Abstract
Background
Approximately 20–30 % of patients who undergo Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) will not meet the goals of weight loss surgery. Revisional surgery is associated with higher morbidity compared to initial operative management, and results in terms of weight loss have been inconsistent. Endoscopic plication has been seen as a less invasive option, with encouraging initial results. The objective was to analyze the outcomes after Restorative Obesity Surgery, Endolumenal (ROSE) procedure.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed patients who underwent ROSE between 5/2008 and 11/2013. All patients had failure of weight loss or regain weight after RYGB. Demographics, operative data, and follow-up were recorded.
Results
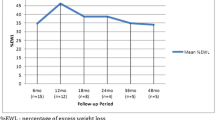
Twenty-seven patients underwent ROSE. One patient was excluded due to lack of follow-up. Twenty-five (96 %) patients were female. Mean time since initial RYGB was 11.9 ± 4.3 years. Mean initial weight and BMI were 236 ± 47 lb and 40.6 ± 8.1 kg/m2, respectively. Mean OR time was 77 ± 30 min. Preoperative average pouch length and stoma diameter were 6.8 ± 2.3 and 2.1 ± 0.7 cm, respectively. On average, 4 ± 1.6 stitches were placed. Final pouch length and stoma diameter were 3.4 ± 1.6 (50 % reduction) and 0.86 ± 0.4 cm (61 % reduction). A total of 12 (46 %) and seven (28 %) patients underwent EGD at 3 and 12 months postoperatively. The mean pouch length and stoma diameter were 5 ± 1.9 (26.5 % reduction) and 1.2 ± 0.7 cm (42.9 % reduction) at 3 months and 6.14 ± 1.6 (10 % reduction) and 2.2 ± 1.2 cm (4.7 % increase) at 12 months, respectively. The %EWL was 8.9, 9.3, 8, 6.7, −10.7, −13.5, −5.8, −4.5 at 3, 6, 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, and 72 months, respectively.
Conclusion
Although endoscopic plication achieved the intended reduction in the pouch and stoma diameter at 3 months, these tend toward the preoperative diameter at 12 months. This anatomical failure and the lack of follow-up may explain why most patients failed to achieve sustainable weight loss.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchwald H, Oien DM (2013) Metabolic/bariatric surgery worldwide 2011. Obes Surg 23(4):427–436
Samuel I, Mason EE, Renquist KE, Huang YH, Zimmerman MB, Jamal M (2006) Bariatric surgery trends: an 18-year report from the international bariatric surgery registry. Am J Surg 192(5):657–662
Sugerman HJ, Kellum JM, Engle KM, Wolfe L, Starkey JV, Birkenhauer R, Fletcher P, Sawyer MJ (1992) Gastric bypass for treating severe obesity. Am J Clin Nutr 55(2 Suppl):560S–566S
Yale CE (1989) Gastric surgery for morbid obesity. Complications and long-term weight control. Arch Surg 124(8):941–946
Gloy VL, Briel M, Bhatt DL, Kashyap SR, Schauer PR, Mingrone G, Bucher HC, Nordmann AJ (2013) Bariatric surgery versus non-surgical treatment for obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 347:f5934
Gagner M, Gentileschi P, de Csepel J, Kini S, Patterson E, Inabnet WB, Herron D, Pomp A (2002) Laparoscopic reoperative bariatric surgery: experience from 27 consecutive patients. Obes Surg 12(2):254–260
Brethauer SA, Kothari S, Sudan R, Williams B, English WJ, Brengman M, Kurian M, Hutter M, Stegemann L, Kallies K, Nguyen NT, Ponce J, Morton JM (2014) Systematic review on reoperative bariatric surgery: American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Revision Task Force. Surg Obes Relat Dis 10(5):952–972
Mikami D, Needleman B, Narula V, Durant J, Melvin WS (2010) Natural orifice surgery: initial US experience utilizing the StomaphyX device to reduce gastric pouches after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Surg Endosc 24(1):223–228
Mullady DK, Lautz DB, Thompson CC (2009) Treatment of weight regain after gastric bypass surgery when using a new endoscopic platform: initial experience and early outcomes (with video). Gastrointest Endosc 70(3):440–444
Thompson CC, Jacobsen GR, Schroder GL, Horgan S (2012) Stoma size critical to 12-month outcomes in endoscopic suturing for gastric bypass repair. Surg Obes Relat Dis 8(3):282–287
Horgan S, Jacobsen G, Weiss GD, Oldham JS Jr, Denk PM, Borao F, Gorcey S, Watkins B, Mobley J, Thompson K, Spivack A, Voellinger D, Thompson C, Swanstrom L, Shah P, Haber G, Brengman M, Schroder G (2010) Incisionless revision of post-Roux-en-Y bypass stomal and pouch dilation: multicenter registry results. Surg Obes Relat Dis 6(3):290–295
Yimcharoen P, Heneghan HM, Singh M, Brethauer S, Schauer P, Rogula T, Kroh M, Chand B (2011) Endoscopic findings and outcomes of revisional procedures for patients with weight recidivism after gastric bypass. Surg Endosc 25(10):3345–3352
Heneghan HM, Yimcharoen P, Brethauer SA, Kroh M, Chand B (2012) Influence of pouch and stoma size on weight loss after gastric bypass. Surg Obes Relat Dis 8(4):408–415
Catalano MF, Rudic G, Anderson AJ, Chua TY (2007) Weight gain after bariatric surgery as a result of a large gastric stoma: endotherapy with sodium morrhuate may prevent the need for surgical revision. Gastrointest Endosc 66(2):240–245
Khaitan L, Van Sickle K, Gonzalez R, Lin E, Ramshaw B, Smith CD (2005) Laparoscopic revision of bariatric procedures: is it feasible? Am Surg 71(1):6–10 (discussion 10–2)
Brethauer SA, Pryor AD, Chand B, Schauer P, Rosenthal R, Richards W, Bessler M, American M, Society for, and C. Bariatric Surgery Emerging Technologies (2009) Endoluminal procedures for bariatric patients: expectations among bariatric surgeons. Surg Obes Relat Dis 5(2):231–236
Thompson CC, Slattery J, Bundga ME, Lautz DB (2006) Peroral endoscopic reduction of dilated gastrojejunal anastomosis after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a possible new option for patients with weight regain. Surg Endosc 20(11):1744–1748
Leitman IM, Virk CS, Avgerinos DV, Patel R, Lavarias V, Surick B, Holup JL, Goodman ER, Karpeh MS Jr (2010) Early results of trans-oral endoscopic plication and revision of the gastric pouch and stoma following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. JSLS 14(2):217–220
Ryou M, Mullady DK, Lautz DB, Thompson CC (2009) Pilot study evaluating technical feasibility and early outcomes of second-generation endosurgical platform for treatment of weight regain after gastric bypass surgery. Surg Obes Relat Dis 5(4):450–454
Harper J, Madan AK, Ternovits CA, Tichansky DS (2007) What happens to patients who do not follow-up after bariatric surgery? Am Surg 73(2):181–184
Shen R, Dugay G, Rajaram K, Cabrera I, Siegel N, Ren CJ (2004) Impact of patient follow-up on weight loss after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg 14(4):514–519
Gould JC, Beverstein G, Reinhardt S, Garren MJ (2007) Impact of routine and long-term follow-up on weight loss after laparoscopic gastric bypass. Surg Obes Relat Dis 3(6):627–630 (discussion 630)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Drs. Alberto S. Gallo, Christopher G. DuCoin, Martin A. Berducci, Diego F. Nino, Moneer Almadani, Bryan J. Sandler, Santiago Horgan, and Garth R. Jacobsen have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Presented at the SAGES 2015 Annual Meeting, April 15–18, 2015, Nashville, Tennessee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallo, A.S., DuCoin, C.G., Berducci, M.A. et al. Endoscopic revision of gastric bypass: Holy Grail or Epic fail?. Surg Endosc 30, 3922–3927 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4699-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-015-4699-3