Abstract
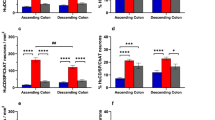
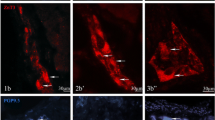
The enteric nervous system (ENS) controls gastrointestinal functions. In large mammals’ intestine, it comprises an inner (ISP) and outer (OSP) submucous plexus and a myenteric plexus (MP). This study quantifies enteric neurons in the ISP, OSP, and MP of the pig ascending (AC) and descending colon (DC) using the HuC/D, choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) neuronal markers in whole mount preparations with multiple labeling immunofluorescence. We established that the ISP contains the highest number of HuC/D neurons/mm2, which were more abundant in AC vs. DC, followed by OSP and MP with similar density in AC and DC. In the ISP, the density of ChAT immunoreactive (IR) neurons was very similar in AC and DC (31% and 35%), nNOS-IR neurons were less abundant in AC than DC (15% vs. 42%, P < 0.001), and ChAT/nNOS-IR neurons were 5% and 10%, respectively. In the OSP, 39–44% of neurons were ChAT-IR in AC and DC, while 45% and 38% were nNOS-IR and 10–12% were ChAT/nNOS-IR (AC vs. DC P < 0.05). In the MP, ChAT-IR neurons were 44% in AC and 54% in DC (P < 0.05), nNOS-IR neurons were 50% in both, and ChAT/nNOS-IR neurons were 12 and 18%, respectively. The ENS architecture with multilayered submucosal plexuses and the distribution of functionally distinct groups of neurons in the pig colon are similar to humans, supporting the suitability of the pig as a model and providing the platform for investigating the mechanisms underlying human colonic diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avetisyan M, Schill EM, Heuckeroth RO (2015) Building a second brain in the bowel. J Clin Invest 125:899–907
Barami K, Iversen K, Furneaux H, Goldman SA (1995) Hu protein as an early marker of neuronal phenotypic differentiation by subependymal zone cells of the adult songbird forebrain. J Neurobiol 28:82–101
Barbiers M, Timmermans J-P, Scheuermann DW, Adriaensen D, Mayer B, De Groodt-Lasseel MHA (1993) Distribution and morphological features of nitrergic neurons in the porcine large intestine. Histochemistry 100:27–34
Barone R (1997) Anatomie Comparée des Mammifères Domestiques. In: Splanchnologie I. Appareil Respiratoire. Vigot Fréres Paris, Appareil Digestif
Bassols A, Costa C, Eckersall PD, Osada J, Sabrià J, Tibau J (2014) The pig as an animal model for human pathologies: a proteomics perspective. Proteomics Clin Appl 8:715–731
Brehmer A, Schrodl F, Neuhuber W, Tooyama I, Kimura H (2004) Co-expression pattern of neuronal nitric oxide synthase and two variants of choline acetyltransferase in myenteric neurons of porcine ileum. J Chem Neuroanat 27:33–41
Brookes SJ (2001) Classes of enteric nerve cells in the guinea-pig small intestine. Anat Rec 262:58–70
Brown DR, Parsons AM, O’Grady SM (1992) Substance P produces sodium and bicarbonate secretion in porcine jejunal mucosa through an action on enteric neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 261:1206–1212.
Brown DR, Timmermans JP (2004) Lessons from the porcine enteric nervous system. Neurogastroenterol Motil 16:50–54
Chandan R, Hildebrand KR, Seybold VS, Soldani G, Brown DR (1991a) Cholinergic neurons and muscarinic receptors regulate anion secretion in pig distal jejunum. Eur J Pharmacol 193:265–273
Chandan R, Megarry BH, O'Grady SM, Seybold VS, Brown DR (1991b) Muscarinic cholinergic regulation of electrogenic chloride secretion in porcine proximal jejunum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 257:908–917
Furness JB (2000) Types of neurons in the enteric nervous system. J Auton Nerv Syst 81:87–96
Furness JB (2012) The enteric nervous system and neurogastroenterology. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 9:286–294
Furness JB, Callaghan BP, Rivera LR, Cho HJ (2014) The enteric nervous system and gastrointestinal innervation: integrated local and central control. Adv Exp Med Biol 817:39–71
Harrington AM, Hutson JM, Southwell BR (2010) Cholinergic neurotransmission and muscarinic receptors in the enteric nervous system. Prog Histochem Cytochem 44:173–202
Hens J, Schrödl F, Brehmer A, Adriaensen D, Neuhuber W, Scheuermann DW, Schemann M, Timmermans JP (2000) Mucosal projections of enteric neurons in the porcine small intestine. J Comp Neurol 421:429–436
Ho A, Lievore A, Patierno S, Kohlmeier SE, Tonini M, Sternini C (2003) Neurochemically distinct classes of myenteric neurons express the μ-opioid receptor in the guinea pig ileum. J Comp Neurol 458:404–411
Kararli TT (1995) Comparison of the gastrointestinal anatomy, physiology, and biochemistry of humans and commonly used laboratory animals. Biopharm Drug Dispos 16:351–380
Leonhard-Marek S, Hempe J, Schroeder B, Breves G (2009) Electrophysiological characterization of chloride secretion across the jejunum and colon of pigs as affected by age and weaning. J Comp Physiol B 179:883–896
Lomax AE, Furness JB (2000) Neurochemical classification of enteric neurons in the guinea pig distal colon. Cell Tissue Res 302:59–78
Lunney JK (2007) Advances in swine biomedical model genomics. Int J Biol Sci 3:179–184
Miller ER, Ullrey DE (1987) The pig as a model for human nutrition. Annu Rev Nutr 7:361–382
Murphy EM, Defontgalland D, Costa M, Brookes SJ, Wattchow DA (2007) Quantification of subclasses of human colonic myenteric neurons by immunoreactivity to Hu, choline acetyltransferase and nitric oxide synthase. Neurogastroenterol Motil 19:126–134
Ng KS, Montes-Adrian NA, Mahns DA, Gladman MA (2018) Quantification and neurochemical coding of the myenteric plexus in humans: no regional variation between the distal colon and rectum. Neurogastroenterol Motil 30. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13193
Pang X, Hua X, Yang Q, Ding D, Che C, Cui L, Jia W, Bucheli P, Zhao L (2007) Inter-species transplantation of gut microbiota from human to pigs. ISME J 1:156–162
Petto C, Gäbel G, Pfannkuche H (2015) Architecture and chemical coding of the inner and outer submucous plexus in the colon of piglets. PLoS One 10:e0133350
Pfannkuche H, Mauksch A, Gabel G (2011) Modulation of electrogenic transport processes in the porcine proximal colon by enteric neurotransmitters. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 96:482–493
Porter AJ, Wattchow DA, Brookes SJ, Schemann M, Costa M (1996) Choline acetyltransferase immunoreactivity in the human small and large intestine. Gastroenterology 111:401–408
Porter AJ, Wattchow DA, Brookes SJ, Costa M (1997) The neurochemical coding and projections of circular muscle motor neurons in the human colon. Gastroenterology 113:1916–1923
Porter AJ, Wattchow DA, Brookes SJ, Costa M (2002) Cholinergic and nitrergic interneurones in the myenteric plexus of the human colon. Gut 51:70–75
Russo D, Clavenzani P, Sorteni C, Bo Minelli L, Botti M, Gazza F, Panu R, Ragionieri L, Chiocchetti R (2013) Neurochemical features of boar lumbosacral dorsal root ganglion neurons and characterization of sensory neurons innervating the urinary bladder trigone. J Comp Neurol 521:342–366
Sanders KM, Ward SM (2019) Nitric oxide and its role as a non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory neurotransmitter in the gastrointestinal tract. Br J Pharmacol 176:212–227
Sang Q, Young HM (1998) The identification and chemical coding of cholinergic neurons in the small and large intestine of the mouse. Anat Rec 251:185–199
Timmermans JP, Scheuermann DW, Stach W, Adriaensen D, De Groodt-Lasseel MH (1990) Distinct distribution of CGRP-, enkephalin-, galanin-, neuromedin U-, neuropeptide Y-, somatostatin-, substance P-, VIP- and serotonin-containing neurons in the two submucosal ganglionic neural networks of the porcine small intestine. Cell Tissue Res 260:367–379
Timmermans JP, Scheuermann DW, Stach W, Adriaensen D, de Groodt-Lesseal MHA (1992) Functional morphology of the enteric nervous system with special reference to large mammals. Eur J Morphol 30:113–122
Timmermans JP, Barbiers M, Scheuermann DW, Stach W, Adriaensen D, Mayer B, De Groodt-Lasseel MHA (1994a) Distributional pattern, neurochemical features and projections of nitrergic neurons in the pig small intestine. Ann Anat 176:515–525
Timmermans JP, Barbiers M, Scheuermann DW, Bogers JJ, Adriaensen D, Fekete E, Mayer B, Van Marck EA, De Groodt-Lasseel MHA (1994b) Nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity in the enteric nervous system of the developing human digestive tract. Cell Tissue Res 275:235–245
Timmermans JP, Adriaensen D, Cornelissen W, Scheuermann DW (1997) Structural organization and neuropeptide distribution in the mammalian enteric nervous system, with special attention to those components involved in mucosal reflexes. Comp Biochem Physiol A Physiol 118:331–340
Timmermans JP, Hens J, Adriaensen D (2001) Outer submucous plexus: an intrinsic nerve network involved in both secretory and motility processes in the intestine of large mammals and humans. Anat Rec 262:71–78
Wattchow DA, Porter AJ, Brookes SJ, Costa M (1997) The polarity of neurochemically defined myenteric neurons in the human colon. Gastroenterology 113:497–506
Wattchow DA, Brookes S, Murphy E, Carbone S, de Fontgalland D, Costa M (2008) Regional variation in the neurochemical coding of the myenteric plexus of the human colon and changes in patients with slow transit constipation. Neurogastroenterol Motil 20:1298–1305
Wedel T, Roblick U, Gleiss J, Schiedeck T, Bruch HP, Kühnel W, Krammer HJ (1999) Organization of the enteric nervous system in the human colon demonstrated by wholemount immunohistochemistry with special reference to the submucous plexus. Ann Anat 181:327–337
Wedel T, Roblick UJ, Ott V, Eggers R, Schiedeck TH, Krammer HJ, Bruch HP (2002) Oligoneuronal hypoganglionosis in patients with idiopathic slow-transit constipation. Dis Colon rectum 45:54–62
Wester T, O’Brian S, Puri P (1998) Morphometric aspects of the submucous plexus in whole-mount preparations of normal human distal colon. J Pediatr Surg 33:619–622
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. Michael Schemann for kindly providing the primary choline acetyl transferase antibody.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Institute of Health-SPARC (Stimulating Peripheral Activity to Relieve Conditions) Award 1OT2OD24899 (CS), the University of California at Los Angeles/Digestive Diseases Research Center Core P30 DK41301, Imaging Core (CS) and Animal Model Core (MMillion), and the “Fondazione CARISBO” project 2017/0312, Bologna, Italy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Animal care and procedures described in this study were carried out in strict accordance with the National Institutes of Health recommendations for the humane use of animals. The experimental procedures were approved by University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), Chancellor’s Animal Research Committee (ARC) (protocol 2018-074-01).
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mazzoni, M., Caremoli, F., Cabanillas, L. et al. Quantitative analysis of enteric neurons containing choline acetyltransferase and nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivities in the submucosal and myenteric plexuses of the porcine colon. Cell Tissue Res 383, 645–654 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03286-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-020-03286-7