Abstract
Background
To examine the relationship of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25OHD) concentrations with serum parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels, body mass index (BMI), and environmental factors in a population of Caucasian children living at latitude 43°N.
Methods
Cross-sectional study on 288 children aged 1 month to 13 years who presented to a pediatric emergency unit during a 21-month period.
Results
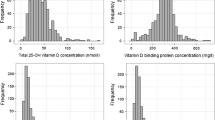
Mean (SD) serum 25OHD concentrations were 40.6 (17.6), 30.9 (12.0), and 26.4 (9.9) ng/ml (1 ng/ml = 2.5 nmol/l), in children aged 0–1, 2–5, and ≥ 6 years, respectively. Serum PTH levels were 26.6 (13.6), 24.3 (11.9), and 32.7 (12.1) pg/ml in the same groups. Infants had 25OHD concentrations significantly higher. PTH levels were significantly higher in children aged ≥ 6 years. There was no significant correlation between serum 25OHD and PTH concentrations. Totals of 15.6 % and 2.1 % of children had 25OHD values less than 20 and 10 ng/ml, respectively, but none had elevated serum PTH or clinical manifestations related with vitamin D deficiency. Age (inverse correlation) and season (higher values in summer), but not BMI, sex, and time spent outdoors, influenced serum 25OHD concentrations.
Conclusions
Our results raise doubt on the assumption of only a serum 25OHD threshold as indicative of vitamin D deficiency in children.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shaw NJ, Mughal MZ (2013) Vitamin D and child health: part 2 (extraskeletal and other aspects). Arch Dis Child 98:368–372
Glade MJ (2013) Vitamin D: health panacea or false prophet? Nutrition 29:37–41
Rey C, Sánchez-Arango D, López-Herce J, Martínez-Camblor P, García-Hernández I, Prieto B, Pallavicini Z (2014) Vitamin D deficiency at pediatric intensive care admission. J Pediatr (Rio J) 90:135–142
Sattar N, Welsh P, Panarelli M, Forouhi NG (2012) Increasing requests for vitamin D measurement: costly confusing, and without credibility. Lancet 379:95–96
Greer FR (2009) Defining vitamin D deficiency in children: beyond 25-OH vitamin D serum concentrations. Pediatrics 124:1471–1473
Hollis BW (2005) Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels indicative of vitamin D sufficiency implications for establishing a new effective dietary intake recommendation for vitamin D. J Nutr 135:317–322
Cranney A, Horsley T, O’Donnell S, Weiler H, Puil L, Ooi D, Atkinson S, Ward L, Moher D, Hanley D, Fang M, Yazdi F, Garritty C, Sampson M, Barrowman N, Tsertsvadze A, Mamaladze V (2007) Effectiveness and safety of vitamin D in relation to bone health. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep) 158:1–235
Ginde AA, Wolfe P, Camargo CA Jr, Schwartz RS (2012) Defining vitamin D status by secondary hyperparathyroidism in the U.S. population. J Endocrinol Invest 35:42–48
Gordon CM, DePeter KC, Feldman HA, Grace E, Emans SJ (2004) Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among healthy adolescents. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 158:531–537
Marwaha RK, Tandon N, Reddy DR, Aggarwal R, Singh R, Sawhney RC, Saluja B, Ganie MA, Singh S (2005) Vitamin D and bone mineral density status of healthy schoolchildren in northern India. Am J Clin Nutr 82:477–482
Gordon CM, Feldman HA, Sinclair L, Williams AL, Kleinman PK, Perez-Rossello J, Cox JE (2008) Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among healthy infants and toddlers. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 162:505–512
Ziegler EE, Hollis BW, Nelson SE, Jeter JM (2006) Vitamin D deficiency in breastfed infants in Iowa. Pediatrics 118:603–610
Greer FR, Marshall S (1989) Bone mineral content, serum vitamin D metabolite concentrations, and ultraviolet B light exposure in infants fed human milk with and without vitamin D2 supplements. J Pediatr 114:204–212
Valcour A, Blocki F, Hawkins DM, Rao SD (2012) Effects of age and serum 25-OH-vitamin D on serum parathyroid hormone levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:3989–3995
Carbone LD, Rosenberg EW, Tolley EA, Holick MF, Hughes TA, Watsky MA, Barrow KD, Chen TC, Wilkin NK, Bhattacharya SK, Dowdy JC, Sayre RM, Weber KT (2008) 25-Hydroxyvitamin D, cholesterol, and ultraviolet irradiation. Metabolism 57:741–748
Ashwell M, Stone EM, Stolte H, Cashman KD, Macdonald H, Lanham-New S, Hiom S, Webb A, Fraser D (2010) UK Food Standards Agency Workshop Report: an investigation of the relative contributions of diet and sunlight to vitamin D status. Br J Nutr 4:1–9
Jamal-Allial A, Griffith JL, Tucker KL (2013) The longitudinal association of vitamin D serum concentrations & adiposity phenotype. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.12.004
Rodríguez-Rodríguez E, Navia-Lombán B, López-Sobaler AM, Ortega RM (2010) Associations between abdominal fat and body mass index on vitamin D status in a group of Spanish schoolchildren. Eur J Clin Nutr 64:461–467
Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Gordon CM, Hanley DA, Heaney RP, Murad MH, Weaver CM, Endocrine Society (2011) Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:1911–1930
Wortsman J, Matsuoka LY, Chen TC, Lu Z, Holick MF (2000) Decreased bioavailability of vitamin D in obesity. Am J Clin Nutr 72:690–693
Wagner CL, Greer FR, the Section on Breastfeeding and Committee on Nutrition (2008) Prevention of rickets and vitamin D deficiency in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatrics 122:1142–1152
Braegger C, Campoy C, Colomb V, Decsi T, Domellof M, Fewtrell M, Hojsak I, Mihatsch W, Molgaard C, Shamir R, Turck D, van Goudoever J, ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition (2013) Vitamin D in the healthy paediatric population: a position paper by the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 56:692–701
National Research Council (2011) Dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC, Assessed at http://www.nap.edu/ca on January 2014
Willis CM, Laing EM, Hall DB, Hausman DB, Lewis RD (2007) A prospective analysis of plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in white and black prepubertal females in the southeastern United States. Am J Clin Nutr 85:124–130
Pearce SH, Cheetham TD (2010) Diagnosis and management of vitamin D deficiency. BMJ 340:140–147
Dawodu A, Agarwal M, Hossain M, Kochiyil J, Zayed R (2003) Hypovitaminosis D and vitamin D deficiency in exclusively breast-feeding infants and their mothers in summer: a justification for vitamin D supplementation of breast-feeding infants. J Pediatr 142:169–173
Roth DE, Martz P, Yeo R, Prosser C, Bell M, Jones AB (2005) Are national vitamin D guidelines sufficient to maintain adequate blood levels in children? Can J Public Health 96:443–449
Kim MJ, Na B, No SJ, Han HS, Jeong EH, Lee W, Han Y, Hyeun T (2010) Nutritional status of vitamin D and the effect of vitamin D supplementation in Korean breast-fed infants. J Korean Med Sci 25:83–89
Consensus Vitamin D position statement (2010) Assessed at http://www.nos.org.uk on September 2013
Carrascosa A, Fernández JM, Fernández A, López-Siguero JP, López D, Sánchez E (2010) Estudios Españoles de Crecimiento. Assessed at: http://www.aeped.es/noticias/estudios-espanoles-crecimiento-2010 on February 2014
Mansbach JM, Ginde AA, Camargo CA (2009) Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels among US children aged 1 to 11 years: do children need more vitamin D? Pediatrics 124:1404–1410
Akman AO, Tumer L, Hasanoglu A, Ilhan M, Caycı B (2011) Frequency of vitamin D insufficiency in healthy children between 1 and 16 years of age in Turkey. Pediatr Int 53:968–973
Yetley EA (2008) Assessing the vitamin D status of the US population. Am J Clin Nutr 88:S558–S564
Pela I (2012) How much vitamin D for children? Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab 9:112–117
Medical Advisory Secretariat (2010) Clinical utility of vitamin D testing: an evidence-based analysis. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser 10:1–95, Assessed at:http://www.health.gov.on.ca/english/providers/program/mas/tech/reviews/pdf/rev_vitamin d_201002.pdf, on March 2013
Ross C (2011) The 2011 dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D: what dietetics practitioners need to know. J Am Diet Assoc 111:524–527
Brannon PM (2012) Key questions in vitamin D research. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 72:154–162
Margolles M, Donate I, Alonso P (2009) Ministry of health and health services. Survey of children’s health in Asturias. Assessed at: www.astursalud.es on Janury 2014
Absoud M, Cummins C, Lim MJ, Wassmer E, Shaw N (2011) Prevalence and predictors of vitamin D insufficiency in children: a Great Britain population-based study. PLoS One 6:e22179
Lapatsanis D, Moulas A, Cholevas V, Soukakos P, Papadopoulou ZL, Challa A (2005) Vitamin D: a necessity for children and adolescents in Greece. Calcif Tissue Int 77:348–355
Alonso A, Rodríguez J, Carvajal I, Prieto ML, Rodríguez RM, Pérez AM, Cepeda A, Nuño F, Santos F, Collaborative Group on Prophylaxis with Vitamin D in Asturias (2011) Prophylactic vitamin D in healthy infants: assessing the need. Metabolism 60:1719–1725
Hashemipour S, Larijani B, Adibi H, Sedaghat M, Pajouhi M, Bastan-Hagh MH, Soltani A, Javadi E, Shafaei AR, Baradar-Jalili R, Hossein-Nezhad A (2006) The status of biochemical parameters in varying degrees of vitamin D deficiency. J Bone Miner Metab 24:213–218
Sancho AJM, Riesco MJ, Jiménez AC, Sánchez de Cos EM, Montero CJ, López BM (2012) Atlas of solar radiation in Spain. EUMETSAT. Assessed at: http://www.aemet.es/documentos/es/serviciosclimaticos/datosclimatologicos/atlas_radiacion_solar/atlas_de_radiacion_24042012.pdf on May 2014
Shaw NJ, Mughal MZ (2013) Vitamin D and child health Part 1 (skeletal aspects). Arch Dis Child 98:363–367
Bischof MG, Heinze G, Vierhapper H (2006) Vitamin D status and its relation to age and body mass index. Horm Res 66:211–215
Reinehr T, De Sousa G, Alexy U, Kersting M, Andler W (2007) Vitamin D status and parathyroid hormone in obese children before and after weight loss. Eur J Endocrinol 157:225–232
Nesby-O’Dell S, Scanlon KS, Cogswell ME, Gillespie C, Hollis BW, Looker AC, Allen C, Doughertly C, Gunter EW, Bowman BA (2002) Hypovitaminosis D prevalence and determinants among African American and white women of reproductive age: third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1988–94. Am J Clin Nutr 76:187–192
Holick MF (2013) Bioavailability of vitamin D and its metabolites in black and white adults. N Engl J Med 369:2047–2048
Powe CE, Evans MK, Wenger J, Zonderman AB, Berg AH, Nalls M, Tamez H, Zhang D, Bhan I, Karumanchi SA, Powe NR, Thadhani R (2013) Vitamin D–binding protein and vitamin D status of black Americans and white Americans. N Engl J Med 369:1991–2000
Schwartz JB, Lai J, Lizaola B, Kane L, Markova S, Weyland P, Terrault NA, Stotland N, Bikle D (2014) A comparison of measured and calculated free 25(OH) vitamin D levels in clinical populations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99:1631–1637
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the infants and their families for their participation in the study and the pediatricians of the Hospital Universitario Central of Asturias who recruited children for the study. This work was partly presented at the 47th ESPN Annual Scientific Meeting of the European Society for Pediatric Nephrology.
Funding/support
Partly supported by grant FIS ECO8/00238 from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III and by the Fundación Nutrición y Crecimiento.
Author contributions
Dra. Alonso had full access to all of the data in the study and took responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Study concept and design: Alonso, Rodríguez, Santos. Obtainment of data: Pallavicini, Avello. Analysis and interpretation of data: Alonso, Santos, Pallavicini. Drafting of the manuscript: Alonso, Santos. Critical revision of the manuscript: Santos. Statistical analysis: Martínez-Camblor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alonso, M.A., Pallavicini, Z.F., Rodríguez, J. et al. Can vitamin D status be assessed by serum 25OHD in children?. Pediatr Nephrol 30, 327–332 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-2927-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-014-2927-z