Abstract
Background
This study aimed to evaluate the risk factors related to a technical failure after laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for subcapsular hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs).
Materials and methods
A total of 110 patients with 114 HCCs who underwent laparoscopic RFA for HCCs (new HCC [n = 85] and local tumor progression [LTP] [n = 29]) between January 2013 and December 2018 were included. We evaluated the incidence of technical failure on immediate post-RFA CT images. Risk factors for a technical failure after laparoscopic RFA were assessed using univariable logistic regression analyses. The cumulative LTP rate was estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method.
Results
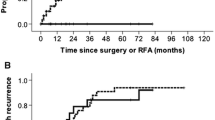
Technical failure was noted in 3.5% (4/114) of the tumors. All four tumors that showed a technical failure were cases of LTP from previous treatment and were invisible on laparoscopy. On univariate analysis, LTP lesion, invisibility of the index tumor on laparoscopy, and peri-hepatic vein location of the tumor were identified as risk factors for a technical failure. The cumulative LTP rates at 1, 3, and 5 years were estimated to be 2.8%, 4.8%, and 4.8%, respectively.
Conclusions
LTP lesion, invisibility of the index tumor on laparoscopy, and peri-hepatic vein location of the tumor were identified as the risk factors for a technical failure after laparoscopic RFA.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
European Association for the Study of the Liver (2018) EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 69:182–236
Marrero JA, Kulik LM, Sirlin CB, Zhu AX, Finn RS, Abecassis MM, Roberts LR, Heimbach JK (2018) Diagnosis, staging, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2018 practice guidance by the American association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology 68:723–750
Kim JE, Kim YS, Rhim H, Lim HK, Lee MW, Choi D, Shin SW, Cho SK (2011) Outcomes of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma referred for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation at a tertiary center: analysis focused on the feasibility with the use of ultrasonography guidance. Eur J Radiol 79:e80-84
Lee MW, Kim YJ, Park HS, Yu NC, Jung SI, Ko SY, Jeon HJ (2010) Targeted sonography for small hepatocellular carcinoma discovered by CT or MRI: factors affecting sonographic detection. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:W396-400
Worakitsitisatorn A, Lu DS, Lee MW, Asvadi NH, Moshksar A, Yuen AD, McWilliams J, Raman SS (2020) Percutaneous thermal ablation of subcapsular hepatocellular carcinomas: influence of tumor-surface contact and protrusion on therapeutic efficacy and safety. Eur Radiol 30:1813–1821
Song KD, Lim HK, Rhim H, Lee MW, Kang TW, Paik YH, Kim JM, Joh JW (2019) Hepatic resection vs percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma abutting right diaphragm. World J Gastrointest Oncol 11:227–237
Lai ZC, Liang JY, Chen LD, Wang Z, Ruan SM, Xie XY, Lu MD, Hu HT, Wang W (2018) Do hepatocellular carcinomas located in subcapsular space or in proximity to vessels increase the rate of local tumor progression? A meta-analysis. Life Sci 207:381–385
Rhim H, Lim HK, Kim YS, Choi D (2008) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation with artificial ascites for hepatocellular carcinoma in the hepatic dome: initial experience. AJR Am J Roentgenol 190:91–98
Rhim H, Lim HK (2009) Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma abutting the diaphragm: the value of artificial ascites. Abdom Imaging 34:371–380
Topal B, Aerts R, Penninckx F (2003) Laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation of unresectable liver malignancies: feasibility and clinical outcome. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 13:11–15
Santambrogio R, Barabino M, De Nicola E, Galfrascoli E, Giovenzana M, Zappa MA (2020) Laparoscopic ablation therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: could specific indications for the laparoscopic approach influence the effectiveness? Updates Surg 72:435–443
de la Serna S, Vilana R, Sanchez-Cabus S, Calatayud D, Ferrer J, Molina V, Fondevila C, Bruix J, Fuster J, Garcia-Valdecasas JC (2015) Results of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation for HCC. Could the location of the tumour influence a complete response to treatment? A single European centre experience. HPB (Oxford) 17:387–393
Sakaguchi H, Seki S, Tsuji K, Teramoto K, Suzuki M, Kioka K, Isoda N, Ido K, Japan Society for Laparoscopic Therapy R (2009) Endoscopic thermal ablation therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: a multi-center study. Hepatol Res 39:47–52
Korean Liver Cancer Study Group, National Cancer Center Korea (2015) 2014 Korean liver cancer study group-national cancer center Korea practice guideline for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Radiol 16:465–522
Lu DS, Raman SS, Limanond P, Aziz D, Economou J, Busuttil R, Sayre J (2003) Influence of large peritumoral vessels on outcome of radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:1267–1274
Lee MW, Rhim H, Cha DI, Kim YJ, Lim HK (2013) Planning US for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of small hepatocellular carcinomas (1–3 cm): value of fusion imaging with conventional US and CT/MR images. J Vasc Interv Radiol 24:958–965
Na BG, Kim JM, Oh DK, Lee KW, Kang TW, Choi GS, Lee MW, Kwon CHD, Lim HC, Joh JW (2017) Clinical outcomes of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation of single primary or recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma (</=3 cm). Ann Surg Treat Res 92:355–360
Ahmed M, Solbiati L, Brace CL, Breen DJ, Callstrom MR, Charboneau JW, Chen MH, Choi BI, de Baere T, Dodd GD, 3rd, Dupuy DE, Gervais DA, Gianfelice D, Gillams AR, Lee FT, Jr., Leen E, Lencioni R, Littrup PJ, Livraghi T, Lu DS, McGahan JP, Meloni MF, Nikolic B, Pereira PL, Liang P, Rhim H, Rose SC, Salem R, Sofocleous CT, Solomon SB, Soulen MC, Tanaka M, Vogl TJ, Wood BJ, Goldberg SN, International Working Group on Image-guided Tumor Ablation, Interventional Oncology Sans Frontieres Expert Panel, Technology Assessment Committee of the Society of Interventional Radiology, and SoPCotC, Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (2014) Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria–a 10-year update. Radiology 273:241–260
Austin PC, Allignol A, Fine JP (2017) The number of primary events per variable affects estimation of the subdistribution hazard competing risks model. J Clin Epidemiol 83:75–84
Peduzzi P, Concato J, Feinstein AR, Holford TR (1995) Importance of events per independent variable in proportional hazards regression analysis. II. Accuracy and precision of regression estimates. J Clin Epidemiol 48:1503–1510
Hirooka M, Kisaka Y, Uehara T, Ishida K, Kumagi T, Watanabe Y, Abe M, Matsuura B, Hiasa Y, Onji M (2009) Efficacy of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma compared to percutaneous radiofrequency ablation with artificial ascites. Dig Endosc 21:82–86
Birsen O, Aliyev S, Aksoy E, Taskin HE, Akyuz M, Karabulut K, Siperstein A, Berber E (2014) A critical analysis of postoperative morbidity and mortality after laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. Ann Surg Oncol 21:1834–1840
Eun HS, Lee BS, Kwon IS, Yun GY, Lee ES, Joo JS, Sung JK, Moon HS, Kang SH, Kim JS, Shin HJ, Kim TK, Chun K, Kim SH (2017) Advantages of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation over percutaneous radiofrequency ablation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 62:2586–2600
Santambrogio R, Barabino M, Bruno S, Costa M, Ceretti AP, Angiolini MR, Zuin M, Meloni F, Opocher E (2016) Long-term outcome of laparoscopic ablation therapies for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a single European center experience of 426 patients. Surg Endosc 30:2103–2113
Santambrogio R, Barabino M, D’Alessandro V, Galfrascoli E, Zappa MA, Piccolo G, Zuin M, Opocher E (2020) Laparoscopic thermoablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with liver cirrhosis: an effective procedure for tricky tumors. Med Oncol 37:32
Odeberg S, Ljungqvist O, Svenberg T, Gannedahl P, Backdahl M, von Rosen A, Sollevi A (1994) Haemodynamic effects of pneumoperitoneum and the influence of posture during anaesthesia for laparoscopic surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 38:276–283
Asahina Y, Nakanishi H, Izumi N (2009) Laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Endosc 21:67–72
Kang TW, Lee MW, Choi SH, Rhim H, Lim S, Song KD, Min JH, Choi SY, Lim HK, Yang J (2015) A novel electrode with electromagnetic tip tracking in ultrasonography-guided radiofrequency ablation: a phantom, ex vivo, and in vivo experimental study. Invest Radiol 50:81–87
Herbold T, Wahba R, Bangard C, Demir M, Drebber U, Stippel DL (2013) The laparoscopic approach for radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma–indication, technique and results. Langenbecks Arch Surg 398:47–53
Kang TW, Lee MW, Hye MJ, Song KD, Lim S, Rhim H, Lim HK, Cha DI (2014) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumours: factors affecting technical failure of artificial ascites formation using an angiosheath. Clin Radiol 69:1249–1258
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Drs. Seong Eun Ko, Min Woo Lee, Ji Hye Min, Soo Hyun Ahn, Hyunchul Rhim, Tae Wook Kang, Kyoung Doo Song, Jong Man Kim, Gyu-Seong Choi, Dong Ik Cha, and Hyo Keun Lim have no conflict of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ko, S.E., Lee, M.W., Min, J.H. et al. Laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation of subcapsular hepatocellular carcinomas: risk factors related to a technical failure. Surg Endosc 36, 504–514 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08310-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08310-7