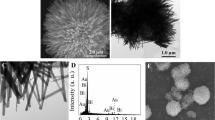
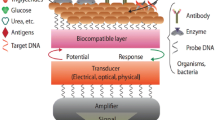
Abstract
Multiheme cytochrome c (Cyt c) can function as a redox protein on electrode to accomplish bioelectrocatalysis. However, the direct electron transfer (DET) between the redox site of Cyt c and electrode is low due to the large coupling distance. A close proximity or a connection pathway from the deeply buried active site to the protein surface can be established by modifying the electrode with carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to improve the DET. Therefore, the isolated Cyt c has been assembled or casted with CNTs by various processes to form Cyt c-CNTs bioelectrodes that can be further applied to biosensing and bioanalysis. These strategies can be transplanted to the fabrication of biofilm-CNTs based electrodes by complexing the out membrane (OM) Cyt c of natural electricigen with CNTs to realize the application of the electrochemical properties of “in vivo” Cyt c to bioelectrochemical systems (BESs). This review intends to highlight the preparation strategies of bioelectrodes that have been well studied in electrochemical biosensors and improving approaches of the DET from the CNTs surface to Cyt c in their hybrids. The efficient fabrication processes of the biofilm-CNTs based electrodes that can be considered as “in vivo” Cyt c-CNTs based electrodes for BES designs are also summarized, aiming to provide an inspiration source and a reference to the related studies of BES downstream.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eddowes MJ, Hill HAO (1977) Novel method for the investigation of the electrochemistry of metalloproteins: cytochrome c. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 21:771b–7772
Molinas M, Meibom KL, Faizova R, Mazzanti M, BernierLatmani R (2023) Mechanism of reduction of aqueous U(V)-dpaea and solid-phase U(VI)-dpaea complexes: the role of multiheme c-Type cytochromes. Environ Sci Technol 57:7537–7546
Zhang HQ, Quan HT, Zhou SN, Sun LP, Lu H (2022) Enhanced performance and electron transfer of sulfur-mediated biological process under polyethylene terephthalate microplastics exposure. Water Res 223:119038
Tasca F, Harreither W, Ludwig R, Gooding JJ, Gorton L (2011) Cellobiose dehydrogenase aryl diazonium modified single walled carbon nanotubes: enhanced direct electron transfer through a positively charged surface. Anal Chem 83:3042–3049
Tominaga M, Nomura S, Taniguchi I (2008) Bioelectrocatalytic current based on direct heterogeneous electron transfer reaction of glucose oxidase adsorbed onto multi-walled carbon nanotubes synthesized on platinum electrode surfaces. Electrochem Commun 10:888–890
Léger C, Bertrand P (2008) Direct electrochemistry of redox enzymes as a tool for mechanistic studies. Chem Rev 108:2379–2438
Shen Y, Qian XM, Mi XN, Tu YF (2022) An ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescent sensing platform for oxygen metabolism based on bioactive magnetic beads. Bioelectrochemistry 145:108086
Shukla AK, Abidi SMS, Sharma C, Chand Saini T, Acharya A (2022) Single-walled carbon nanotube conjugated cytochrome c as exogenous nano catalytic medicine to combat intracellular oxidative stress. Free Radical Biol Med 193:238–252
Bozorgzadeh S, Hamidi H, Ortiz R, Ludwig R, Gorton L (2015) Direct electron transfer of Phanerochaete chrysosporium cellobiose dehydrogenase at platinum and palladium nanoparticles decorated carbon nanotubes modified electrodes. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:24157–24165
Manikandan N, Suresh KVP, Siva MS, Rathis G, Vishnu SK, Shabariganesh TK (2021) Carbon nanotubes and their properties-the review. Mater Today Proc 47:4682–4685
Prasad MM, Manikandan N, Sutharsan S (2021) Investigation on mechanical properties of reinforced glass fibre/epoxy with hybrid nano composites. Dig J Nanomater Biostruct 16:455–469
Mehra NK, Mishra V, Jain NK (2014) A review of ligand tethered surface engineered carbon nanotubes. Biomaterials 35:1267–1283
González-Domínguez JM, Ansón-Casaos A, Grasa L, Abenia L, Salvador A, Colom E, Mesonero JE, García-Bordejé JE, Benito AM, Maser WK (2019) Unique properties and behavior of nonmercerized type-II cellulose nanocrystals as carbon nanotube biocompatible dispersants. Biomacromol 20:3147–3160
Chen H, Dong FY, Minteer SD (2020) The progress and outlook of bioelectrocatalysis for the production of chemicals, fuels and materials. Nat Catal 3:225–244
Yazdi AA, D’Angelo L, Omer N, Windiasti G, Lu X, Xu J (2016) Carbon nanotube modification of microbial fuel cell electrodes. Biosens Bioelectron 85:536–552
Liu YY, Dolidze TD, Singhal S, Khoshtariya DE, Wei JJ (2015) New evidence for a quasi-simultaneous proton-coupled two-electron transfer and direct wiring for glucose oxidase captured by the carbon nanotube–polymer matrix. J Phys Chem C 119:14900–14910
Meredith MT, Minson M, Hickey D, Artyushkova K, Glatzhofer DT, Minteer SD (2011) Anthracene-modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes as direct electron transfer scaffolds for enzymatic oxygen reduction. ACS Catal 1:1683–1690
Lalaoui N, Rousselot-Pailley P, Robert V, Mekmouche Y, Villalonga R, Holzinger M, Cosnier S, Tron T, Le Goff A (2016) Direct electron transfer between a site-specific pyrene-modified laccase and carbon nanotube/gold nanoparticle supramolecular assemblies for bioelectrocatalytic dioxygen reduction. ACS Catal 6:1894–1900
Lei DN, Wu JP, Zi YL, Pan CF, Cui HZ, Li XY (2023) Self-powered sterilization system for wearable devices based on biocompatible materials and triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Appl Electron Mater 5:2819–2828
Arunasri K, Mohan SV (2019) Biofilms: microbial life on the electrode surface. In: Mohan SV, Varjani S, Pandey A (eds) Microbial electrochemical technology sustainable platform for fuels chemicals and remediation biomass biofuels and biochemicals series. Elsevier Science Publishers. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-64052-9.00011-X
Xu S, Barrozo A, Tender LM, Krylov AI, El-Naggar MY (2018) Multiheme cytochrome mediated redox conduction through shewanella oneidensis MR-1 cells. J Am Chem Soc 140:10085–10089
Blumberger J (2018) Electron transfer and transport through multi-heme proteins: recent progress and future directions. Curr Opin Chem Biol 47:24–31
Chong GW, Karbelkar AA, El-Naggar MY (2018) Nature’s conductors: what can microbial multi-heme cytochromes teach us about electron transport and biological energy conversion? Curr Opin Chem Biol 47:7–17
Logan BE, Rossi R, Ragab A, Saikaly PE (2019) Electroactive microorganisms in bioelectrochemical systems. Nat Rev Microbiol 17:307–319
Yu SS, Chen JJ, Liu XY, Yu HQ (2018) Interfacial electron transfer from the outer membrane cytochrome OmcA to graphene oxide in a microbial fuel cell: spectral and electrochemical insights. ACS Energy Lett 3:2449–2456
Tahir K, Maile N, Ghani AA, Kim B, Jang J, Lee DS (2022) Development of a three-dimensional macroporous sponge biocathode coated with carbon nanotube–MXene composite for high-performance microbial electrosynthesis systems. Bioelectrochemistry 146:108140
Xu B, Li Z, Jiang YJ, Chen MJ, Chen B, Xin FX, Dong WL, Jiang M (2022) Recent advances in the improvement of bi-directional electron transfer between abiotic/biotic interfaces in electron-assisted biosynthesis system. Biotechnol Adv 54:107810
Cao BC, Zhao ZP, Peng LL, Shiu HY, Ding MN, Song F, Guan X, Lee CK, Huang J, Zhu D, Fu XY, Wong GCL, Liu C, Nealson K, Weiss PS, Duan XF, Huang Y (2021) Silver nanoparticles boost charge-extraction efficiency in Shewanella microbial fuel cells. Science (New York, N.Y.) 373:1336–1340
Logan BE, Rabaey K (2012) Conversion of wastes into bioelectricity and chemicals by using microbial electrochemical technologies. Science (New York, N.Y.) 337(6095):686–690
Nagendranatha Reddy C, Kondaveeti S, Mohanakrishna G, Min B (2022) Application of bioelectrochemical systems to regulate and accelerate the anaerobic digestion processes. Chemosphere 287:132299
Nyangau EO, Abe H, Nakayasu Y, Umetsu M, Watanabe M, Tada C (2023) Iron azaphthalocyanine electrocatalysts for enhancing oxygen reduction reactions under neutral conditions and power density in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour Technol Rep 23:101565
Zhang C, Li XY, Wang ZC, Huang XQ, Ge ZP, Hu BF (2020) Influence of structured water layers on protein adsorption process: a case study of cytochrome c and carbon nanotube interactions and its implications. J Phys Chem B 124:684–694
Peng L, You SJ, Wang JY (2010) Carbon nanotubes as electrode modifier promoting direct electron transfer from shewanella oneidensis. Biosens Bioelectron 25:1248–1251
Suma Y, Kang CS, Kim HS (2016) Noncovalent and covalent immobilization of oxygenase on single-walled carbon nanotube for enzymatic decomposition of aromatic hydrocarbon intermediates. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:1015–1024
Senthil Kumar A, Vishnu N, Dinesh B (2020) Studies on controlled protein folding versus direct electron-transfer reaction of cytochrome c on MWCNT/Nafion modified electrode surface and its selective bioelectrocatalytic H2O2 reduction and sensing function. In: Singh L (ed) Novel catalyst materials for bioelectrochemical systems fundamentals and applications. ACS Symposium Series ACS Publications, Washington
Murphy M, Theyagarajan K, Ganesan P, Senthilkumar S, Thenmozhi K (2019) Electrochemical biosensor for the detection of hydrogen peroxide using cytochrome c covalently immobilized on carboxyl functionalized ionic liquid/multiwalled carbon nanotube hybrid. Appl Surf Sci 492:718–725
Baldacchini C, Herrero Chamorro MA, Prato M, Cannistraro S (2011) Highly conductive redox protein–carbon nanotube complex for biosensing applications. Adv Func Mater 21:153–157
Gandhi M, Rajagopal D, Senthil Kumar A (2021) Molecularly wiring of cytochrome c with carboxylic acid functionalized hydroquinone on MWCNT surface and its bioelectrocatalytic reduction of H2O2 relevance to biomimetic electron-transport and redox signalling. Electrochim Acta 368:137596
Chen QP, Ai SY, Zhu XB, Yin HS, Ma Q, Qiu YY (2009) A nitrite biosensor based on the immobilization of cytochrome c on multi-walled carbon nanotubes–PAMAM–chitosan nanocomposite modified glass carbon electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 24:2991–2996
Lata S, Batra B, Karwasra N, Pundir CS (2012) An amperometric H2O2 biosensor based on cytochrome c immobilized onto nickel oxide nanoparticles/carboxylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes/polyaniline modified gold electrode. Process Biochem 47:992–998
Zhang M, Zhou GY, Feng Y, Xiong TR, Hou HQ, Guo QH (2016) Flexible 3D nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes nanostructure: a good matrix for enzyme immobilization and biosensing. Sens Actuators B Chem 222:829–838
Wang YT, Yu L, Wang J, Lou L, Du WJ, Zhu ZQ, Peng H, Zhu JZ (2011) A novel l-lactate sensor based on enzyme electrode modified with ZnO nanoparticles and multiwall carbon nanotubes. J Electroanal Chem 661:8–12
Jia WZ, Schwamborn S, Jin C, Xia W, Muhler M, Schuhmann W, Stoica L (2010) Towards a high potential biocathode based on direct bioelectrochemistry between horseradish peroxidase and hierarchically structured carbon nanotubes. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:10088–10092
Shumyantseva VV, Bulko TV, Kuzikov AV, Masamrekh RA, Pergushov DV, Schacher FH, Sigolaeva LV (2020) Electrochemical fingerprint of cytochrome c on a polymer/MWCNT nanocomposite electrode. Mendeleev Commun 30:299–301
Eguílaz M, Agüí L, Sedeño YP, Pingarrón JM (2010) A biosensor based on cytochrome c immobilization on a poly-3-methylthiophene/multi-walled carbon nanotubes hybrid-modified electrode. Application to the electrochemical determination of nitrite. J Electroanal Chem 644:30–35
Zhang M, Zheng J, Wang JP, Xu JL, Hayat T, Alharbi NS (2019) Direct electrochemistry of cytochrome c immobilized on one dimensional Au nanoparticles functionalized magnetic N-doped carbon nanotubes and its application for the detection of H2O2. Sens Actuators B Chem 282:85–95
Kilele JC, Chokkareddy R, Rono N, Redhi GG (2020) A novel electrochemical sensor for selective determination of theophylline in pharmaceutical formulations. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 111:228–238
Lee KP, Gopalan AI, Komathi S (2009) Direct electrochemistry of cytochrome c and biosensing for hydrogen peroxide on polyaniline grafted multi-walled carbon nanotube electrode. Sens Actuators B Chem 141:518–525
Bathinapatla A, Kanchi S, Singh P, Sabela MI, Bisetty K (2016) An ultrasensitive performance enhanced novel cytochrome c biosensor for the detection of rebaudioside A. Biosens Bioelectron 77:116–123
Aghamiri ZS, Mohsennia M, RafieeP HA (2018) Fabrication and characterization of cytochrome c-immobilized polyaniline/multi-walled carbon nanotube composite thin film layers for biosensor applications. Thin Solid Films 660:484–492
Eguílaz M, Gutiérrez A, Rivas G (2016) Non-covalent functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with cytochrome c: Enhanced direct electron transfer and analytical applications. Sens Actuators B Chem 225:74–80
Aghamiri ZS, Mohsennia M, Rafiee-Pour HA (2019) Immobilization of cytochrome c on polyaniline/polypyrrole/carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotube/glassy carbon electrode: biosensor fabrication. J Solid State Electrochem 23:2233–2242
Mozayan E, Rafiee-Pour H-A, Ghasemi F (2023) CNT-FET for sensitive hydrogen peroxide biosensing via immobilized cytochrome c. Arch Biochem Biophys 744:109695
Wang L, Ambrosi A, Pumera M (2013) Carbonaceous impurities in carbon nanotubes are responsible for accelerated electrochemistry of acetaminophen. Electrochem Commun 26:71–73
Eguílaz M, Venegas CJ, Gutiérrez A, Rivas GA, Bollo S (2016) Carbon nanotubes non-covalently functionalized with cytochrome c: a new bioanalytical platform for building bienzymatic biosensors. Microchem J 128:161–165
Gong YP, Liu QF, Wilt JS, Gong MG, Ren SQ, Wu J (2015) Wrapping cytochrome c around single-wall carbon nanotube: engineered nanohybrid building blocks for infrared detection at high quantum efficiency. Sci Rep 5:11328
Haldorai Y, Hwang S-K, Gopalan A-I, Huh YS, Han Y-K, Voit W, Sai-Anand G, Lee K-P (2016) Direct electrochemistry of cytochrome c immobilized on titanium nitride/multi-walled carbon nanotube composite for amperometric nitrite biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 79:543–552
Gorby YA, Yanina S, McLean JS, Rosso KM, Moyles D, Dohnalkova A, Beveridge TJ, Chang IS, Kim BH, Kim KS, Culley DE, Reed SB, Romine MF, Saffarini DA, Hill EA, Shi L, Elias DA, Kennedy DW, Pinchuk G, Watanabe K, Ishii S, Logan B, Nealson KH, Fredrickson JK (2006) Electrically conductive bacterial nanowires produced by shewanella oneidensis strain MR-1 and other microorganisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:11358–11363
Christwardana M, Joelianingsih J, Yoshi LA, Hadiyanto H (2022) Binderless carbon nanotube/carbon felt anode to improve yeast microbial fuel cell performance. Curr Res Green Sustain Chem 5:100323
Wang YP, Cheng XS, Liu K, Dai XF, Qi JT, Ma Z, Qiu YF, Liu SQ (2022) 3D hierarchical Co8FeS8-FeCo2O4/N-CNTs@CF with an enhanced microorganisms–anode interface for improving microbial fuel cell performance. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 14:35809–35821
Zhao JK, Feng K, Lu Y, Cheng ZW, Ye JX, Shen Y, Hu J, Chen JM, Zhang SH, Li W (2022) 3D pore-matched PANI@CNT bioanode for efficient electron extraction from toluene. J Power Sources 536:231509
Song RB, Zhao CE, Jiang LP, Abdel HES, Zhang JR, Zhu JJ (2016) Bacteria-affinity 3D macroporous graphene/MWCNTs/Fe3O4 foams for high-performance microbial fuel cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:16170–16177
Liu YF, Sun YX, Li HY, Ren TL, Li CJ (2022) Co-filtration of bacteria/electrospun oriented carbon nanofibers integrating with carbon nanotubes for microbial fuel cell. J Environ Chem Eng 10:107664
Jyoti J, Gupta TK, Singh BP, Sandhu M, Tripathi SK (2022) Recent advancement in three dimensional graphene-carbon nanotubes hybrid materials for energy storage and conversion applications. J Energy Storage 50:104235
Xie X, Hu LB, Pasta M, Wells GF, Kong DS, Criddle CS, Cui Y (2011) Three-dimensional carbon nanotube-textile anode for high-performance microbial fuel cells. Nano Lett 11:291–296
Qi LJ, Wu JS, Chen Y, Wen Q, Xu HT, Wang YY (2020) Shape-controllable binderless self-supporting hydrogel anode for microbial fuel cells. Renew Energy 156:1325–1335
Xie X, Ye M, Hu LB, Liu N, McDonough JR, Chen W, Alshareef HN, Criddle CS, Cui Y (2012) Carbon nanotube-coated macroporous sponge for microbial fuel cell electrodes. Energy Environ Sci 5:5265–5270
Cai T, Huang MH, Huang YX, Zheng W (2019) Enhanced performance of microbial fuel cells by electrospinning carbon nanofibers hybrid carbon nanotubes composite anode. Int J Hydrog Energy 44:3088–3098
Qi LJ, Xu HT, Tang R, Liu LL, Chen Y, Wen Q (2022) Study on power generation and Congo red decolorization of 3D conductive PPy-CNT hydrogel in bioelectrochemical system. Int J Hydrog Energy 47:16568–16579
Luo H, Gao HF, Zhang XD, Yang F, Liu C, Xu KW, Guo DG (2023) Caterpillar-like 3D graphene nanoscrolls@CNTs hybrids decorated with Co-doped MoSe2 nanosheets for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J Mater Sci Technol 136:43–53
Erbay C, Yang G, de Figueiredo P, Sadr R, Yu C, Han A (2015) Three-dimensional porous carbon nanotube sponges for high-performance anodes of microbial fuel cells. J Power Sources 298:177–183
Liu XW, Huang YX, Sun XF, Sheng GP, Zhao F, Wang SG, Yu HQ (2014) Conductive carbon nanotube hydrogel as a bioanode for enhanced microbial electrocatalysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:8158–8164
Sun JJ, Zhao HZ, Yang QZ, Song J, Xue A (2010) A novel layer-by-layer self-assembled carbon nanotube-based anode: Preparation, characterization, and application in microbial fuel cell. Electrochim Acta 55:3041–3047
Yang QZ, Zhao XD, Yang J, Zhou B, Wang JZ, Dong YS, Zhao HZ (2019) Welding assembly of 3D interconnected carbon nanotubes on carbon fiber as the high-performance anode of microbial fuel cells. Int J Hydrog Energy 44:20304–20311
Liang P, Wang HY, Xia X, Huang X, Mo YH, Cao XX, Fan MZ (2011) Carbon nanotube powders as electrode modifier to enhance the activity of anodic biofilm in microbial fuel cells. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3000–3004
Zhang P, Liu J, Qu YP, Zhang J, Zhong YJ, Feng YJ (2017) Enhanced performance of microbial fuel cell with a bacteria/multi-walled carbon nanotube hybrid biofilm. J Power Sources 361:318–325
Pinck S, Etienne M, Dossot M, Jorand FPA (2017) A rapid and simple protocol to prepare a living biocomposite that mimics electroactive biofilms. Bioelectrochemistry 118:131–138
Amen MT, Barakat NAM, Jamal MAHM, Hong ST, Mohamed IMA, Salama A (2018) Anolyte in-situ functionalized carbon nanotubes electrons transport network as novel strategy for enhanced performance microbial fuel cells. Appl Energy 228:167–175
Kou TY, Yang Y, Yao B, Li Y (2018) Interpenetrated bacteria-carbon nanotubes film for microbial fuel cells. Small Methods 2:1800152
Plekhanova Y, Tarasov S, Bykov A, Reshetilov A (2019) Electrochemical assessment of the interaction of microbial living cells and carbon nanomaterials. IET Nanobiotechnol 13:332–338
Pinck S, Jorand FPA, Xu MJ, Etienne M (2019) Protamine promotes direct electron transfer between shewanella oneidensis cells and carbon nanomaterials in bacterial biocomposites. ChemElectroChem 6:2349–2349
Christwardana M, Kwon Y (2017) Yeast and carbon nanotube based biocatalyst developed by synergetic effects of covalent bonding and hydrophobic interaction for performance enhancement of membraneless microbial fuel cell. Biores Technol 225:175–182
Zhao CE, Wu JS, Ding YZ, Wang VB, Zhang YD, Kjelleberg S, Loo JSC, Cao B, Zhang QC (2015) Hybrid conducting biofilm with built-in bacteria for high-performance microbial fuel cells. ChemElectroChem 2:654–658
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Open Research Fund of Songshan Lake Materials Laboratory (Grant No.2021SLABFN19), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (Grant No. ZR2021MC016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, X., Liu, X., Dong, H. et al. Implementation of cytochrome c proteins and carbon nanotubes hybrids in bioelectrodes towards bioelectrochemical systems applications. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 47, 159–168 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-023-02933-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-023-02933-x