Abstract
Background
Enuresis (NE) is a clinical condition of multifactorial etiology that leads to difficulties in child/adolescent social interaction.
Methods
This was a prospective study on the impact of multidisciplinary assessment of 6- to 17-year-old patients with monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis (MNE), including a structured history, clinical/neurological examination, bladder and bowel diaries, sleep diary and questionnaires, psychological evaluation [Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL) and PedsQL 4.0 questionnaires], urinary sonography, blood and urine laboratory tests, polysonography (PSG), and balance evaluation.
Results
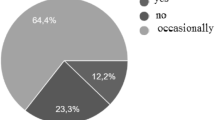
A total of 140 enuretic participants were evaluated, of whom 27 were diagnosed with NE complicated by urinary disorder, four with hypercalciuria, three with nephropathy and one with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Among the 87 participants who underwent PSG, six were diagnosed with severe apnea. Of the 82 MNE patients who underwent full assessment, 62 were male (75.6 %), and the mean age was 9.5 (±2.6) years. A family history of NE was diagnosed in 91.1 % of first- and second-degree relatives, constipation in 89.3 % and mild/moderate apnea in 40.7 %. Balance control alteration was identified by physical therapy evaluation of MNE patients. Participants’ quality of life evaluation scores were significantly lower than those of their parents.
Conclusion
Enuresis is a multifactorial disorder that requires a structured diagnostic approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nevéus T, von Gontard A, Hoebeke P, Hjälmås K, Bauer S, Bower W, Jørgensen TM, Rittig S, Walle JV, Yeung CK, Djurhuus JC (2006) The standardization of terminology of lower urinary tract function in children and adolescents: report from the Standardisation Committee of the International Children’s Continence Society. J Urol 176:314–324
Austin PF, Bauer SB, Bower W, Chase J, Franco I, Hoebeke P, Rittig S, Walle JV, von Gontard A, Wright A, Yang SS, Nevéus T (2014) The standardization of terminology of lower urinary tract function in children and adolescents: update report from the Standardization Committee of the International Children’s Continence Society. J Urol 191:1863–1865
Yeung CK, Sihoe JD, Sit FK, Bower W, Sreedhar B, Lau J (2004) Characteristics of primary nocturnal enuresis in adults: an epidemiological study. Br J Urol Int 93:341–345
Von Gontard A, Schaumburg H, Hollmann E, Eiberg H, Rittig S (2001) The genetics of enuresis—a review. J Urol 166:2438
Butler RJ, Holland P (2000) The three systems: A conceptual way of understanding nocturnal enuresis. Scand J Urol Nephrol 34:270–277
von Gontard A, Niemczyk J, Weber M, Equit M (2014) Specific behavioral comorbidity in a large sample of children with functional incontinence: Report of 1,001 cases. Neurourol Urodyn 34:763–768
von Gontard A, Equit M (2015) Comorbidity of ADHD and incontinence in children. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 24:127–140
Niemczyk J, Equit M, Braun-Bither K, Klein AM, Gontard V (2014) Prevalence of incontinence, attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder and oppositional defiant disorder in preschool children. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 24:837–843
Borch L, Hagstroem S, Bower WF, Rittig CS, Rittig S (2013) Bladder and bowel dysfunction (BBD) and the resolution of urinary incontinence with succesfull management of bowel symptoms in children. Acta Paediatr 102:e215–e220
Nevéus T, Stenberg A, Läckgren G, Tuvemo T, Hetta J (1999) Sleep of children with enuresis: a polysomnographic study. Pediatrics 103:1193–1197
Baeyens D, Roeyers H, Naert S, Hoebeke P, Vande Walle J (2007) The impact of maturation of brainstem inhibition on enuresis: a startle eye blink modification study with 2-year followup. J Urol 178:2621–2625
von Gontard A, Freitag CM, Seifen S, Pukrop R, Rohling D (2006) Neuromotor development in nocturnal enuresis. Dev Med Child Neurol 48:744–750
Esposito M, Gallai B, Parisi L, Roccella M, Marotta R, Lavano SM, Mazzotta G, Patriciello G, Precenzano F, Carotenuto M (2013) Visuomotor competencies and primary monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis in prepubertal aged children. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 9:921–926
Street E, Broughton L (1990) The treatment of childhood nocturnal enuresis in the community. Child Care Health Dev 16:365–372
Critério de Classificação Econômica Brasil 2009. Diretrizes de ordem geral, a serem consideradas pelas entidades prestadoras de serviços e seus clientes, a respeito da adoção do novo critério de classificação econômica brasil. Available at: http://www.abep.org/criterioBrasil.aspx. Accessed 26 April 2015
Santos EOL, Silvares EFM (2006) Enuretical children and referred children for university mental health services: a comparative study of their parents’ perception. Psicol Reflex Crit 19:277–282
Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA (2001) Manual for the ASEBA school—age forms and profiles. University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youths, and Families, Burlington
Ferreira VR, Carvalho LBC, Ruotolo F, Morais JF, Prado LBF, Prado GF (2009) Sleep disturbance scale for children: translation, cultural adaptation, and validation. Sleep Med 10:457–463
Vaz AP, Drummond M, Mota PC, Severo M, Almeida J, Winck JC (2011) Translation of Berlin questionnaire to Portuguese language and its application in OSA identification in a sleep disordered breathing clinic. Rev Port Pneumol 17:59–65
Bertolazi AN, Fagondes SC, Hoff LS, Pedro VD, Barreto SSM, Johns MW (2009) Portuguese-language version of the Epworth sleepiness scale: validation for use in Brazil. J Bras Pneumol 35:877–883
Klatchoian DA, Len CA, Terreri MT, Silva M, Itamoto C, Ciconelli RM, Varni JW, Hilário MO (2008) Quality of life of children and adolescents from São Paulo: reliability and validity of the Brazilian version of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory version 4.0 Generic Core Scales. J Pediatr 84:308–315
Winter DA (1995) Human balance and posture control during standing and walking. Gait Posture 3:193–214
Berry RB, Brooks R, Gamaldo CE, Harding SM, Marcus CL, Vauhn BV; for the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (2012) The AASM manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology and technical specifications, version 2.0. www.aasmnet.org. American Academy of Sleep Medicine, Darien
Jequier S, Rousseau O (1987) Sonographic measurements of the normal bladder wall in children. AJR Am J Roentgenol 149:563–566
Joensson IM, Siggaard C, Rittig S, Hagstroem S, Djurhuus JC (2008) Transabdominal ultrasound of rectum as a diagnostic tool in childhood constipation. J Urol 179:1997–2002
Rasquin A, Di Lorenzo LC, Forbes D, Guiraldes E, Hyams JS, Staiano A, Walker LS (2006) Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders: child/adolescent. Gastroenterology 130:1527–1537
Lewis SJ, Heaton KW (1997) Stool form scale as a useful guide to intestinal transit time. Scand J Gastroenterol 32:920–924
Naseri M, Hiradfar M (2012) Monosymptomatic and non-monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis: a clinical evaluation. Arch Iran Med 15:702–706
Fockema MW, Candy GP, Kruger D, Haffejee M (2012) Enuresis in South African children: prevalence, associated factors and parental perception of treatment. BJU Int 110(11 Pt C):E1114–E1120
Ozkan KU, Garipardic M, Toktamis A, Karabiber H, Sahinkanat T (2004) Enuresis prevalence and accompanying factors in schoolchildren: a questionnaire study from southeast Anatolia. Urol Int 73:149–155
Yeung CK, Sreedhar B, Sihoe JD, Sit FK, Lau J (2006) Differences in characteristics of nocturnal enuresis between children and adolescents: a critical appraisal from a large epidemiological study. BJU Int 97:1069–1073
Aljefri HM, Basurreh OA, Yunus F, Bawazir AA (2013) Nocturnal enuresis among primary school children. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 24:1233–1241
Butler RJ, Golding J, Northstone K (2005) Nocturnal enuresis at 7.5 years old: Prevalence and analysis of clinical signs. BJU Int 96:404–410
Morais MB, Maffei HV (2006) Constipation. J Pediatr 76[Suppl 2]:S147–S156
Wolfish N, Pivik R, Busby K (1997) Elevated sleep arousal thresholds in enuretic boys: clinical implications. Acta Paediatr 86:381–384
Hunsballe JM (2000) Increased delta component in computerized sleep electroencephalographic analysis suggests abnormally deep sleep in primary monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis. Scand J Urol Nephrol 34:294–302
Reimão R, Pachelli LC, Carneiro R, Faiwichow G (1993) Primary sleep enuresis in childhood: polysomnography evidences of sleep stage and time modulation. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 51:41–45
Inoue M, Shimojima H, Chiba H, Tsukahara N (1987) Rhythmic slow wave observed on nocturnal sleep encephalogram in children with idiopathic nocturnal enuresis. Sleep 10:570–579
Marcus CL, Brooks LJ, Draper KA, Gozal D, Halbower AC, Jones J, Schechter MS, Ward SD, Sheldon SH, Shiffman RN, Lehmann C, Spruyt K, American Academy of Pediatrics (2012) Diagnosis and management of childhood obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Pediatrics 130(3):e714–e755
Brooks LJ, Topol HI (2003) Enuresis in children with sleep apnea. J Pediatr 142:515–518
Weider DJ, Sateia MJ, West RP (1991) Nocturnal enuresis in children with upper airway obstruction. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 105:427–432
Alexopoulos EI, Kaditis AG, Kostadima E, Gourgoulianis K (2005) Resolution of nocturnal enuresis in snoring children after treatment with nasal budesonide. Urology 66:194
Alexopoulos EI, Kostadima E, Pagonari I, Zintzaras E, Gourgoulianis K, Kaditis AG (2006) Association between primary nocturnal enuresis and habitual snoring in children. Urology 68:406–409
Nevéus T, Leissner L, Rudblad S, Bazargani F (2014) Respiration during sleep in children with therapy-resistant enuresis. Acta Paediatr 103:300–304
Alexopoulos EI, Malakasioti G, Varlami V, Miligkos M, Gourgoulianis K, Kaditis AG (2014) Nocturnal enuresis is associated with moderate-to-severe obstructive sleep apnea in children with snoring. Pediatr Res 76:555–559
Dhondt K, Baert E, Van Herzeele C, Raes A, Groen LA, Hoebeke P, Vande Walle J (2014) Sleep fragmentation and increased periodic limb movements are more common in children with nocturnal enuresis. Acta Paediatr 103:e268–e272
Dhondt K, Van Herzeele C, Roels SP, Raes A, Groen LA, Hoebeke P, Walle JV (2015) Sleep fragmentation and periodic limb movements in children with monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis and polyuria. Pediatr Nephrol 30:1157–1162
Rocha MM, Costa NJ, Silvares EFM (2008) Changes in parents’ and self-reports of behavioral problems in Brazilian adolescents after behavioral treatment with urine alarm for nocturnal enuresis. Int Braz J Urol 34:749–757
Equit M, Hill J, Hübner A, von Gontard A (2014) Health-related quality of life and treatment effects on children with functional incontinence, and their parents. J Pediatr Urol 10:922–928
Naitoh Y, Kawauchi A, Soh J, Kamoi K, Miki T (2012) Health related quality of life for monosymptomatic enuretic children and their mothers. J Urol 188:1910–1914
Neveus T, Eggert P, Evans J, Macedo A, Rittig S, Tekgül S, Vande Walle J, Yeung CK, Robson L, International Children’s Continence Society (2010) Evaluation of and treatment for monosymptomatic enuresis: a standardization document from the International children’s continence society. J Urol 183:441–447
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. J.W. Varni for permission to use the Peds QL 4.0 questionnaires and the MAPI Institute for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
This work was supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) Grant # 2011/17589-1.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Instituto da Criança of Hospital das Clínicas of the University of São Paulo Medical School in Research, number 0649/10, and informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nascimento Fagundes, S., Azevedo Soster, L., Lebl, A.S. et al. Impact of a multidisciplinary evaluation in pediatric patients with nocturnal monosymptomatic enuresis. Pediatr Nephrol 31, 1295–1303 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-016-3316-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-016-3316-6