Abstract
Background
To facilitate accurate localization of small lung lesions in thoracoscopic surgery, we employed a micro-radiofrequency identification tag designed to be delivered through the 2-mm working channel of a flexible bronchoscope. This report presents the results of preclinical studies of our novel localizing technique in a canine model.
Methods
To evaluate functional placement, three types of tags [Group A, tag alone (n = 18); Group B, tag + resin anchor (n = 15); and Group C, tag + NiTi coil anchor (n = 15)] were bronchoscopically placed in subpleural areas and subsegmental bronchi via our new delivery device; tags were examined radiographically on days 0–7 and day 14. In addition, eight tags, which were placed at a mean depth of 13.3 mm (range 9–15.7 mm) from visceral pleura in bronchi with a mean diameter of 1.46 mm (range 0.9–2.3 mm), were recovered by partial lung resection under video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery using a 13.56-MHz wand-shaped probe with a 30-mm communication range.
Results
Peripheral airway placement: Group C had a significantly higher retention rate than the other two groups (retention rate at day 14: Group A, 11.1 %; Group B, 26.7 %; Group C, 100.0 %; P < 0.0001). Central airway placement: Overall retention rate was 73.3 % in Group C, and placement was possible in bronchi of up to 3.3 mm in diameter. Outcomes of partial resection: Tag recovery rate was 100 %, mean time required for tag detection was 10.8 s (range 8–15 s), and mean surgical margin from the delivered tag was 9.13 mm (range 6–13 mm).
Conclusion
Radiofrequency identification marking enabled accurate localization with depth, which could ensure effective deep resection margins.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, Black WC, Clapp JD, Fagerstrom RM, Gareen IF, Gatsonis C, Marcus PM, Sicks JD (2011) Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med 365(5):395–409. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1102873
Veronesi G, Maisonneuve P, Rampinelli C, Bertolotti R, Petrella F, Spaggiari L, Bellomi M (2013) Computed tomography screening for lung cancer: results of ten years of annual screening and validation of cosmos prediction model. Lung Cancer 82(3):426–430. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.08.026
Menezes RJ, Roberts HC, Paul NS, McGregor M, Chung TB, Patsios D, Weisbrod G, Herman S, Pereira A, McGregor A, Dong Z, Sitartchouk I, Boerner S, Tsao MS, Keshavjee S, Shepherd FA (2010) Lung cancer screening using low-dose computed tomography in at-risk individuals: the Toronto experience. Lung Cancer 67(2):177–183. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2009.03.030
Bach PB, Mirkin JN, Oliver TK, Azzoli CG, Berry DA, Brawley OW, Byers T, Colditz GA, Gould MK, Jett JR, Sabichi AL, Smith-Bindman R, Wood DE, Qaseem A, Detterbeck FC (2012) Benefits and harms of CT screening for lung cancer: a systematic review. JAMA 307(22):2418–2429. doi:10.1001/jama.2012.5521
Masuda M, Kuwano H, Okumura M, Arai H, Endo S, Doki Y, Kobayashi J, Motomura N, Nishida H, Saiki Y, Tanaka F, Tanemoto K, Toh Y, Yokomise H (2015) Thoracic and cardiovascular surgery in Japan during 2013: annual report by The Japanese Association for Thoracic Surgery. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 63(12):670–701. doi:10.1007/s11748-015-0590-3
Zaman M, Bilal H, Woo CY, Tang A (2012) In patients undergoing video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery excision, what is the best way to locate a subcentimetre solitary pulmonary nodule in order to achieve successful excision? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 15(2):266–272. doi:10.1093/icvts/ivs068
Sakiyama S, Kondo K, Matsuoka H, Yoshida M, Miyoshi T, Yoshida S, Monden Y (2003) Fatal air embolism during computed tomography-guided pulmonary marking with a hook-type marker. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 126(4):1207–1209. doi:10.1016/s0022
Horan TA, Pinheiro PM, Araujo LM, Santiago FF, Rodrigues MR (2002) Massive gas embolism during pulmonary nodule hook wire localization. Ann Thorac Surg 73(5):1647–1649
Mayo JR, Clifton JC, Powell TI, English JC, Evans KG, Yee J, McWilliams AM, Lam SC, Finley RJ (2009) Lung nodules: CT-guided placement of microcoils to direct video-assisted thoracoscopic surgical resection. Radiology 250(2):576–585. doi:10.1148/radiol.2502080442
Watanabe K, Nomori H, Ohtsuka T, Kaji M, Naruke T, Suemasu K (2006) Usefulness and complications of computed tomography-guided lipiodol marking for fluoroscopy-assisted thoracoscopic resection of small pulmonary nodules: experience with 174 nodules. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 132(2):320–324. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2006.04.012
Okumura T, Kondo H, Suzuki K, Asamura H, Kobayashi T, Kaneko M, Tsuchiya R (2001) Fluoroscopy-assisted thoracoscopic surgery after computed tomography-guided bronchoscopic barium marking. Ann Thorac Surg 71(2):439–442
Asano F, Shindoh J, Shigemitsu K, Miya K, Abe T, Horiba M, Ishihara Y (2004) Ultrathin bronchoscopic barium marking with virtual bronchoscopic navigation for fluoroscopy-assisted thoracoscopic surgery. Chest 126(5):1687–1693. doi:10.1378/chest.126.5.1687
Miyoshi T, Kondo K, Takizawa H, Kenzaki K, Fujino H, Sakiyama S, Tangoku A (2006) Fluoroscopy-assisted thoracoscopic resection of pulmonary nodules after computed tomography-guided bronchoscopic metallic coil marking. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 131(3):704–710. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2005.09.019
Kojima F, Sato T, Takahata H, Okada M, Sugiura T, Oshiro O, Date H, Nakamura T (2014) A novel surgical marking system for small peripheral lung nodules based on radio frequency identification technology: feasibility study in a canine model. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 147(4):1384–1389. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2013.05.048
Takahata H, Kojima F, Okada M, Sugiura T, Sato T, Oshiro O (2012) Thoracoscopic surgery support system using passive RFID marker. In: Conference proceedings: annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society annual conference, pp 183–186. doi:10.1109/embc.2012.6345901
Landreneau RJ, Sugarbaker DJ, Mack MJ, Hazelrigg SR, Luketich JD, Fetterman L, Liptay MJ, Bartley S, Boley TM, Keenan RJ, Ferson PF, Weyant RJ, Naunheim KS (1997) Wedge resection versus lobectomy for stage I (T1 N0 M0) non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 113(4):691–698. doi:10.1016/s0022-5223(97)70226-5 (discussion 698–700)
Chute CG, Greenberg ER, Baron J, Korson R, Baker J, Yates J (1985) Presenting conditions of 1539 population-based lung cancer patients by cell type and stage in New Hampshire and Vermont. Cancer 56(8):2107–2111
Hyde L, Hyde CI (1974) Clinical manifestations of lung cancer. Chest 65(3):299–306
Jaklitsch MT, Jacobson FL, Austin JH, Field JK, Jett JR, Keshavjee S, MacMahon H, Mulshine JL, Munden RF, Salgia R, Strauss GM, Swanson SJ, Travis WD, Sugarbaker DJ (2012) The American Association for Thoracic Surgery guidelines for lung cancer screening using low-dose computed tomography scans for lung cancer survivors and other high-risk groups. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 144(1):33–38. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2012.05.060
Gould MK, Donington J, Lynch WR, Mazzone PJ, Midthun DE, Naidich DP, Wiener RS (2013) Evaluation of individuals with pulmonary nodules: when is it lung cancer? Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 143(5 Suppl):e93S–e120S. doi:10.1378/chest.12-2351
Wallace MJ, Krishnamurthy S, Broemeling LD, Gupta S, Ahrar K, Morello FA Jr, Hicks ME (2002) CT-guided percutaneous fine-needle aspiration biopsy of small (< or =1-cm) pulmonary lesions. Radiology 225(3):823–828. doi:10.1148/radiol.2253011465
Wang Memoli JS, Nietert PJ, Silvestri GA (2012) Meta-analysis of guided bronchoscopy for the evaluation of the pulmonary nodule. Chest 142(2):385–393. doi:10.1378/chest.11-1764
Suzuki K, Nagai K, Yoshida J, Ohmatsu H, Takahashi K, Nishimura M, Nishiwaki Y (1999) Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for small indeterminate pulmonary nodules: indications for preoperative marking. Chest 115(2):563–568
Ohtaki Y, Shimizu K (2014) Anatomical thoracoscopic segmentectomy for lung cancer. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 62(10):586–593. doi:10.1007/s11748-014-0409-7
Sato M, Omasa M, Chen F, Sato T, Sonobe M, Bando T, Date H (2014) Use of virtual assisted lung mapping (VAL-MAP), a bronchoscopic multispot dye-marking technique using virtual images, for precise navigation of thoracoscopic sublobar lung resection. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 147(6):1813–1819. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2013.11.046
Miyoshi K, Toyooka S, Gobara H, Oto T, Mimura H, Sano Y, Kanazawa S, Date H (2009) Clinical outcomes of short hook wire and suture marking system in thoracoscopic resection for pulmonary nodules. Eur J Cardio Thorac Surg 36(2):378–382. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2009.03.039
Dendo S, Kanazawa S, Ando A, Hyodo T, Kouno Y, Yasui K, Mimura H, Akaki S, Kuroda M, Shimizu N, Hiraki Y (2002) Preoperative localization of small pulmonary lesions with a short hook wire and suture system: experience with 168 procedures. Radiology 225(2):511–518. doi:10.1148/radiol.2252011025
Westra BL (2009) Radio frequency identification. Am J Nurs 109(3):34–36. doi:10.1097/01.NAJ.0000346925.67498.a4
Rogers A, Jones E, Oleynikov D (2007) Radio frequency identification (RFID) applied to surgical sponges. Surg Endosc 21(7):1235–1237. doi:10.1007/s00464-007-9308-7
Kusuda K, Yamashita K, Ohnishi A, Tanaka K, Komino M, Honda H, Tanaka S, Okubo T, Tripette J, Ohta Y (2016) Management of surgical instruments with radio frequency identification tags. Int J Healthc Qual Assur 29(2):236–247. doi:10.1108/ijhcqa-03-2015-0034
Dauphine C, Reicher JJ, Reicher MA, Gondusky C, Khalkhali I, Kim M (2015) A prospective clinical study to evaluate the safety and performance of wireless localization of nonpalpable breast lesions using radiofrequency identification technology. AJR Am J Roentgenol 204(6):W720–W723. doi:10.2214/ajr.14.13201
Schwarz Y, Greif J, Becker HD, Ernst A, Mehta A (2006) Real-time electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy to peripheral lung lesions using overlaid CT images: the first human study. Chest 129(4):988–994. doi:10.1378/chest.129.4.988
Chen-Yoshikawa TF, Date H (2016) Update on three-dimensional image reconstruction for preoperative simulation in thoracic surgery. J Thorac Dis 8(Suppl 3):S295–S301. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2016.02.39
Eberhardt R, Anantham D, Herth F, Feller-Kopman D, Ernst A (2007) ELectromagnetic navigation diagnostic bronchoscopy in peripheral lung lesions. Chest 131(6):1800–1805. doi:10.1378/chest.06-3016
Anantham D, Feller-Kopman D, Shanmugham LN, Berman SM, DeCamp MM, Gangadharan SP, Eberhardt R, Herth F, Ernst A (2007) Electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy-guided fiducial placement for robotic stereotactic radiosurgery of lung tumors: a feasibility study. Chest 132(3):930–935. doi:10.1378/chest.07-0522
Anayama T, Qiu J, Chan H, Nakajima T, Weersink R, Daly M, McConnell J, Waddell T, Keshavjee S, Jaffray D, Irish JC, Hirohashi K, Wada H, Orihashi K, Yasufuku K (2015) Localization of pulmonary nodules using navigation bronchoscope and a near-infrared fluorescence thoracoscope. Ann Thorac Surg 99(1):224–230. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2014.07.050
Toba H, Kondo K, Miyoshi T, Kajiura K, Yoshida M, Kawakami Y, Takizawa H, Kenzaki K, Sakiyama S, Tangoku A (2013) Fluoroscopy-assisted thoracoscopic resection after computed tomography-guided bronchoscopic metallic coil marking for small peripheral pulmonary lesions. Eur J Cardio Thorac Surg 44(2):e126–e132. doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezt220
Petersen J, Wille MM, Raket LL, Feragen A, Pedersen JH, Nielsen M, Dirksen A, de Bruijne M (2014) Effect of inspiration on airway dimensions measured in maximal inspiration CT images of subjects without airflow limitation. Eur Radiol 24(9):2319–2325. doi:10.1007/s00330-014-3261-3
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Seiki Hasegawa (Hyogo College of Medicine, Hyogo, Japan), Tatsuo Nakagawa (Tenri Hospital, Nara, Japan), and Hiromichi Katakura (Otsu Red Cross Hospital, Shiga, Japan) for providing valuable suggestions regarding this project.
Funding
Hogy Medical Co., Ltd. provided the radiofrequency identification system and financial support by means of an institutional research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
We guarantee that all authors are aware of and agree to the contents of the paper and their being listed as an author on this paper. All authors have contributed significantly to the content of the article. All authors have read and approved the submission of the manuscript to Surgical Endoscopy. Subject to acceptance, authors will sign an exclusive license to publish. Drs. J. Zhang, Y. Muranishi, Y. Sakaguchi, T. Komatsu, F. Kojima, and T. Nakamura have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose. Y. Yutaka, T, Sato, and H. Date have a financial relationship with Hogy Medical Co., Ltd., which developed the radiofrequency identification system used in this study. The results were collected and analyzed independent from any sponsor.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
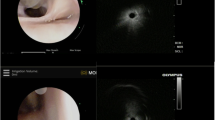
A marking tag placed at a depth of 13.3 mm in left S6 as indicated on computed tomography was recovered by video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery partial lung resection. The implanted tag was detected in the plastic grasper. The lung was resected by electrocautery with accurate adjustment of the resection line by detecting tag position. (MP4 42859 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yutaka, Y., Sato, T., Zhang, J. et al. Localizing small lung lesions in video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery via radiofrequency identification marking. Surg Endosc 31, 3353–3362 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5302-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5302-2