Abstract
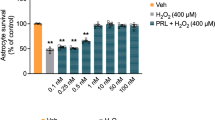
Lycium barbarum polysaccharides (LBP) have been reported to have a wide range of beneficial effects including neuroprotection, anti-aging and anticancer. However, the anti-inflammation mechanism of LBP on primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons injured by oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/RP) is incompletely understood. We investigate the neuroprotective effects of LBP on neonatal rat primary cultured hippocampal neurons injured by OGD/RP with different approaches: MTT assay was used to detect cell viability, lactate dehydrogenase leakage was used to detect neuronal damage, formation of reactive oxygen species was determined by using fluorescent probe DCFH-DA. Hoechst 33,342 staining and TUNEL staining were used to determine the cell apoptosis. JC-1 was used to evaluate loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP). The fluorescence intensity of [Ca2+]i in hippocampal neurons was determined by laser scanning confocal microscopy. The expression of various apoptotic markers such as TLR4, IκB, IL-6 and NF-κB were investigated by RT-PCR and western blot analysis. Results from each approach demonstrated that LBP increased the cell abilities and decreased the cell morphologic impairment. Furthermore, LBP increased MMP but inhibited [Ca2+]i elevation and significantly suppressed overexpression of NF-κB, IL-6 TLR4 and increased IκB expression.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonaventura A, Liberale L, Vecchié A, Casula M, Carbone F, Dallegri F, Montecucco F (2016) Update on Inflammatory Biomarkers and Treatments in Ischemic Stroke. Int J Mol Sci 17(12)
Burke JF, Lisabeth LD, Brown DL, Reeves MJ, Morgenstern LB (2012) Determining stroke’s rank as a cause of death using multicause mortality data. Stroke 43:2207–2211. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.656967
Chang RC, So KF (2008) Use of anti-aging herbal medicine, Lycium barbarum,against aging-associated diseases. What do we know so far? Cell Mol Neurobiol 28:643–652
Chumboatong W, Thummayot S, Govitrapong P, Tocharus C, Jittiwat J, Tocharus J (2017) Neuroprotection of agomelatine against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through an antiapoptotic pathway in rat. Neurochem Int 102:114–122. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2016.12.011
Deng L, Pan J, Peng Q, Dong Z, Wang Y (2016) Toll-like receptor 3 and interferon β mRNA expressions were increased in peripheral blood of ischemic stroke patients with good outcome. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2016.11.122
Eltzschig HK, Eckle T (2011) Ischemia and reperfusion--from mechanism to translation. Nat Med 17:1391-401. doi:10.1038/nm.2507
Gertz K, Kronenberg G, Kälin RE, Baldinger T, Werner C, Balkaya M, Eom GD, Hellmann-Regen J, Kröber J, Miller KR, Lindauer U, Laufs U, Dirnagl U, Heppner FL, Endres M (2012) Essential role of interleukin-6 in post-stroke angiogenesis. Brain 135:1964–1980. doi:10.1093/brain/aws075
Gu JH, Ge JB, Li M, Wu F, Zhang W, Qin ZH (2012) Inhibition of NF- kB activation is associated with anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of Ginkgolide B in a mouse model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Eur J Pharm Sci 47:652–660. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2012.07.016
Gwag BJ, Lobner D, Koh JY, Wie MB, Choi DW (1995) Blochade of glutamate receptors unmasks neuronal apoptosis after oxygen-glucose deprivation in vitro. Neuroscience 68:615–619
Han J, Zou C, Mei L, Zhang Y, Qian Y, You S, Pan Y, Xu Z, Bai B, Huang W, Liang G (2017) MD2 mediates angiotensin II-induced cardiac inflammation and remodeling via directly binding to Ang II and activating TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Basic Res Cardiol 112:9. doi:10.1007/s00395-016-0599-5
He M, Pan H, Chang RC, So KF, Brecha NC, Pu M (2014) Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant pathway contributes to the protective effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides in the rodent retina after ischemia-reperfusion-induced damage. PLoS ONE 9:e84800. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0084800 eCollection 2014
Huyan T, Li Q, Yang H, Jin M-L, Zhang M-J, Ye L-J, Li J, Huang Q-S, Yin D-C (2014) Protective effect of polysaccharides on simulated microgravity-induced functional inhibition of human NK cells. Carbohydr Polym 101:819–827. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.10.021
Ji X, Luo Y, Ling F, Stetler RA, Lan J, Cao G, Chen J (2007) Mild hypothermia diminishes oxidative DNA damage and pro-death signaling events after cerebral ischemia: a mechanism for neuroprotection. Front Biosci 12:1737–1747
Kaczorowski DJ, Mollen KP, Edmonds R, Billiar TR (2008) Early events in the recognition of danger signals after tissue injury. J Leukoc Biol 83:546–552
Karki R, Igwe OJ (2013) Toll-like receptor 4–mediated nuclear factor kappa B activation is essential for sensing exogenous oxidants to propagate and maintain oxidative/Nitrosative cellular stress. PLoS ONE 8(9):e73840. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0073840 eCollection 2013
Krmpotić L, Zirdum D, Gorup D et al (2013) Expression analysis of genes involved in TLR2-related signaling pathway: inflammation and apoptosis after ischemic brain injury. Neuroscience 238:87–96
Li Y, Wang M, Wang S (2016) Effect of inhibiting mitochondrial fission on energy metabolism in rat hippocampal neurons during ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neurol Res 14:1–8
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Ma Y, He M, Qiang L (2013) Exercise therapy down regulates the overexpression of TLR4, TLR2, MyD88 and NF-κB after cerebral ischemia in rats. Int J Mol Sci 14:3718–3733. doi:10.3390/ijms14023718
Maciejczyk M, Mikoluc B, Pietrucha B, Heropolitanska-Pliszka E, Pac M, Motkowski R, Car H (2016) Oxidative stress, mitochondrial abnormalities and antioxidant defense in ataxia-telangiectasia. Bloom Syndr Nijmegen Breakage Syndr 11:375–383. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2016.12.030
Nagayama T, Lan J, Henshall DC, Chen D, O'Horo C, Simon RP, Chen J (2000) Induction of oxidative DNA damage in the peri-infarct region after permanent focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem 75:1716–1728
Reers M, Smith TW, Chen LB (1991) J-aggregate formation of a carbocyanine as a quantitative fluorescent indicator of membrane potential. Biochemistry 30:4480–4486
Rui C, Yuxiang L, Yinju H, Qingluan Z, Yang W, Qipeng Z, Hao W, Lin M, Juan L, Chengjun Z, Yuanxu J, Yanrong W, Xiuying D, Wannian Z, Tao S, Jianqiang Y (2012) Protective effects of Lycium barbarumpolysaccharide on neonatal rat primary cultured hippocampal neurons injured by oxygen-glucose deprivation and reperfusion. J Mol Histol 43:535–542. doi:10.1007/s10735-012-9420-4
Strong K, Mathers C, Bonita R (2007) Preventing stroke: saving lives around the world. Lancet Neurol 6:182–187
Su F, Guo AC, Li WW, Zhao YL, Qu ZY, Wang YJ, Wang Q, Zhu YL (2016) Low-Dose Ethanol Preconditioning Protects Against Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation-Induced Neuronal Injury By Activating Large Conductance, Ca2+-Activated K+ Channels In Vitro. Neurosci Bull
Tu XK, Yang WZ, Shi SS, Wang CH, Zhang GL, Ni TR, Chen CM, Wang R, Jia JW, Song QM (2010) Spatio-temporal distribution of inflammatory reaction and expression of TLR2/4 signaling pathway in rat brain following permanent focal cerebral ischemia. Neurochem Res 35:1147–1155. doi:10.1007/s11064-010-0167-6
Valero T (2014) Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches. Curr Pharm Des 20:5507–5509
Varoni MV, Pasciu V, Gadau SD, Baralla E, Serra E, Palomba D, Demontis MP (2016) Possible antioxidant effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides on hepatic cadmium-induced oxidative stress in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int
Wang T, Li Y, Wang Y, Zhou R, Ma L, Hao Y, Jin S, Du J, Zhao C, Sun T, Yu J (2014) Lycium barbarum Polysaccharide prevents focal cerebral ischemic injury by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis in mice. PLoS ONE 9:e90780. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090780 eCollection 2014
Wang H, Lau BW, Wang NL, Wang SY, Lu QJ, Chang RC, So KF (2015a) Lycium barbarum polysaccharides promotes in vivo proliferation of adult rat retinal progenitor cells. Neural Regen Res 10(12):1976–1981. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.172315
Wang PF, Xiong XY, Chen J, Wang YC, Duan W, Yang QW (2015b) Function and mechanism of toll-like receptors in cerebral ischemic tolerance: from preconditioning to treatment. J Neuroinflammation 12:80. doi:10.1186/s12974-015-0301-0
Wang Y, Chen G, Yu X, Li Y, Zhang L, He Z, Zhang N, Yang X, Zhao Y, Li N, Qiu H (2016) Salvianolic acid B ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through inhibiting TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway. Inflammation 39:1503–1513. doi:10.1007/s10753-016-0384-5
Willcox JM, Summerlee AJ (2014) Relaxin protects astrocytes from hypoxia in vitro. PLoS ONE 9:e90864. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090864 eCollection 2014
Winters L, Winters T, Gorup D, Mitrečić D, Curlin M, Križ J, Gajović S (2013) Expression analysis of genes involved in TLR2-related signaling pathway: inflammation and apoptosis after ischemic brain injury. Neuroscience 238:87–96. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.02.001
Wu GJ, Chen JT, Tsai HC, Chen TL, Liu SH, Chen RM (2016) Protection of dexmedetomidine against ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptotic insults to neuronal cells occurs via an intrinsic mitochondria-dependent pathway. J Cell Biochem. doi:10.1002/jcb.25847
Xiao J, Xing F, Huo J, Fung ML, Liong EC, Ching YP, Xu A, Chang RC, So KF, Tipoe GL (2014) Lycium barbarum polysaccharides therapeutically improve hepatic functions in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis rats and cellular steatosis model. Sci Rep 4:5587. doi:10.1038/srep05587
Yuan S, Zhang J, Zhang L, Huang L, Peng J, Huang S, Chen S, Xu A (2013) The archaic roles of the amphioxus NF-κB/IκB complex in innate immune responses. J Immunol 19:1220–1230. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1203527
Zhang M, Chen H, Huang J, Li Z, Zhu C, Zhang S (2005) Effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on human hepatoma QGY7703 cells: inhibition of proliferation and induction of apoptosis. Life Sci 76:2115–2124
Zhang XJ, Yu HY, Cai YJ, Ke M (2016) Lycium barbarum polysaccharides inhibit proliferation and migration of bladder cancer cell lines BIU87 by suppressing Pi3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.13963
Zhao J, Liu R (2016) Stroke 1-2-0: a rapid response programme for stroke in China. Lancet Neurol. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(16)30283-6
Zhao J, Wu Y, Sun M, Wang J, Li YH, Zhang K, Yu JQ (2012) Protective effects and mechanisms of OSR on primary cultured hippocampus neurons subjected to anoxic injury in neonatal rat. Chin J Chin Mater Med 37:94–98
Zhao R, Qiu B, Li Q, Zhang T, Zhao H, Chen Z, Cai Y, Ruan H, Ge W, Zheng X (2014) LBP-4a improves insulin resistance via translocation and activation of GLUT4 in OLETF rats. Food Funct 5:811–820. doi:10.1039/c3fo60602c
Zhou JM, Gu SS, Mei WH, Zhou J, Wang ZZ, Xiao W (2016a) Ginkgolides and bilobalide protect BV2 microglia cells against OGD/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting TLR2/4 signaling pathways. Cell Stress Chaperones 21:1037–1053
Zhou J, Pang H, Li W, Liu Q, Xu L, Liu Q, Liu Y (2016b) Effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides on apoptosis, cellular adhesion, and oxidative damage in bone marrow mononuclear cells of mice exposed to ionizing radiation injury. Biomed Res Int 2016:4147879. doi:10.1155/2016/4147879
Zhu XJ, Shi Y, Peng J, Guo CS, Shan NN, Qin P, Ji XB, Hou M (2009) The effects of BAFF and BAFF-R-Fc fusion protein in immune thrombocytopenia. Blood 114:5362–5367. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-05-217513
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no 81360649), the Natural Science Foundation of Ningxia (Grant no. NZ13278) and Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, colleges and universities of science and technology research projects (grant no. XM2011017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, P., Ma, NT., Chang, RY. et al. Mechanism of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides on primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Cell Tissue Res 369, 455–465 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-017-2648-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-017-2648-2