Abstract
Background and aims
Self-expandable metal stent (SEMS) insertion is the standard palliative treatment for unresectable malignant extrahepatic biliary obstruction (MBO). Drawbacks of conventional fully covered SEMS (FCSEMS) and uncovered SEMS (USEMS) include stent migration and tumor ingrowth, respectively. This study aimed to compare stent patency in MBO with the newly design multi-hole SEMS (MHSEMS), which has multiple small side holes in the stent membrane, with conventional FCSEMS and UCSEMS.
Patients and methods
This retrospective study using a propensity score matching design and stent patency times of 40 patients with MHSEMS was compared to 40 and 34 patients with FCSEMS and UCSEMS during the same period, respectively. Secondary outcomes were procedure-related adverse events, clinical success rate, time to recurrent biliary obstruction (RBO), and etiology of RBO. RBO was compared using Kaplan–Meier analysis.
Results
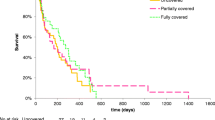
Baseline characteristics after matching were comparable among the 3 groups. RBO rates were 21%, 37%, and 55% for MHSEMS, FCSEMS, and UCSEMS, respectively (p = 0.014), at a mean time of 479, 353, and 306 days, respectively (MHSEMS vs UCSEMS, p = 0.002). Rate of tumor ingrowth was highest in the UCSEMS group (42.4% vs 13.2% in MHSEMS; p = 0.005 and vs 0% in FCSEMS; p < 0.001). Stent migration rate was highest in the FCSEMS group at 15.8% vs 2.6% in MHSEMS (p = 0.047) and 0% in UCSEMS (p = 0.005).
Conclusion
MHSEMS provided the longest stent patency time with lowest RBO rate compared to conventional SEMS by showing a lower stent migration rate than FCSEMS and a lower tumor ingrowth rate than UCSEMS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh A, Gelrud A, Agarwal B (2015) Biliary strictures: diagnostic considerations and approach. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf) 3:22–31
Esnaola NF, Meyer JE, Karachristos A, Maranki JL, Camp ER, Denlinger CS (2016) Evaluation and management of intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer 122:1349–1369
Ryan DP, Hong TS, Bardeesy N (2014) Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 371:1039–1049
Fernandez YVM, Arvanitakis M (2019) Early diagnosis and management of malignant distal biliary obstruction: a review on current recommendations and guidelines. Clin Exp Gastroenterol 12:415–432
Dumonceau JM, Tringali A, Papanikolaou IS, Blero D, Mangiavillano B, Schmidt A, Vanbiervliet G, Costamagna G, Devière J, García-Cano J, Gyökeres T, Hassan C, Prat F, Siersema PD, van Hooft JE (2018) Endoscopic biliary stenting: indications, choice of stents, and results: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) clinical guideline—updated October 2017. Endoscopy 50:910–930
Nakai Y, Isayama H, Wang HP, Rerknimitr R, Khor C, Yasuda I, Kogure H, Moon JH, Lau J, Lakhtakia S, Ratanachu-Ek T, Seo DW, Lee DK, Makmun D, Dy F, Liao WC, Draganov PV, Almadi M, Irisawa A, Katanuma A, Kitano M, Ryozawa S, Fujisawa T, Wallace MB, Itoi T, Devereaux B (2020) International consensus statements for endoscopic management of distal biliary stricture. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 35:967–979
Soderlund C, Linder S (2006) Covered metal versus plastic stents for malignant common bile duct stenosis: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc 63:986–995
Walter D, van Boeckel PG, Groenen MJ, Weusten BL, Witteman BJ, Tan G, Brink MA, Nicolai J, Tan AC, Alderliesten J, Venneman NG, Laleman W, Jansen JM, Bodelier A, Wolters FL, van der Waaij LA, Breumelhof R, Peters FT, Scheffer RC, Leenders M, Hirdes MM, Steyerberg EW, Vleggaar FP, Siersema PD (2015) Cost efficacy of metal stents for palliation of extrahepatic bile duct obstruction in a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology 149:130–138
Isayama H, Komatsu Y, Tsujino T, Sasahira N, Hirano K, Toda N, Nakai Y, Yamamoto N, Tada M, Yoshida H, Shiratori Y, Kawabe T, Omata M (2004) A prospective randomised study of “covered” versus “uncovered” diamond stents for the management of distal malignant biliary obstruction. Gut 53:729–734
Conio M, Mangiavillano B, Caruso A, Filiberti RA, Baron TH, De Luca L, Signorelli S, Crespi M, Marini M, Ravelli P, Conigliaro R, De Ceglie A (2018) Covered versus uncovered self-expandable metal stent for palliation of primary malignant extrahepatic biliary strictures: a randomized multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc 88:283-291.e283
Kullman E, Frozanpor F, Söderlund C, Linder S, Sandström P, Lindhoff-Larsson A, Toth E, Lindell G, Jonas E, Freedman J, Ljungman M, Rudberg C, Ohlin B, Zacharias R, Leijonmarck CE, Teder K, Ringman A, Persson G, Gözen M, Eriksson O (2010) Covered versus uncovered self-expandable nitinol stents in the palliative treatment of malignant distal biliary obstruction: results from a randomized, multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc 72:915–923
Lee JH, Krishna SG, Singh A, Ladha HS, Slack RS, Ramireddy S, Raju GS, Davila M, Ross WA (2013) Comparison of the utility of covered metal stents versus uncovered metal stents in the management of malignant biliary strictures in 749 patients. Gastrointest Endosc 78:312–324
Almadi MA, Barkun AN, Martel M (2013) No benefit of covered vs uncovered self-expandable metal stents in patients with malignant distal biliary obstruction: a meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 11:27-37.e21
Li J, Li T, Sun P, Yu Q, Wang K, Chang W, Song Z, Zheng Q (2016) Covered versus uncovered self-expandable metal stents for managing malignant distal biliary obstruction: a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 11:e0149066
Tringali A, Hassan C, Rota M, Rossi M, Mutignani M, Aabakken L (2018) Covered vs. uncovered self-expandable metal stents for malignant distal biliary strictures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy 50:631–641
Liao WC, Angsuwatcharakon P, Isayama H, Dhir V, Devereaux B, Khor CJ, Ponnudurai R, Lakhtakia S, Lee DK, Ratanachu-Ek T, Yasuda I, Dy FT, Ho SH, Makmun D, Liang HL, Draganov PV, Rerknimitr R, Wang HP (2017) International consensus recommendations for difficult biliary access. Gastrointest Endosc 85:295–304
Isayama H, Hamada T, Yasuda I, Itoi T, Ryozawa S, Nakai Y, Kogure H, Koike K (2015) TOKYO criteria 2014 for transpapillary biliary stenting. Dig Endosc 27:259–264
Cotton PB, Lehman G, Vennes J, Geenen JE, Russell RC, Meyers WC, Liguory C, Nickl N (1991) Endoscopic sphincterotomy complications and their management: an attempt at consensus. Gastrointest Endosc 37:383–393
Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, Tsiotos GG, Vege SS (2013) Classification of acute pancreatitis—2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 62:102–111
Kobayashi M (2019) Development of a biliary multi-hole self-expandable metallic stent for bile tract diseases: a case report. World J Clin Cases 7:1323–1328
Park JS, Jeong S, Kobayashi M, Lee DH (2019) Safety, efficacy, and removability of a fully covered multi-hole metal stent in a swine model of hilar biliary stricture: a feasibility study. Endosc Int Open 7:E498-E503
Zhu H-D, Guo J-H, Zhu G-Y, He S-C, Fang W, Deng G, Qin Y-L, Li G-Z, Coldwell DM, Teng G-J (2012) A novel biliary stent loaded with 125I seeds in patients with malignant biliary obstruction: preliminary results versus a conventional biliary stent. J Hepatol 56:1104–1111
Mohan BP, Canakis A, Khan SR, Chandan S, Ponnada S, McDonough S, Adler DG (2021) Drug eluting versus covered metal stents in malignant biliary strictures—is there a clinical benefit? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Gastroenterol 55(3):271–277
Han YM, Hwang SB, Lee ST, Lee JM, Chung GH (2002) Polyurethane-covered self-expandable nitinol stent for malignant biliary obstruction: preliminary results. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 25:381–387
Nakai Y, Isayama H, Kogure H, Hamada T, Togawa O, Ito Y, Matsubara S, Arizumi T, Yagioka H, Mizuno S, Sasaki T, Yamamoto N, Hirano K, Tada M, Koike K (2014) Risk factors for covered metallic stent migration in patients with distal malignant biliary obstruction due to pancreatic cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 29:1744–1749
Park DH, Lee SS, Lee TH, Ryu CH, Kim HJ, Seo D-W, Park S-H, Lee S-K, Kim M-H, Kim S-J (2011) Anchoring flap versus flared end, fully covered self-expandable metal stents to prevent migration in patients with benign biliary strictures: a multicenter, prospective, comparative pilot study (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 73:64–70
Hiroyuki I, Kazumichi K, Yousuke N, Kouta I, Chimyon G, Saburo M, Hirofumi K, Yukiko I, Takeshi T, Suguru M, Tsuyoshi H, Rie U, Koji M, Keisuke Y, Takashi S, Natsuyo Y, Kenji H, Naoki S, Minoru T, Kazuhiko K (2013) A novel, fully covered laser-cut nitinol stent with antimigration properties for nonresectable distal malignant biliary obstruction: a multicenter feasibility study. Gut Liver 7:725–730
Chandrasekhara V, Khashab MA, Muthusamy VR, Acosta RD, Agrawal D, Bruining DH, Eloubeidi MA, Fanelli RD, Faulx AL, Gurudu SR, Kothari S, Lightdale JR, Qumseya BJ, Shaukat A, Wang A, Wani SB, Yang J, DeWitt JM (2017) Adverse events associated with ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc 85:32–47
Kawakubo K, Isayama H, Nakai Y, Togawa O, Sasahira N, Kogure H, Sasaki T, Matsubara S, Yamamoto N, Hirano K, Tsujino T, Toda N, Tada M, Omata M, Koike K (2012) Risk factors for pancreatitis following transpapillary self-expandable metal stent placement. Surg Endosc 26:771–776
Nakai Y, Isayama H, Kawakubo K, Kogure H, Hamada T, Togawa O, Ito Y, Matsubara S, Arizumi T, Yagioka H, Takahara N, Uchino R, Mizuno S, Miyabayashi K, Yamamoto K, Sasaki T, Yamamoto N, Hirano K, Tada M, Koike K (2014) Metallic stent with high axial force as a risk factor for cholecystitis in distal malignant biliary obstruction. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 29:1557–1562
Acknowledgements
All authors acknowledge Dr. Makoto Kobayashi, Division of Gastroenterology, Yokkaichi Municipal Hospital, Yokkaichi, Mie 5108657, Japan, for the conceptual design of this MHSEMS, and also Prof. Stephen J Kerr PhD, Biostatistics Excellence Center, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand, for the advice of statistical analysis. Part of the abstract in this study was presented at Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2022, San Diego, USA.
Funding
This research received funding from Grant for International Research Integration: Chula Research Scholar, Ratchadaphiseksomphot Endowment Fund, Chulalongkorn University, and the Center of Excellence for Innovation and Endoscopy in Gastrointestinal Oncology. M.I. Tech Co. provided all MHSEMS used in this study and supported the study with an unrestricted grant without direct discretion to this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and design (RR, SK), data collection (RR, SK, PP, PA, PK, WR, PM), data analysis and interpretation (SK, PP), manuscript drafting (SK), critical revision of the article for important intellectual content (RR, PA, PK, WR, PM), and final approval of the article (RR, SK, PP, PA, PK, WR, PM).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Santi Kulpatcharapong, Panida Piyachaturawat, Parit Mekaroonkamol, Phonthep Angsuwatcharakon, Wiriyaporn Ridtitid, Pradermchai Kongkam, and Rungsun Rerknimitr have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kulpatcharapong, S., Piyachaturawat, P., Mekaroonkamol, P. et al. Efficacy of multi-hole self-expandable metal stent compared to fully covered and uncovered self-expandable metal stents in patients with unresectable malignant distal biliary obstruction: a propensity analysis. Surg Endosc 38, 212–221 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-023-10541-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-023-10541-9