Abstract
Background
Gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy (G-POEM) has emerged as an effective management approach for patients with refractory gastroparesis. This study aims to comprehensively study the safety of G-POEM and describe the predictive factors of adverse events (AEs) occurrence.
Methods
This study is a retrospective study involving 13 tertiary care centers (7 USA, 1 South America, 4 Europe, and 1 Asia). Patients who underwent G-POEM for refractory gastroparesis were included. Cases were identified by the occurrence of AEs. For each case, two controls were randomly selected and matched for age (± 10 years), gender, and etiology of gastroparesis.
Results
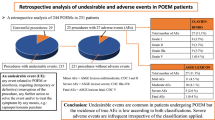
A total of 216 patients underwent G-POEM for gastroparesis. Overall, 31 (14%) AEs were encountered [mild 24 (77%), moderate 5 (16%), and severe 2 (6%)] during the duration of the study. The most common AE was abdominal pain (n = 16), followed by mucosotomy (n = 5) and capnoperitoneum (n = 4), and AEs were most commonly identified within the first 48-h post-procedure 18 (58%). The risk of adverse event occurrence was significantly higher for endoscopists with experience of < 20 G-POEM procedures (OR 3.03 [1.03–8.94], p < 0.05).
Conclusion
G-POEM seems to be a safe intervention for refractory gastroparesis. AEs are most commonly mild and managed conservatively. Longitudinal mucosal incision, use of hook knife, use of clips for mucosal closure and endoscopist’s experience with > 20 G-POEM procedures is significantly associated with decreased incidence of AEs.

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
18 May 2020
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-020-07651-z
Abbreviations
- G-POEM:
-
Gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy
- AEs:
-
Adverse events
- ESD:
-
Endoscopic submucosal dissection
References
Parkman HP, Hasler WL, Fisher RS (2004) American Gastroenterological Association technical review on the diagnosis and treatment of gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 127:1592–1622
Cherian D, Parkman HP (2012) Nausea and vomiting in diabetic and idiopathic gastroparesis. Neurogastroenterol Motil 24(217–222):e103
Dudekula A, O'Connell M, Bielefeldt K (2011) Hospitalizations and testing in gastroparesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26:1275–1282
Tang DM, Friedenberg FK (2011) Gastroparesis: approach, diagnostic evaluation, and management. Dis Mon 57:74–101
Hasler WL (2011) Gastroparesis: pathogenesis, diagnosis and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8:438–453
Sangnes DA, Softeland E, Biermann M, Gilja OH, Thordarson H, Dimcevski G (2016) Gastroparesis—causes, diagnosis and treatment. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen 136:822–826
Jones MP, Maganti K (2003) A systematic review of surgical therapy for gastroparesis. Am J Gastroenterol 98:2122–2129
Abrahamsson H (2007) Treatment options for patients with severe gastroparesis. Gut 56:877–883
Khashab MA, Stein E, Clarke JO, Saxena P, Kumbhari V, Chander Roland B, Kalloo AN, Stavropoulos S, Pasricha P, Inoue H (2013) Gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy for refractory gastroparesis: first human endoscopic pyloromyotomy (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 78:764–768
Aghaie Meybodi M, Qumseya BJ, Shakoor D, Lobner K, Vosoughi K, Ichkhanian Y, Khashab MA (2019) Efficacy and feasibility of G-POEM in management of patients with refractory gastroparesis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc Int Open 7:E322–e329
Camilleri M, Parkman HP, Shafi MA, Abell TL, Gerson L (2013) Clinical guideline: management of gastroparesis. Am J Gastroenterol 108:18–37
Vosoughi K et al (2019) 644 Gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy (G-POEM) for the treatment of refractory gastroparesis: results from the first international prospective trial. Gastrointest Endosc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2019.04.098
Louazon T, Rivory J, Roman S, Mion F, Ponchon T, Pioche M (2016) Temporary dumping syndrome after gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy: should we control the glycemia? Endoscopy 48(Suppl 1 UCTN):E10–11
Cotton PB, Eisen GM, Aabakken L, Baron TH, Hutter MM, Jacobson BC, Mergener K, Nemcek A Jr, Petersen BT, Petrini JL, Pike IM, Rabeneck L, Romagnuolo J, Vargo JJ (2010) A lexicon for endoscopic adverse events: report of an ASGE workshop. Gastrointest Endosc 71:446–454
Benias PC, Khashab MA (2017) Gastric peroral endoscopic pyloromyotomy therapy for refractory gastroparesis. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol 15:637–647
Gonzalez JM, Benezech A, Vitton V, Barthet M (2017) G-POEM with antro-pyloromyotomy for the treatment of refractory gastroparesis: mid-term follow-up and factors predicting outcome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 46:364–370
Mekaroonkamol P, Dacha S, Wang L, Li X, Jiang Y, Li L, Li T, Shahnavaz N, Sakaria S, LeVert FE, Keilin S, Willingham F, Christie J, Cai Q (2019) Gastric peroral endoscopic pyloromyotomy reduces symptoms, increases quality of life, and reduces health care use for patients with gastroparesis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 17:82–89
Tao J, Patel V, Mekaroonkamol P, Luo H, Li B, Guan Q, Shen S, Chen H, Cai Q (2019) Technical aspects of peroral endoscopic pyloromyotomy. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 29:117–126
Geyl S, Legros R, Charissou A, Mesturoux L, Couquet CY, Carrier P, Brayette A, El-Ouafi Z, Loustaud-Ratti V, Sautereau D, Monteil J, Jacques J (2016) Peroral endoscopic pyloromyotomy accelerates gastric emptying in healthy pigs: proof of concept. Endosc Int Open 4:E796–799
Chaves DM, Gusmon CC, Mestieri LH, de Moura EG, Veras MM, Pessorrusso FC, Sakai P (2014) A new technique for performing endoscopic pyloromyotomy by gastric submucosal tunnel dissection. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 24:e92–94
Jung Y, Lee J, Gromski MA, Kato M, Rodriguez S, Chuttani R, Matthes K (2015) Assessment of the length of myotomy in peroral endoscopic pyloromyotomy (G-POEM) using a submucosal tunnel technique (video). Surg Endosc 29:2377–2384
Jacques J, Pagnon L, Hure F, Legros R, Crepin S, Fauchais AL, Palat S, Ducrotte P, Marin B, Fontaine S, Boubaddi NE, Clement MP, Sautereau D, Loustaud-Ratti V, Gourcerol G, Monteil J (2019) Peroral endoscopic pyloromyotomy is efficacious and safe for refractory gastroparesis: prospective trial with assessment of pyloric function. Endoscopy 51:40–49
Kahaleh M, Gonzalez JM, Xu MM, Andalib I, Gaidhane M, Tyberg A, Saumoy M, Baptista Marchena AJ, Barthet M (2018) Gastric peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of refractory gastroparesis: a multicenter international experience. Endoscopy 50:1053–1058
Li L, Spandorfer R, Qu C, Yang Y, Liang S, Chen H, Xue H, Cai Q (2018) Gastric per-oral endoscopic myotomy for refractory gastroparesis: a detailed description of the procedure, our experience, and review of the literature. Surg Endosc 32:3421–3431
Malik Z, Kataria R, Modayil R, Ehrlich AC, Schey R, Parkman HP, Stavropoulos SN (2018) Gastric per oral endoscopic myotomy (G-POEM) for the treatment of refractory gastroparesis: early experience. Dig Dis Sci 63:2405–2412
Shlomovitz E, Pescarus R, Cassera MA, Sharata AM, Reavis KM, Dunst CM, Swanstrom LL (2015) Early human experience with per-oral endoscopic pyloromyotomy (POP). Surg Endosc 29:543–551
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Dr. Khashab is consultant for Boston Scientific, Medtronic and Olympus. Dr. Jeremie Jacques is a consultant for Olympus and Boston Scientific. Dr. Sethi is a consultant for Boston Scientific, Olympus, and Fujifilm. Dr. Aadam is consultant for Boston Scientific. Dr. Benias is a consultant for Medtronic and Fuji Film. Dr. Chavez is consultant for Medtronic and Fuji Film. Dr. Law is consultant for Olympus America. Dr. Draganov is a consultant for Boston Scientific. Dr. Triggs is supported by NIH/NIDDK grant number T32DK101363. Dr. Ujiki is a consultant for Olympus and Boston Scientific. Dr. Ichkhanian, Dr. Vosoughi, Dr. Aghaie Meybodi, Dr. Patel, Dr. Bapaye, Dr. Dorwat, Dr. Barret, Ms. Browers, Dr. Pioche, Dr. Kotzev, Dr. Estremera, Dr. Albeniz, Dr. Callahan, Dr. Itani, and Dr. Brewer have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Ethical approval
IRB approval for this study across the multiple centers performed in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The formal informed consent was waived.
Informed consent
The formal informed consent was waived.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article was updated to correct author M.I. Itani’s name in the author listing.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1 (MOV 20495 kb)
Video 2. Symptomatic capnoperitoneum that occurred during G-POEM and managed intraoperatively using Veress needle.
Supplementary file3 (MPG 183322 kb)
Video 1. G-POEM in 43-year-old female for treatment of refractory gastroparesis complicated by Intra-procedural duodenal mucosotomy and managed by endoscopic clipping and stent placement.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ichkhanian, Y., Vosoughi, K., Aghaie Meybodi, M. et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Adverse Events Associated with Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy: An International Multicenter Study. Surg Endosc 35, 1755–1764 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-020-07570-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-020-07570-z