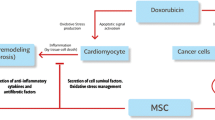
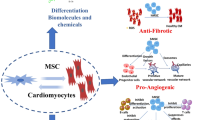
Abstract
Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)–based tissue regeneration therapy has been extensively investigated for cardiac regeneration over the past two decades. Numerous animal and clinical investigations demonstrated the efficacy of various types of MSCs towards myocardial protection and restoration against anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity (AIC). It has been established that local or systemic administration of MSCs considerably improved the cardiac function, while ameliorating inflammatory responses and myocardial fibrosis. Several factors influence the outcomes of MSC treatment for AIC, including MSC types, dosages, and routes and duration of administration. In this review, we discuss the recent (from 2015 to 2020) experimental and clinical research on the preventive and regeneration efficacy of different types of MSCs (with or without supporting agents) against AIC, as well as the key factors responsible for MSC-mediated cardiac repair. In addition, challenges and future perspectives of MSC-based cardiac regeneration therapy are also outlined.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Soliman N, Abd-Allah SH, Hussein S, Alaa Eldeen M et al (2017) Factors enhancing the migration and the homing of mesenchymal stem cells in experimentally induced cardiotoxicity in rats. IUBMB Life 69:162–169. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1600
Abd Allah SH, Hussein S, Hasan MM et al (2017) Functional and structural assessment of the effect of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. J Cell Biochem 118:3119–3129. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26168
Abushouk AI, Muhammad A, Salem A et al (2019) Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy : potential mechanisms, governing factors, and implications of the heart stem cell debate. Front Pharmacol 10:635. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00635
Al-Abd AM, Mahmoud AM, El-Sherbiny GA et al (2011) Resveratrol enhances the cytotoxic profile of docetaxel and doxorubicin in solid tumour cell lines in vitro. Cell Prolif 44:591–601. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2184.2011.00783.x
Al-Shabanah OA, El-Kashef HA, Badary OA et al (2000) Effect of streptozotocin-induced hyperglycaemia on intravenous pharmacokinetics and acute cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin in rats. Pharmacol Res 41:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1006/phrs.1999.0568
Ammar HI, Sequiera GL, Nashed MB et al (2015) Comparison of adipose tissue- and bone marrow- derived mesenchymal stem cells for alleviating doxorubicin-induced cardiac dysfunction in diabetic rats. Stem Cell Res Ther 6:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-015-0142-x
Armenian SH, Hudson MM, Mulder RL et al (2015) Recommendations for cardiomyopathy surveillance for survivors of childhood cancer: a report from the International Late Effects of Childhood Cancer Guideline Harmonization Group. Lancet Oncol 16:e123–e136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70409-7
Baker N, Boyette LB, Tuan RS et al (2015) Characterization of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in aging. Bone 70:37–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2014.10.014
Bansal N, Adams MJ, Ganatra S et al (2019) Strategies to prevent anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity in cancer survivors. Cardio-Oncology 5:18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40959-019-0054-5
Bartolucci J, Verdugo FJ, González PL et al (2017) Safety and efficacy of the intravenous infusion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in patients with heart failure: a phase 1/2 randomized controlled trial (RIMECARD trial [Randomized clinical trial of intravenous infusion umbilical cord mesenchymal. Circ Res 121:1192–1204. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.310712
Bolli R, Hare JM, Henry TD et al (2018) Rationale and design of the SENECA (StEm cell iNjECtion in cAncer survivors) trial. Am Heart J 201:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2018.02.009
Burridge PW, Li YF, Matsa E et al (2016) Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes recapitulate the predilection of breast cancer patients to doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Nat Med 22:547–556. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4087
Can A, Celikkan FT, Cinar O et al (2017) Umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cell transplantations: a systemic analysis of clinical trials. Cytotherapy 19:1351–1382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcyt.2017.08.004
Cardinale D, Colombo A, Bacchiani G et al (2015) Early detection of anthracycline cardiotoxicity and improvement with heart failure therapy. Circulation 131:1981–1988. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.013777
Chao KC, Chao KF, Fu YS, Liu SH et al (2008) Islet-like clusters derived from mesenchymal stem cells in Wharton’s Jelly of the human umbilical cord for transplantation to control type 1 diabetes. PLoS ONE 3:e1451. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001451
Chen L, Xia W, Hou M et al (2018) Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate doxorubicin-induced cellular senescence through the VEGF/Notch/TGF-β signaling pathway in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Int J Mol Med 42:674–684. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3635
Chen Q, Zhang Y, Zhu H et al (2020) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviate the daunorubicin-induced subacute myocardial injury in rats through inhibiting infiltration of T lymphocytes and antigen-presenting cells. Biomed Pharmacother 121:109157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109157
Chen Y, Liu W, Li W, Gao C et al (2010) Autologous bone marrow mesenchymal cell transplantation improves left ventricular function in a rabbit model of dilated cardiomyopathy. Exp Mol Pathol 88:311–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2009.12.002
Chen Y, Wan Y, Wang Y et al (2011) Anticancer efficacy enhancement and attenuation of side effects of doxorubicin with titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine 6:2321–2326. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S25460
Deng B, Wang J xin, Hu X xing et al (2017) Nkx2.5 enhances the efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in treatment heart failure in rats. Life Sci 182:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.06.014
Dey S, DeMazumder D, Sidor A et al (2018) Mitochondrial ROS drive sudden cardiac death and chronic proteome remodeling in heart failure. Circ Res 123:356–371. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.312708
Di G-H, Jiang S, Li F-Q et al (2012) Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells mitigate chemotherapy-associated tissue injury in a pre-clinical mouse model. Cytotherapy 14:412–422. https://doi.org/10.3109/14653249.2011.646044
Dias C, Francisco JC, Cardoso MA et al (2015) Cardiac analysis of autologous transplantation of cocultured skeletal myoblasts and mesenchymal cells in a rat model doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: histopathological and functional studies. J Clin Exp Cardiolog 6:. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9880.1000407
Dickey JS, Gonzalez Y, Aryal B et al (2013) Mito-tempol and dexrazoxane exhibit cardioprotective and chemotherapeutic effects through specific protein oxidation and autophagy in a syngeneic breast tumor preclinical model. PLoS ONE 8:e70575. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070575
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I et al (2006) Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 8:315–317. https://doi.org/10.1080/14653240600855905
Eirin A, Zhu X-Y, Puranik AS et al (2016) Comparative proteomic analysis of extracellular vesicles isolated from porcine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Sci Rep 6:36120. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36120
Eulalio A, Mano M, Ferro MD et al (2012) Functional screening identifies miRNAs inducing cardiac regeneration. Nature 492:376–381. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11739
Gao LR, Chen Y, Zhang NK et al (2015) Intracoronary infusion of Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells in acute myocardial infarction: double-blind, randomized controlled trial. BMC Med 13:162. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-015-0399-z
Garreta E, Prado P, Izpisua Belmonte JC, Montserrat N et al (2017) Non-coding microRNAs for cardiac regeneration: exploring novel alternatives to induce heart healing. Non-coding RNA Res 2:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncrna.2017.05.001
Gong X, Wang P, Wu Q et al (2016) Human umbilical cord blood derived mesenchymal stem cells improve cardiac function in cTnTR141W transgenic mouse of dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur J Cell Biol 95:57–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejcb.2015.11.003
Gopinath S, Vanamala SK, Gondi CS, Rao JS et al (2010) Human umbilical cord blood derived stem cells repair doxorubicin-induced pathological cardiac hypertrophy in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 395:367–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.04.021
Hare JM, DiFede DL, Rieger AC et al (2017) Randomized comparison of allogeneic versus autologous mesenchymal stem cells for nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy: POSEIDON-DCM Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 69:526–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2016.11.009
Haydardedeoglu AE, Boztok Özgermen DB, Yavuz O et al (2018) Mesenchymal stem cells reduce left ventricular mass in rats with doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. Int J Morphol 36:48–53. https://doi.org/10.4067/s0717-95022018000100048
Hendrikx M, Fanton Y, Willems L et al (2016) From Bone marrow to cardiac atrial appendage stem cells for cardiac repair: a review. Curr Med Chem 23:2421–2438. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867323666160525114735
Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Ardehali H, Fischmeister R et al (2019) Late onset heart failure after childhood chemotherapy. Eur Heart J 40:798–800. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehz046
Hu G, Li Q, Niu X et al (2015) Exosomes secreted by human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate limb ischemia by promoting angiogenesis in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther 6:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt546
Huang W, Feng Y, Liang J et al (2018) Loss of microRNA-128 promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and heart regeneration. Nat Commun 9:700. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03019-z
Ichikawa Y, Ghanefar M, Bayeva M et al (2014) Cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin is mediated through mitochondrial iron accumulation. J Clin Invest 124:617–630. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI72931
Ivey KN, Muth A, Arnold J et al (2008) MicroRNA regulation of cell lineages in mouse and human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2:219–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2008.01.016
Izarra A, Moscoso I, Levent E et al (2014) miR-133a enhances the protective capacity of cardiac progenitors cells after myocardial infarction. Stem Cell Reports 3:1029–1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.10.010
Jinghai C, Zhan-Peng H, Young SH et al (2013) mir-17–92 Cluster is required for and sufficient to induce cardiomyocyte proliferation in postnatal and adult hearts. Circ Res 112:1557–1566. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.300658
Kalam K, Marwick TH (2013) Role of cardioprotective therapy for prevention of cardiotoxicity with chemotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer 49:2900–2909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2013.04.030
Kalay N, Basar E, Ozdogru I et al (2006) Protective effects of carvedilol against anthracycline-induced cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 48:2258–2262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2006.07.052
Kang SK, Shin IS, Ko MS et al (2012) Journey of mesenchymal stem cells for homing: strategies to enhance efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy. Stem Cells Int 2012:342968. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/342968
Kim SW, Kim HW, Huang W et al (2013) Cardiac stem cells with electrical stimulation improve ischaemic heart function through regulation of connective tissue growth factor and miR-378. Cardiovasc Res 100:241–251. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvt192
Lancellotti P, Suter TM, López-Fernández T et al (2019) Cardio-Oncology Services: rationale, organization, and implementation. Eur Heart J 40:1756–1763. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehy453
Le Blanc K, Frassoni F, Ball L et al (2008) Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II study. Lancet 371:1579–1586. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60690-X
Li T, Ma Q, Ning M et al (2014) Cotransplantation of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells and umbilical cord blood-derived CD34+ cells in a rabbit model of myocardial infarction. Mol Cell Biochem 387:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1874-5
Liu C-B, Huang H, Sun P et al (2016) Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells improve left ventricular function, perfusion, and remodeling in a porcine model of chronic myocardial ischemia. Stem Cells Transl Med 5:1004–1013. https://doi.org/10.5966/sctm.2015-0298
Mao C, Hou X, Wang B et al (2017) Intramuscular injection of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves cardiac function in dilated cardiomyopathy rats. Stem Cell Res Ther 8:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-017-0472-y
Mazzola M, Di Pasquale E (2020) Toward cardiac regeneration: combination of pluripotent stem cell-based therapies and bioengineering strategies. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:455. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00455
Mohammadi Gorji S, Karimpor Malekshah AA, Hashemi-Soteh MB et al (2012) Effect of mesenchymal stem cells on Doxorubicin-induced fibrosis. Cell J 14:142–151
Mousa HSE, Abdel Aal SM, Abbas NAT et al (2018) Umbilical cord blood-mesenchymal stem cells and carvedilol reduce doxorubicin- induced cardiotoxicity: possible role of insulin-like growth factor-1. Biomed Pharmacother 105:1192–1204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.051
Murabito A, Hirsch E, Ghigo A et al (2020) Mechanisms of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: is mitochondrial dysfunction the answer? Front Cardiovasc Med 7:35. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2020.00035
Nebigil CG, Désaubry L (2018) Updates in anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity Front Pharmacol 9:1262. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01262
Obrien C, Ozen M, Evgenia V et al (2019) Abstract 12922: microvesicles rescue cardiomyocytes from doxorubicin injury via mitochondrial transfer in a patient specific model of anthracycline induced cardiomyopathy. Circulation 140:A12922–A12922. https://doi.org/10.1161/circ.140.suppl_1.12922
Obrien CG, Ozen MO, Vaskova E et al (2018) Abstract 16965: Microvesicles rescue cardiomyocytes from doxorubicin injury in a patient specific model of anthracycline induced cardiomyopathy. Circulation 138:A16965–A16965. https://doi.org/10.1161/circ.138.suppl_1.16965
Oliveira MS, Melo MB, Carvalho JL et al (2013) Doxorubicin cardiotoxicity and cardiac function improvement after stem cell therapy diagnosed by strain echocardiography. J Cancer Sci Ther 5:52–57. https://doi.org/10.4172/1948-5956.1000184
Olson A, Jahdami V Al, Timmons M et al (2019) A clinical trial of intravenous mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of anthracycline associated cardiomyopathy. Cytotherapy 21:S50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcyt.2019.03.408
Pang JKS, Phua QH, Soh B-S et al (2019) Applications of miRNAs in cardiac development, disease progression and regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther 10:336. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-019-1451-2
Pınarlı FA, Turan NN, Güçlü Pınarlı F et al (2013) Resveratrol and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells are effective in the prevention and treatment of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in rats. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 30:226–238. https://doi.org/10.3109/08880018.2012.762962
Porrello ER, Johnson BA, Aurora AB et al (2011) MiR-15 family regulates postnatal mitotic arrest of cardiomyocytes. Circ Res 109:670–679. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.248880
Psaltis PJ, Carbone A, Nelson AJ et al (2010) Reparative effects of allogeneic mesenchymal precursor cells delivered transendocardially in experimental nonischemic cardiomyopathy. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 3:974–983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcin.2010.05.016
Qi Z, Zhang Y, Liu L et al (2012) Mesenchymal stem cells derived from different origins have unique sensitivities to different chemotherapeutic agents. Cell Biol Int 36:857–862. https://doi.org/10.1042/CBI20110637
Rajesh K, Federica R, Kathryn M et al (2011) Transplantation of human pericyte progenitor cells improves the repair of infarcted heart through activation of an angiogenic program involving micro-RNA-132. Circ Res 109:894–906. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.251546
Reichardt P, Tabone M-D, Mora J et al (2018) Risk-benefit of dexrazoxane for preventing anthracycline-related cardiotoxicity: re-evaluating the European labeling. Future Oncol 14:2663–2676. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2018-0210
Sabapathy V, Kumar S (2016) hiPSC-derived iMSCs: NextGen MSCs as an advanced therapeutically active cell resource for regenerative medicine. J Cell Mol Med 20:1571–1588. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12839
Santos Nascimento D, Mosqueira D, Sousa LM et al (2014) Human umbilical cord tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate remodeling after myocardial infarction by proangiogenic, antiapoptotic, and endogenous cell-activation mechanisms. Stem Cell Res Ther 5:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt394
Scully RE, Lipshultz SE (2007) Anthracycline cardiotoxicity in long-term survivors of childhood cancer. Cardiovasc Toxicol 7:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-007-0006-4
Shafei AE-S, Ali MA, Ghanem HG et al (2017) Mesenchymal stem cell therapy: a promising cell-based therapy for treatment of myocardial infarction. J Gene Med 19:e2995. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgm.2995
Shijun H, Mei H, K. NP et al (2011) Novel microRNA prosurvival cocktail for improving engraftment and function of cardiac progenitor cell transplantation. Circulation 124:S27–S34. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.017954
Sluijter JPG, van Mil A, van Vliet P et al (2010) MicroRNA-1 and -499 regulate differentiation and proliferation in human-derived cardiomyocyte progenitor cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 30:859–868. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.197434
Szydlak R (2019) Mesenchymal stem cells’ homing and cardiac tissue repair. Acta Biochim Pol 66:483–489. https://doi.org/10.18388/abp.2019_2890
Tacar O, Sriamornsak P, Dass CR et al (2013) Doxorubicin: an update on anticancer molecular action, toxicity and novel drug delivery systems. J Pharm Pharmacol 65:157–170. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.2012.01567.x
Tian Y, Liu Y, Wang T et al (2015) A microRNA-Hippo pathway that promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and cardiac regeneration in mice. Sci Transl Med 7:279ra38. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3010841
Tong Z, Jiang B, Wu Y et al (2015) MiR-21 protected cardiomyocytes against doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by targeting BTG2. Int J Mol Sci 16:14511–14525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160714511
van Mil A, Vrijsen KR, Goumans M-J et al (2013) microRNA-1 enhances the angiogenic differentiation of human cardiomyocyte progenitor cells. J Mol Med 91:1001–1012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-013-1017-1
Vijay V, Moland CL, Han T et al (2016) Early transcriptional changes in cardiac mitochondria during chronic doxorubicin exposure and mitigation by dexrazoxane in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 295:68–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2016.02.003
Wei H, Tan G, Manasi et al (2012) One-step derivation of cardiomyocytes and mesenchymal stem cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Res 9:87–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scr.2012.04.003
Xia W, Hou M (2018) Mesenchymal stem cells confer resistance to doxorubicin-induced cardiac senescence by inhibiting microRNA-34a. Oncol Lett 15:10037–10046. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8438
Yang Y, Cheng H-W, Qiu Y et al (2015) MicroRNA-34a plays a key role in cardiac repair and regeneration following myocardial infarction. Circ Res 117:450–459. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.305962
Yu Q, Li Q, Na R et al (2014) Impact of repeated intravenous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells infusion on myocardial collagen network remodeling in a rat model of doxorubicin-induced dilated cardiomyopathy. Mol Cell Biochem 387:279–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1894-1
Yun S, Vincelette ND, Abraham I et al (2015) Cardioprotective role of beta-blockers and angiotensin antagonists in early-onset anthracyclines-induced cardiotoxicity in adult patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Postgrad Med J 91:627–633. https://doi.org/10.1136/postgradmedj-2015-133535
Zaki SM, Algaleel WA, Imam RA, Abdelmoaty MM et al (2019) Mesenchymal stem cells pretreated with platelet-rich plasma modulate doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Hum Exp Toxicol 38:857–874. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327119842613
Zeng YL, Zheng H, Chen QR et al (2017) Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing MiR-21 efficiently repair myocardial damage in rats. Oncotarget 8:29161–29173. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16254
Zhang S, Liu X, Bawa-Khalfe T et al (2012) Identification of the molecular basis of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Nat Med 18:1639–1642. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2919
Zhang Y, Liang X, Liao S et al (2015) Potent Paracrine Effects of human induced Pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. Sci Rep 5:11235. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11235
Zhang Y, Yu Z, Jiang D et al (2016) iPSC-MSCs with high intrinsic MIRO1 and sensitivity to TNF-α yield efficacious mitochondrial transfer to rescue anthracycline-induced cardiomyopathy. Stem Cell Reports 7:749–763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.08.009
Zhang Z, Lin H, Shi M et al (2012) Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve liver function and ascites in decompensated liver cirrhosis patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27(Suppl 2):112–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.07024.x
Zhao L, Liu X, Zhang Y et al (2016) Enhanced cell survival and paracrine effects of mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing hepatocyte growth factor promote cardioprotection in myocardial infarction. Exp Cell Res 344:30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.03.024
Zhao M, Song B, Pu J et al (2006) Electrical signals control wound healing through phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase-γ and PTEN. Nature 442:457–460. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04925
Zhao Y, Samal E, Srivastava D et al (2005) Serum response factor regulates a muscle-specific microRNA that targets Hand2 during cardiogenesis. Nature 436:214–220. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03817
Funding
This work was supported by Zhejiang Provincial Science and Technology Projects (grants no. GF20H020041 to HS, LGD19H160001 to JKT), Shaoxing Municiple Science and Technology Projects (grant no. 2018C30016 to FXL), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants No. 81772537 to JKT; 81374014 to JKT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, H., Xue, Q., Liu, Y. et al. The emerging therapeutic role of mesenchymal stem cells in anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity. Cell Tissue Res 384, 1–12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03364-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03364-w