Abstract
Background
Bleeding pancreatic pseudocysts (PPCs) are a rare but lethal complication of pancreatitis. Transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE) is the first-line treatment of acute hemorrhage, but consensus on the definitive management of bleeding PPCs is lacking. The aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the combination of TAE and therapeutic endoscopy in the treatment of bleeding PPCs.
Methods
Patients with acute or chronic pancreatitis treated for bleeding PPCs in Helsinki University Hospital during 2004–2014 comprised the study group. Inpatients with acute necrotizing pancreatitis were excluded. Patients underwent TAE as the primary treatment to control the bleeding. Therapeutic endoscopy performed on an outpatient visit after TAE allowed the definitive treatment of PPCs.
Results
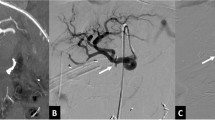
A total of 58 patients underwent TAE. Re-bleeding rate (<30 days) was 15.5 %, necessitating re-embolization on seven and surgical intervention on two patients. Overall, TAE success rate was 96.6 %. Mortality rate (<30 days) was 3.4 %. Of the 58, 47 patients were followed up for their PPCs in our unit. PPCs resolved spontaneously in 13 (27.1 %). The remaining 34 had an endoscopic treatment attempt with endoscopic draining performed on 32 and unsuccessful cannulation on two (5.9 %). Of the 32 patients with initially successful endoscopy, 7 (21.9 %) needed an additional drainage procedure (six non-surgical and one surgical). Overall success rate of non-surgical management was 91.5 %. Post-endoscopy mortality rate (<30 days) was 2.9 %. Our follow-up continued for 15 (1–75) months. By the time of data retrieval, 35 of 58 patients had died with alcohol liver disease being the most common cause of death. Five-year survival estimate was 63 %.
Conclusions
Bleeding pancreatic pseudoaneurysms require non-surgical management. We need more data on the optimal timing of therapeutic endoscopy and on the role of empirical embolizations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrén-Sandberg Å, Dervenis C (2004) Pancreatic pseudocysts in the 21st century. Part I: classification, pathophysiology, anatomic considerations and treatment. J Pancreas 5:8–24
Balthazar EJ, Fisher LA (2001) Hemorrhagic complications of pancreatitis: radiologic evaluation with emphasis on CT imaging. Pancreatology 1:306–313. doi:10.1159/000055829
Bergert H, Hinterseher I, Kersting S, Leonhardt J, Bloomenthal A, Saeger HD (2005) Management and outcome of hemorrhage due to arterial pseudoaneurysms in pancreatitis. Surgery 137:323–328. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2004.10.009
Udd M, Leppäniemi AK, Bidel S, Keto P, Roth W-D, Haapiainen RK (2007) Treatment of bleeding pseudoaneurysms in patients with chronic pancreatitis. World J Surg 31:504–510. doi:10.1007/s00268-006-0209-z
Chiang K-C, Chen T-H, Hsu J-T (2014) Management of chronic pancreatitis complicated with a bleeding pseudoaneurysm. WJG 20:16132–16137. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16132
Kim J, Shin JH, Yoon H-K, Ko G-Y, Gwon DI, Kim E-Y, Sung K-B (2015) Endovascular intervention for management of pancreatitis-related bleeding: a retrospective analysis of thirty-seven patients at a single institution. Diagn Interv Radiol 21:140–147. doi:10.5152/dir.2014.14085
Nicholson AA, Patel J, McPherson S, Shaw DR, Kessel D (2006) Endovascular treatment of visceral aneurysms associated with pancreatitis and a suggested classification with therapeutic implications. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17:1279–1285. doi:10.1097/01.RVI.0000231948.08617.04
Balachandra S, Siriwardena AK (2005) Systematic appraisal of the management of the major vascular complications of pancreatitis. Am J Surg 190:489–495. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2005.03.009
Kirby JM, Vora P, Midia M, Rawlinson J (2007) Vascular complications of pancreatitis: imaging and intervention. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 31:957–970. doi:10.1007/s00270-007-9138-y
Dumonceau J-M (2013) Endoscopic management of complications of chronic pancreatitis. WJG 19:7308–7309. doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7308
Tandan M (2013) Endotherapy in chronic pancreatitis. WJG 19:6156–6164. doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i37.6156
Dumonceau JM, Delhaye M, Tringali A, Dominguez-Munoz J, Poley JW, Arvanitaki M, Costamagna G, Costea F, Devière J, Eisendrath P, Lakhtakia S, Reddy N, Fockens P, Ponchon T, Bruno M (2012) Endoscopic treatment of chronic pancreatitis: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Clinical Guideline. Endoscopy 44:784–800. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1309840
Varadarajulu S, Bang JY, Sutton BS, Trevino JM, Christein JD, Wilcox CM (2013) Equal efficacy of endoscopic and surgical cystogastrostomy for pancreatic pseudocyst drainage in a randomized trial. Gastroenterology 145(583–590):e1. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2013.05.046
Johnson MD, Walsh M, Henderson JM, Brown N, Ponsky J, Dumont J, Zuccaro G, Vargo J (2009) Surgical versus nonsurgical management of pancreatic pseudocysts. J Clin Gastroenterol 43:586–590
Bhasin DK, Rana SS, Sharma V, Rao C, Gupta V, Gupta R, Kang M, Singh K (2013) Non-surgical management of pancreatic pseudocysts associated with arterial pseudoaneurysm. Pancreatology 13:250–253. doi:10.1016/j.pan.2013.02.011
Elton E, Howell D, Amberson S, Dykes T (1997) Combined angiographic and endoscopic management of bleeding pancreatic pseudoaneurysms. Gastrointest Endosc 46:544–549
Sayilir A, Onal IK, Beyazit Y, Surmelioglu A, Salper Okten R, Odemis B, Parlak E, Sasmaz N (2011) A rare cause of upper gastrointestinal bleeding: hemosuccus pancreaticus: angiographic and endoscopic combined treatment. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutaneous Techn 21:e286–e287. doi:10.1097/SLE.0b013e31822f50b6
Cotton PB, Lehman G, Vennes J, Geenen JE, Russel RC, Meyers WC, Liguory C, Nickl N (1991) Endoscopic sphincterotomy complications and their management: an attempt at consensus. Gastrointest Endosc 37:383–393
Barge JU, Lopera JE (2012) Vascular complications of pancreatitis: role of interventional therapy. Korean J Radiol 13:S45–S55. doi:10.3348/kjr.2012.13.S1.S45
Park D, Lee S, Moon SH, Choi S, Jung S, Seo D, Lee S, Kim MH (2009) Endoscopic ultrasound-guided versus conventional transmural drainage for pancreatic pseudocysts: a prospective randomized trial. Endoscopy 41:842–848. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1215133
Weckman L, Kylänpää ML, Puolakkainen P, Halttunen J (2006) Endoscopic treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts. Surg Endosc 20:603–607. doi:10.1007/s00464-005-0201-y
Arvanitakis M, Delhaye M, Bali MA, Matos C, De Maertelaer V, Le Moine O, Devière J (2007) Pancreatic-fluid collections: a randomized controlled trial regarding stent removal after endoscopic transmural drainage. Gastrointest Endosc 65:609–619. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2006.06.083
Cahen D, Rauws E, Fockens P, Weverling G, Huibregtse K, Bruno M (2005) Endoscopic drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts: long-term outcome and procedural factors associated with safe and successful treatment. Endoscopy 37:977–983. doi:10.1055/s-2005-870336
Yang D, Amin S, Gonzalez S, Mullady D, Hasak S, Gaddam S, Edmundowicz S, Gromski M, DeWitt J, Zein MD, El M, Khashab M, Wang A, Gaspar J, Uppal D, Nagula S, Kapadia S, Buscaglia J, Bucobo JC, Schlachterman A, Wagh M, Draganov P, Kyu Jung M, Stevens T, Vargo J, Khara H, Huseini M, Diehl D, Keswani R, Law R, Komanduri S, Yachimski P, DaVee T, Prabhu A, Lapp R, Kwon R, Watson R, Goodman A, Chhabra N, Wang W, Benias P, Carr-Locke D, DiMaio C (2016) Transpapillary drainage has no added benefit on treatment outcomes in patients undergoing EUS-guided transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts: a large multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc 83:720–729. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2015.10.040
Andersson E, Ansari D, Andersson R (2010) Major haemorrhagic complications of acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg 97:1379–1384. doi:10.1002/bjs.7113
Lankisch PG, Weber-Dany B, Maisonneuve P, Lowenfels AB (2012) Pancreatic pseudocysts: prognostic factors for their development and their spontaneous resolution in the setting of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 12:85–90. doi:10.1016/j.pan.2012.02.007
Mehta R, Suvarna D, Sadasivan S, John A, Raj V, Nair P, Balakrishnan V (2004) Natural course of asymptomatic pancreatic pseudocyst: a prospective study. Indian J Gastroenterol 23:140–142
Andrén-Sandberg Å, Dervenis C (2004) Pancreatic pseudocysts in the 21st century. Part II: natural history. J Pancreas 5:64–70
Bradley EL, Gonzalez AC, Clements JR Jr (1976) Acute pancreatic pseudocysts: incidence and implications. Ann Surg 184:734–737
Acknowledgments
One-month researcher’s salary paid for Taina Nykänen by the Helsinki University Hospital Research Fund to allow full-time research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Marianne Udd, Erno Peltola, Ari Leppäniemi and Leena Kylänpää have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nykänen, T., Udd, M., Peltola, E.K. et al. Bleeding pancreatic pseudoaneurysms: management by angioembolization combined with therapeutic endoscopy. Surg Endosc 31, 692–703 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5023-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-016-5023-6