Abstract
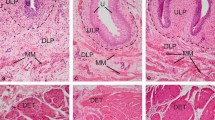
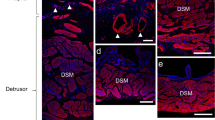
With most research on interstitial cells (IC) in the bladder being conducted on animal models, it remains unclear whether all structural and functional data on IC from animal models can be translated to the human context. This prompted us to compare the structural and immunohistochemical properties of IC in bladders from mouse, rat and human. Tissue samples were obtained from the bladder dome and subsequently processed for immunohistochemistry and electron microscopy. The ultrastructural properties of IC were compared by means of electron microscopy and IC were additionally characterized with single/double immunohistochemistry/immunofluorescence. Our results reveal a similar organization of the IC network in the upper lamina propria (ULP), the deep lamina propria (DLP) and the detrusor muscle in human, rat and mouse bladders. Furthermore, despite several similarities in IC phenotypes, we also found several obvious inter-species differences in IC, especially in the ULP. Most remarkably in this respect, ULP IC in human bladder predominantly displayed a myoid phenotype with abundant presence of contractile micro-filaments, while those in rat and mouse bladders showed a fibroblast phenotype. In conclusion, the organization of ULP IC, DLP IC and detrusor IC is comparable in human, rat and mouse bladders, although several obvious inter-species differences in IC phenotypes were found. The present data show that translating research data on IC in laboratory animals to the human setting should be carried out with caution.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson K-E, McCloskey KD (2014) Lamina propria: the functional center of the bladder? Neurourol Urodyn 33:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.22465
Davidson RA, McCloskey KD (2005) Morphology and localization of interstitial cells in the guinea pig bladder: structural relationships with smooth muscle and neurons. J Urol 173:1385–1390. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000146272.80848.37
De Wachter S (2011) Afferent signaling from the bladder: species differences evident from extracellular recordings of pelvic and hypogastric nerves. Neurourol Urodyn 30:647–652. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.21135
Drake MJ, Fry CH, Eyden B (2006) Structural characterization of myofibroblasts in the bladder. BJU Int 97:29–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2006.05818.x
El Sayegh TY, Kapus A, McCulloch CA (2007) Beyond the epithelium: cadherin function in fibrous connective tissues. FEBS Lett 581:167–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2006.12.029
Eyden B (2009) Are there myofibroblasts in normal bladder? Eur Urol 56:427–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2009.03.060
Gevaert T, Hutchings G, Everaerts W et al (2014) Administration of imatinib mesylate in rats impairs the neonatal development of intramuscular interstitial cells in bladder and results in altered contractile properties. Neurourol Urodyn 33:461–468. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.22415
Gevaert T, Ridder DD, Vanstreels E et al (2016) The stem cell growth factor receptor KIT is not expressed on interstitial cells in bladder. J Cell Mol Med. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13054
Gevaert T, Rietjens R, Voets T et al (2016) Topographies and isoforms of the progesterone receptor in female human, rat and mouse bladder. Cell Tissue Res 364:385–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2329-y
Gevaert T, Vanstreels E, Daelemans D et al (2014) Identification of different phenotypes of interstitial cells in the upper and deep lamina propria of the human bladder dome. J Urol 192:1555–1563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2014.05.096
Gillespie JI, Markerink-van Ittersum M, de Vente J (2005) Expression of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) and nitric-oxide-induced changes in cGMP in the urothelial layer of the guinea pig bladder. Cell Tissue Res 321:341–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-005-1151-3
Hashitani H (2006) Interaction between interstitial cells and smooth muscles in the lower urinary tract and penis. J Physiol 576:707–714. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2006.116632
Isogai A, Lee K, Mitsui R, Hashitani H (2016) Functional coupling of TRPV4 channels and BK channels in regulating spontaneous contractions of the guinea pig urinary bladder. Pflugers Arch 468:1573–1585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-016-1863-0
Kadekawa K, Yoshimura N, Majima T et al (2016) Characterization of bladder and external urethral activity in mice with or without spinal cord injury--a comparison study with rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 310:R752–R758. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00450.2015
Kanai A, Fry C, Hanna-Mitchell A et al (2014) Do we understand any more about bladder interstitial cells?-ICI-RS 2013. Neurourol Urodyn 33:573–576. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.22591
Kanai A, Fry C, Ikeda Y et al (2016) Implications for bidirectional signaling between afferent nerves and urothelial cells-ICI-RS 2014. Neurourol Urodyn 35:273–277. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.22839
Lagou M, Drake MJ, Markerink-Van Ittersum M et al (2006) Interstitial cells and phasic activity in the isolated mouse bladder. BJU Int 98:643–650. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2006.06255.x
McCloskey KD, Gurney AM (2002) Kit positive cells in the guinea pig bladder. J Urol 168:832–836
Monaghan KP, Johnston L, McCloskey KD (2012) Identification of PDGFRα positive populations of interstitial cells in human and guinea pig bladders. J Urol 188:639–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2012.03.117
Popescu LM, Faussone-Pellegrini M-S (2010) TELOCYTES - a case of serendipity: the winding way from interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC), via interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) to TELOCYTES. J Cell Mol Med 14:729–740. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01059.x
Rasmussen H, Rumessen JJ, Hansen A et al (2009) Ultrastructure of Cajal-like interstitial cells in the human detrusor. Cell Tissue Res 335:517–527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-008-0736-z
Revenu C, Athman R, Robine S, Louvard D (2004) The co-workers of actin filaments: from cell structures to signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:635–646. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1437
Robinson MS (2015) Forty years of clathrin-coated vesicles. Traffic Cph Den 16:1210–1238. https://doi.org/10.1111/tra.12335
Root JA, Davey DA, Af Forselles KJ (2015) Prostanoid receptors mediating contraction in rat, macaque and human bladder smooth muscle in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol 769:274–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.11.030
Sui GP, Rothery S, Dupont E et al (2002) Gap junctions and connexin expression in human suburothelial interstitial cells. BJU Int 90:118–129
Vannucchi M-G, Traini C, Guasti D et al (2014) Telocytes subtypes in human urinary bladder. J Cell Mol Med 18:2000–2008. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12375
Wiseman OJ, Fowler CJ, Landon DN (2003) The role of the human bladder lamina propria myofibroblast. BJU Int 91:89–93
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the excellent technical assistance of Mrs. Sarah Cumps, Mrs. Nathalie Volders, Mrs. Kathleen Van Den Eynde (Leuven), Mrs. Annett Weimann and Mrs. Mandy Berndt-Paetz (Leipzig). TG, JN, IP, FVDA and DDR designed the research study; TG, CS, JN, EV and IP performed the research; TG, JN, DDR, JPT, DD, EV and WE analyzed the data; TG, WE, JPT, JN, TR and DDR wrote the manuscript.
Funding
The Leica Ultracut EM UC7 (AUHA/11/01) and the Tecnai G2 BioTwin electron microscope (AUHA/004) for the EM work were purchased with support of the Hercules Foundation. CS and JN received financial support from the Dr. Siegfried Krüger Stiftung, Leipzig. This study was further supported by the Research Council of the KU Leuven Grant EF/95/010. Dirk De Ridder is a clinical-fundamental researcher of FWO Vlaanderen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Thomas Gevaert and Jochen Neuhaus are sharing first authorships
Isabel Pintelon and Dirk De Ridder are sharing last authorships
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gevaert, T., Neuhaus, J., Vanstreels, E. et al. Comparative study of the organisation and phenotypes of bladder interstitial cells in human, mouse and rat. Cell Tissue Res 370, 403–416 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-017-2694-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-017-2694-9