, Cole SR, Moxey-Mims M, Kaskel F, Mak R, Schwartz G, Wong C, Munoz A, Warady BA (2006) Design and methods of the chronic kidney disease in children (CKiD) prospective cohort study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1:1006–1015. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.01941205
Schwartz GJ, Munoz A, Schneider MF, Mak RH, Kaskel F, Warady BA, Furth SL (2009) New equations to estimate GFR in children with CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:629–637. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2008030287
Haase M, Bellomo R, Devarajan P, Schlattmann P, Haase-Fielitz A, NGAL Meta-analysis Investigator Group (2009) Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 54:1012–1024. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.07.020
Dubin RF, Judd S, Scherzer R, Shlipak M, Warnock DG, Cushman M, Sarnak M, Parikh C, Bennett M, Powe N, Peralta CA (2018) Urinary tubular injury biomarkers are associated with ESRD and death in the REGARDS study. Kidney Int Rep 3:1183–1192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ekir.2018.05.013
Forster CS, Devarajan P (2017) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: utility in urologic conditions. Pediatr Nephrol 32:377–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-016-3540-0
Bienias B, Sikora P (2018) Potential novel biomarkers of obstructive nephropathy in children with Hydronephrosis. Dis Markers 2018:1015726. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1015726
Gupta S, Jackson AR, DaJusta DG, McLeod DJ, Alpert SA, Jayanthi VR, McHugh K, Schwaderer AR, Becknell B, Ching CB (2018) Urinary antimicrobial peptides: potential novel biomarkers of obstructive uropathy. J Pediatr Urol 14:238 e231–238 e236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpurol.2018.03.006
Gupta S, Nicassio L, Yepes Junquera G, Jackson A, Fuchs M, McLeod D, Alpert S, Jayanthi R, DaJusta D, McHugh K, Becknell B, Ching C (2019) Urinary HIP/PAP and BD-1 indicate surgical success after pediatric ureteropelvic junction obstruction surgery. Pediatric Urology Fall Congress Scottsdale, Arizona https://fallcongressspuonlineorg/multimedia/files/2019/presentations/Thursday/0112_Chingpdf Acccessed May 2020
Chou KM, Lee CC, Chen CH, Sun CY (2013) Clinical value of NGAL, L-FABP and albuminuria in predicting GFR decline in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. PLoS One 8:e54863. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0054863
Bennett MR, Nehus E, Haffner C, Ma Q, Devarajan P (2015) Pediatric reference ranges for acute kidney injury biomarkers. Pediatr Nephrol 30:677–685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-2989-y
Viswanathan V, Sivakumar S, Sekar V, Umapathy D, Kumpatla S (2015) Clinical significance of urinary liver-type fatty acid binding protein at various stages of nephropathy. Indian J Nephrol 25:269–273. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-4065.145097
Bani-Hani AH, Leslie JA, Asanuma H, Dinarello CA, Campbell MT, Meldrum DR, Zhang H, Hile K, Meldrum KK (2009) IL-18 neutralization ameliorates obstruction-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and renal fibrosis. Kidney Int 76:500–511. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2009.216
Daemen MA, van't Veer C, Wolfs TG, Buurman WA (1999) Ischemia/reperfusion-induced IFN-gamma up-regulation: involvement of IL-12 and IL-18. J Immunol 162:5506–5510
Faust J, Menke J, Kriegsmann J, Kelley VR, Mayet WJ, Galle PR, Schwarting A (2002) Correlation of renal tubular epithelial cell-derived interleukin-18 up-regulation with disease activity in MRL-Faslpr mice with autoimmune lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum 46:3083–3095. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.10563
Striz I, Krasna E, Honsova E, Lacha J, Petrickova K, Jaresova M, Lodererova A, Bohmova R, Valhova S, Slavcev A, Vitko S (2005) Interleukin 18 (IL-18) upregulation in acute rejection of kidney allograft. Immunol Lett 99:30–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2005.01.010
Parikh CR, Abraham E, Ancukiewicz M, Edelstein CL (2005) Urine IL-18 is an early diagnostic marker for acute kidney injury and predicts mortality in the intensive care unit. J Am Soc Nephrol 16(10):3046–3052. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2005030236
Chiang CK, Hsu SP, Pai MF, Peng YS, Ho TI, Liu SH, Hung KY, Tsai TJ, Hsieh BS (2005) Plasma interleukin-18 levels in chronic renal failure and continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Blood Purif 23:144–148. https://doi.org/10.1159/000083620
Zhou J, Shi F, Xun W (2018) Leptin, hs-CRP, IL-18 and urinary protein before and after treatment of children with nephrotic syndrome. Exp Ther Med 15:4426–4430. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.5923
Wang YB, Shan NN, Chen O, Gao Y, Zou X, Wei DE, Wang CX, Zhang Y (2011) Imbalance of interleukin-18 and interleukin-18 binding protein in children with Henoch-Schonlein purpura. J Int Med Res 39:2201–2208. https://doi.org/10.1177/147323001103900616
Chung HL, Shin JY, Ju M, Kim WT, Kim SG (2011) Decreased interleukin-18 response in asthmatic children with severe mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Cytokine 54:218–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2011.02.008
Acknowledgment
Data in this manuscript were collected by the Chronic Kidney Disease in Children (CKiD) prospective cohort study with clinical coordinating centers (principal investigators) at Children’s Mercy Hospital and the University of Missouri, Kansas City (Bradley Warady, MD), and Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (Susan Furth, MD, PhD), Central Biochemistry Laboratory (George Schwartz, MD) at the University of Rochester Medical Center, and data coordinating center (Alvaro Muñoz, PhD and Derek Ng, PhD) at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
Funding
The CKiD study is supported by grants from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, with additional funding from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (U01DK66143, U01DK66174, U24DK082194, U24DK066116). The CKiD website is located at https://statepi.jhsph.edu/ckid/.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McLeod, D.J., Sebastião, Y.V., Ching, C.B. et al. Longitudinal kidney injury biomarker trajectories in children with obstructive uropathy. Pediatr Nephrol 35, 1907–1914 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-020-04602-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-020-04602-7