Abstract
Background
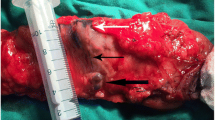
Accurate identification of lymph nodes localized around inferior mesenteric artery (IMA), with or without metastasis, is of crucial importance for surgeons when dissecting D2 or D3 lymph nodes in patients with rectal cancer (RC). The following study evaluates whether carbon nanoparticles can be used for detection of decision-making lymph nodes (DLNs) in station 253 lymph nodes found around IMA during RC surgery.
Methods
A total of 66 patients with rectal adenocarcinomas were recruited between January 2014 and August 2017. Patients were divided into carbon nanoparticle (CN) group and control (CL) group; for the CN group, 1 ml nanoparticles were endoscopically injected into submucosal layer of primary tumor 1 day before surgery. DLNs were defined as black-dyed nodes in CN group or macroscopic lymph nodes in CL group localized along the IMA, proximal to the origin of the left colic artery. D3 lymph nodes were dissected using laparoscopic radical resection, and then examined using pathological approach. Intra-operative and post-operative data were compared between the two groups.
Results
In CN group, black-dyed DLNs were easily found under laparoscopy; the median number of DLNs was 3 (range 1–9). In CL group, the median number of DLNs was 0 (range 0–3). Consistency between intra-operative DLNs and post-operative station 253 nodes were confirmed by pathological examination. Significant higher number of DLNs in station 253 nodes (2.91 ± 2.47 vs 0.58 ± 0.75, p < 0.001), number of station 251 nodes (12.85 ± 8.99 vs 8.09 ± 5.85, p = 0.014), number of station 253 nodes (5.21 ± 5.26 vs 3.15 ± 2.32, p = 0.045), and the number of total lymph nodes (24.06 ± 13.20 vs 16.21 ± 9.09, p = 0.007) were found in the CN group compared to CL group.
Conclusions
Carbon nanoparticles are useful for identifying DLNs in station 253 LNs around IMA in RC. It is not necessary to perform D3 lymph node dissection if there are no intra-operative DLNs metastases in RC.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cirocchi R, Trastulli S, Farinella E, Desiderio J, Vettoretto N, Parisi A, Boselli C, Noya G (2012) High tie versus low tie of the inferior mesenteric artery in colorectal cancer: a RCT is needed. Surg Oncol 21:e111–e123
Lange MM, Buunen M, van de Velde CJ, Lange JF (2008) Level of arterial ligation in rectal cancer surgery: low tie preferred over high tie. A review. Dis Colon Rectum 51:1139–1145
Allaix ME, Fichera A (2013) Extended lymphadenectomy in rectal cancer is debatable. World J Surg 37:1814–1820
Chin CC, Yeh CY, Tang R, Changchien CR, Huang WS, Wang JY (2008) The oncologic benefit of high ligation of the inferior mesenteric artery in the surgical treatment of rectal or sigmoid colon cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis 23:783–788
Kanemitsu Y, Hirai T, Komori K, Kato T (2006) Survival benefit of high ligation of the inferior mesenteric artery in sigmoid colon or rectal cancer surgery. Br J Surg 93:609–615
Ubukata M, Itabashi M, Kameoka S (2014) Japanese D3 lymph node dissection in low rectal cancer with inferior mesenteric lymph node metastases. World J Surg 38:2724–2729
Kobayashi M, Okamoto K, Namikawa T, Okabayashi T, Araki K (2006) Laparoscopic lymph node dissection around the inferior mesenteric artery for cancer in the lower sigmoid colon and rectum. Surg Endosc 20:563–569
Liang JT, Huang KC, Lai HS, Lee PH, Sun CT (2008) Feasibility of laparoscopic D3 lymphadenectomy for male rectosigmoid cancer with clinically positive lymph nodes. Surg Endosc 22:2514–2517
Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon and Rectum (1998) General rules for clinical and pathological studies on cancer of the colon, rectum and anus, 6th edn. Kanahara Shuppan, Tokyo
Tepper JE, O Connell MJ, Niedzwiecki D, Hollis D, Compton C, Benson AB, Cummings B, Gunderson L, Macdonald JS, Mayer RJ (2001) Impact of number of nodes retrieved on outcome in patients with rectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 19:157–163
Labianca R, Nordlinger B, Beretta GD, Brouquet A, Cervantes A (2010) Primary colon cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, adjuvant treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 21:v70–v77
Kim JC, Lee KH, Yu CS, Kim HC, Kim JR, Chang HM, Kim JH, Kim JS, Kim TW (2004) The clinicopathological significance of inferior mesenteric lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol (EJSO) 30:271–279
Kang J, Hur H, Min BS, Kim NK, Lee KY (2011) Prognostic impact of inferior mesenteric artery lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 18:704–710
Huh JW, Kim YJ, Kim HR (2012) Distribution of lymph node metastases is an independent predictor of survival for sigmoid colon and rectal cancer. Ann Surg 255:70–78
Yan J, Zheng X, Liu Z, Yu J, Deng Z, Xue F, Zheng Y, Chen F, Shi H, Chen G, Lu J, Cai L, Cai M, Xiang G, Hong Y, Chen W, Li G (2016) A multicenter study of using carbon nanoparticles to show sentinel lymph nodes in early gastric cancer. Surg Endosc 30:1294–1300
Wang Y, Deng H, Chen H, Liu H, Xue Q, Yan J, Li G (2015) Preoperative submucosal injection of carbon nanoparticles improves lymph node staging accuracy in rectal cancer after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. J Am Coll Surgeons 221:923–930
Wu X, Lin Q, Chen G, Lu J, Zeng Y, Chen X, Yan J (2015) Sentinel lymph node detection using carbon nanoparticles in patients with early breast cancer. PLoS ONE 10:e0135714
Yan J, Xue F, Chen H, Wu X, Zhang H, Chen G, Lu J, Cai L, Xiang G, Deng Z, Zheng Y, Zheng X, Li G (2014) A multi-center study of using carbon nanoparticles to track lymph node metastasis in T1–2 colorectal cancer. Surg Endosc 28:3315–3321
Wang B, Du Z, Qiu N, Liu M, Liu S, Jiang D, Zhang W, Qiu M (2016) Application of carbon nanoparticles accelerates the rapid recovery of parathyroid function during thyroid carcinoma surgery with central lymph node dissection: a retrospective cohort study. Int J Surg 36:164–169
Wang Q, Chen E, Cai Y, Chen C, Jin W, Zheng Z, Jin Y, Chen Y, Zhang X, Li Q (2016) Preoperative endoscopic localization of colorectal cancer and tracing lymph nodes by using carbon nanoparticles in laparoscopy. World J Surg Oncol 14:231
Li Z, Ao S, Bu Z, Wu A, Wu X, Shan F, Ji X, Zhang Y, Xing Z, Ji J (2016) Clinical study of harvesting lymph nodes with carbon nanoparticles in advanced gastric cancer: a prospective randomized trial. World J Surg Oncol 14:88
Ishikawa K, Yasuda K, Shiromizu A, Etoh T, Shiraishi N, Kitano S (2007) Laparoscopic sentinel node navigation achieved by infrared ray electronic endoscopy system in patients with gastric cancer. Surg Endosc 21:1131–1134
Miyashiro I, Hiratsuka M, Sasako M, Sano T, Mizusawa J, Nakamura K, Nashimoto A, Tsuburaya A, Fukushima N (2014) High false-negative proportion of intraoperative histological examination as a serious problem for clinical application of sentinel node biopsy for early gastric cancer: final results of the Japan Clinical Oncology Group multicenter trial JCOG0302. Gastric Cancer 17:316–323
Quadros CA, Lopes A, Araujo I (2010) Retroperitoneal and lateral pelvic lymphadenectomy mapped by lymphoscintigraphy for rectal adenocarcinoma staging. Jpn J Clin Oncol 40:746–753
Kir G, Alimoglu O, Sarbay BC, Bas G (2014) Ex vivo intra-arterial methylene blue injection in the operation theater may improve the detection of lymph node metastases in colorectal cancer. Pathol Res Pract 210:818–821
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81773117), the Special Fund for Guangdong Province Public Research and Capacity Building (2014B020215002), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2015A030308006), the Guangzhou Industry University Research Cooperative Innovation Major Project (201704020062), the Science Popularization Program of Guangzhou Science and Technology Association, the Clinical Research Project of Southern Medical University (LC2016PY010), the High Level Research Matching Foundation of Nanfang Hospital (2014067), the Scientific Research Foundation for High Level Talents in Nanfang Hospital of Southern Medical University (201404280056), the Special Fund for Clinical Research of Wu Jieping Medical Foundation (320.2710.1851), the Special Funds for the Cultivation of Guangdong College Students’ Scientific and Technological Innovation (pdjh2017b0099, pdjh2017a0093, pdjhb0100), the National Training Program for Undergraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship (201612121008, 201712121052, 201812121039S, 201812121265), the Provincial Training Program for Undergraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship (201712121149, 201712121132), and the Scientific Enlightenment Plan of Southern Medical University (2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Drs. Kai Li, Dexin Chen, Weisheng Chen, Zhangyuanzhu Liu, Wei Jiang, Xiumin Liu, Ziming Cui, Zhiyao Wei, Zhiming Li, and Jun Yan have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, K., Chen, D., Chen, W. et al. A case–control study of using carbon nanoparticles to trace decision-making lymph nodes around inferior mesenteric artery in rectal cancer. Surg Endosc 33, 904–910 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6384-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6384-9