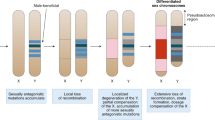
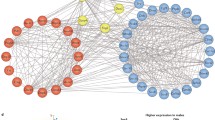
Abstract
In this review, we discuss the way that insights from evolutionary theory and systems biology shed light on form and function in mammalian reproductive systems. In the first part of the review, we contrast the rapid evolution seen in some reproductive genes with the generally conservative nature of development. We discuss directional selection and coevolution as potential drivers of rapid evolution in sperm and egg proteins. Such rapid change is very different from the highly conservative nature of later embryo development. However, it is not unique, as some regions of the sex chromosomes also show elevated rates of evolutionary change. To explain these contradictory trends, we argue that it is not reproductive functions per se that induce rapid evolution. Rather, it is the fact that biotic interactions, such as speciation events and sexual conflict, have no evolutionary endpoint and hence can drive continuous evolutionary changes. Returning to the question of sex chromosome evolution, we discuss the way that recent advances in evolutionary genomics and systems biology and, in particular, the development of a theory of gene balance provide a better understanding of the evolutionary patterns seen on these chromosomes. We end the review with a discussion of a surprising and incompletely understood phenomenon observed in early embryos: namely the Warburg effect, whereby glucose is fermented to lactate and alanine rather than respired to carbon dioxide. We argue that evolutionary insights, from both yeasts and tumor cells, help to explain the Warburg effect, and that new metabolic modeling approaches are useful in assessing the potential sources of the effect.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aagaard JE, Springer SA, Soelberg SD, Swanson WJ (2013) Duplicate abalone egg coat proteins bind sperm lysin similarly, but evolve oppositely, consistent with molecular mimicry at fertilization. PLoS Genet 9:e1003287
Anderson MJ, Dixson AF (2002) Sperm competition: motility and the midpiece in primates. Nature 416:496–496
Anderson MJ, Nyholt J, Dixson AF (2004) Sperm competition affects the structure of the mammalian vas deferens. J Zool 264:97–103
Anderson MJ, Nyholt J, Dixson AF (2005) Sperm competition and the evolution of sperm midpiece volume in mammals. J Zool 267:135–142
Anderson M, Dixson A, Dixson A (2006) Mammalian sperm and oviducts are sexually selected: evidence for co-evolution. J Zool 270:682–686
Bachtrog D (2006) A dynamic view of sex chromosome evolution. Curr Opin Genet Dev 16:578–585
Bellott DW, Skaletsky H, Pyntikova T, Mardis ER, Graves T, Kremitzki C, Brown LG, Rozen S, Warren WC, Wilson RK, Page DC (2010) Convergent evolution of chicken Z and human X chromosomes by expansion and gene acquisition. Nature 466:612–616
Benson GV, Lim H, Paria BC, Satokata I, Dey SK, Maas RL (1996) Mechanisms of reduced fertility in Hoxa-10 mutant mice: uterine homeosis and loss of maternal Hoxa-10 expression. Development 122:2687–2696
Betran E, Thornton K, Long M (2002) Retroposed new genes out of the X in Drosophila. Genome Res 12:1854–1859
Bianchi E, Doe B, Goulding D, Wright GJ (2014) Juno is the egg Izumo receptor and is essential for mammalian fertilization. Nature 508:483–487
Birchler JA (2010) Reflections on studies of gene expression in aneuploids. Biochem J 426:119–123
Birchler JA, Veitia RA (2010) The gene balance hypothesis: implications for gene regulation, quantitative traits and evolution. New Phytol 186:54–62
Birchler JA, Veitia RA (2012) Gene balance hypothesis: connecting issues of dosage sensitivity across biological disciplines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:14746–14753
Blank LM, Lehmbeck F, Sauer U (2005) Metabolic-flux and network analysis of fourteen hemiascomycetous yeasts. FEMS Yeast Res 5:545–558
Bleil JD, Wassarman PM (1980) Mammalian sperm-egg interaction: identification of a glycoprotein in mouse egg zonae pellucidae possessing receptor activity for sperm. Cell 20:873–882
Bucciantini M, Giannoni E, Chiti F, Baroni F, Formigli L, Zurdo J, Taddei N, Ramponi G, Dobson CM, Stefani M (2002) Inherent toxicity of aggregates implies a common mechanism for protein misfolding diseases. Nature 416:507–511
Cairns RA, Harris IS, Mak TW (2011) Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer 11:85–95
Chalbi M, Barraud-Lange V, Ravaux B, Howan K, Rodriguez N, Soule P, Ndzoudi A, Boucheix C, Rubinstein E, Wolf JP, Ziyyat A, Perez E, Pincet F, Gourier C (2014) Binding of sperm protein Izumo1 and its egg receptor Juno drives Cd9 accumulation in the intercellular contact area prior to fusion during mammalian fertilization. Development 141:3732–3739
Chen P (1984) The functional morphology and biochemistry of insect male accessory glands and their secretions. Annu Rev Entomol 29:233–255
Clark NL, Aagaard JE, Swanson WJ (2006) Evolution of reproductive proteins from animals and plants. Reproduction 131:11–22
Clark NL, Findlay GD, Yi X, MacCoss MJ, Swanson WJ (2007) Duplication and selection on abalone sperm lysin in an allopatric population. Mol Biol Evol 24:2081–2090
Clark NL, Gasper J, Sekino M, Springer SA, Aquadro CF, Swanson WJ (2009) Coevolution of interacting fertilization proteins. PLoS Genet 5:e1000570
Claw KG, George RD, Swanson WJ (2014) Detecting coevolution in mammalian sperm–egg fusion proteins. Mol Reprod Dev 81:531–538
Codoner FM, Fares MA (2008) Why should we care about molecular coevolution? Evol Bioinform Online 4:29–38
Conant GC, Wolfe KH (2007) Increased glycolytic flux as an outcome of whole-genome duplication in yeast. Mol Syst Biol 3:129
Cortez D, Marin R, Toledo-Flores D, Froidevaux L, Liechti A, Waters PD, Grützner F, Kaessmann H (2014) Origins and functional evolution of Y chromosomes across mammals. Nature 508:488–493
Cox B, Kotlyar M, Evangelou AI, Ignatchenko V, Ignatchenko A, Whiteley K, Jurisica I, Adamson SL, Rossant J, Kislinger T (2009) Comparative systems biology of human and mouse as a tool to guide the modeling of human placental pathology. Mol Syst Biol 5:279
de Juan D, Pazos F, Valencia A (2013) Emerging methods in protein co-evolution. Nat Rev Genet 14:249–261
Dell’ Antone P (2012) Energy metabolism in cancer cells: how to explain the Warburg and Crabtree effects? Med Hypotheses 79:388–392
Deng X, Hiatt JB, Nguyen DK, Ercan S, Sturgill D, Hillier LW, Schlesinger F, Davis CA, Reinke VJ, Gingeras TR, Shendure J, Waterston RH, Oliver B, Lieb JD, Disteche CM (2011) Evidence for compensatory upregulation of expressed X-linked genes in mammals, Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster. Nat Genet 43:1179–1185
Dhroso A, Korkin D, Conant GC (2014) The yeast protein interaction network has a capacity for self-organization. FEBS J 281:3420–3432
Diaz-Ruiz R, Rigoulet M, Devin A (2011) The Warburg and Crabtree effects: on the origin of cancer cell energy metabolism and of yeast glucose repression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1807:568–576
Disteche CM (2012) Dosage compensation of the sex chromosomes. Annu Rev Genet 46:537
Dobzhansky T (1973) Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution. Am Biol Teach 35:125–129
Dorus S, Evans PD, Wyckoff GJ, Choi SS, Lahn BT (2004) Rate of molecular evolution of the seminal protein gene SEMG2 correlates with levels of female promiscuity. Nat Genet 36:1326–1329
Dumollard R, Carroll J, Duchen MR, Campbell K, Swann K (2009) Mitochondrial function and redox state in mammalian embryos. Semin Cell Dev Biol 20:346–353
Duret L, Chureau C, Samain S, Weissenbach J, Avner P (2006) The Xist RNA gene evolved in eutherians by pseudogenization of a protein-coding gene. Science 312:1653–1655
Edger PP, Pires JC (2009) Gene and genome duplications: the impact of dosage-sensitivity on the fate of nuclear genes. Chromosom Res 17:699–717
Ehrlich PR, Raven PH (1964) Butterflies and plants: a study in coevolution. Evolution 18:586–608
Emerson JJ, Kaessmann H, Betran E, Long M (2004) Extensive gene traffic on the mammalian X chromosome. Science 303:537–540
Fisher RA (1931) The evolution of dominance. Biol Rev 6:345–368
Fitch WM, Leiter J, Li X, Palese P (1991) Positive Darwinian evolution in human influenza A viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:4270–4274
Freeling M (2009) Bias in plant gene content following different sorts of duplication: tandem, whole-genome, segmental, or by transposition. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60:433–453
Gardner DK (2015) Lactate production by the mammalian blastocyst: manipulating the microenvironment for uterine implantation and invasion? BioEssays 37:364–371
Gasper J, Swanson WJ (2006) Molecular population genetics of the gene encoding the human fertilization protein zonadhesin reveals rapid adaptive evolution. Am J Hum Genet 79:820–830
Gelbart ME, Kuroda MI (2009) Drosophila dosage compensation: a complex voyage to the X chromosome. Development 136:1399–1410
Gendron RL, Paradis H, Hsieh-Li HM, Lee DW, Potter SS, Markoff E (1997) Abnormal uterine stromal and glandular function associated with maternal reproductive defects in Hoxa-11 null mice. Biol Reprod 56:1097–1105
Gillott C (2003) Male accessory gland secretions: modulators of female reproductive physiology and behavior. Annu Rev Entomol 48:163–184
Gott AL, Hardy K, Winston RML, Leese HJ (1990) Non-invasive measurement of pyruvate and glucose uptake and lactate production by sigle human preimplantation embryos. Hum Reprod 5:104–108
Gould SJ (1983) The sinkstones of Oeningen. In: Gould SJ (ed) Hen’s teeth and horse’s toes: further reflections in natural history. Norton, New York, pp 94–106
Graves JAM (2006) Sex chromosome specialization and degeneration in mammals. Cell 124:901–914
Graves JAM (2008) Weird animal genomes and the evolution of vertebrate sex and sex chromosomes. Annu Rev Genet 42:565–586
Grayson P, Civetta A (2012) Positive selection and the evolution of izumo genes in mammals. Int J Evol Biol 2012:958164
Halder G, Callaerts P, Gehring WJ (1995) Induction of ectopic eyes by targeted expression of the eyeless gene in Drosophila. Science 267:1788–1792
Hamm D, Mautz BS, Wolfner MF, Aquadro CF, Swanson WJ (2007) Evidence of amino acid diversity-enhancing selection within humans and among primates at the candidate sperm-receptor gene PKDREJ. Am J Hum Genet 81:44–52
Heffer A, Pick L (2013) Conservation and variation in Hox genes: how insect models pioneered the evo-devo field. Annu Rev Entomol 58:161–179
Hellberg ME, Dennis AB, Arbour‐Reily P, Aagaard JE, Swanson WJ (2012) The Tegula tango: a coevolutionary dance of interacting, positively selected sperm and egg proteins. Evolution 66:1681–1694
Hoekstra HE, Hirschmann RJ, Bundey RA, Insel PA, Crossland JP (2006) A single amino acid mutation contributes to adaptive beach mouse color pattern. Science 313:101–104
Houghton FD (2006) Energy metabolism of the inner cell mass and trophectoderm of the mouse blastocyst. Differentiation 74:11–18
Houghton FD, Thompson JG, Kennedy CJ, Leese HJ (1996) Oxygen consumption and energy metabolism of the early mouse embryo. Mol Reprod Dev 44:476–485
Hsieh-Li HM, Witte DP, Weinstein M, Branford W, Li H, Small K, Potter SS (1995) Hoxa 11 structure, extensive antisense transcription, and function in male and female fertility. Development 121:1373–1385
Hughes AL, Nei M (1988) Pattern of nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class I loci reveals overdominant selection. Nature 335:167–170
Hughes AL, Green JA, Piontkivska H, Roberts RM (2003) Aspartic proteinase phylogeny and the origin of pregnancy-associated glycoproteins. Mol Biol Evol 20:1940–1945
Hughes JF, Skaletsky H, Pyntikova T, Graves TA, van Daalen SK, Minx PJ, Fulton RS, McGrath SD, Locke DP, Friedman C, Trask BJ, Mardis ER, Warren WC, Repping S, Rozen S, Wilson RK, Page DC (2010) Chimpanzee and human Y chromosomes are remarkably divergent in structure and gene content. Nature 463:536–539
Immler S, Moore HDM, Breed WG, Birkhead TR (2007) By hook or by crook? Morphometry, competition and cooperation in rodent sperm. PLoS ONE 2:e170
International Chicken Genome Sequencing Consortium (2004) Sequence and comparative analysis of the chicken genome provide unique perspectives on vertebrate evolution. Nature 432:695–716
Kaessmann H (2010) Origins, evolution, and phenotypic impact of new genes. Genome Res 20:1313–1326
Kelleher ES, Markow TA (2009) Duplication, selection and gene conversion in a Drosophila mojavensis female reproductive protein family. Genetics 181:1451–1465
Kelleher ES, Swanson WJ, Markow TA (2007) Gene duplication and adaptive evolution of digestive proteases in Drosophila arizonae female reproductive tracts. PLoS Genet 3:e148
Khil PP, Smirnova NA, Romanienko PJ, Camerini-Otero RD (2004) The mouse X chromosome is enriched for sex-biased genes not subject to selection by meiotic sex chromosome inactivation. Nat Genet 36:642–646
Kimura M (1983) The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kitano H (2002) Systems biology: a brief overview. Science 295:1662–1664
Korbel JO, Tirosh-Wagner T, Urban AE, Chen XN, Kasowski M, Dai L et al (2009) The genetic architecture of Down syndrome phenotypes revealed by high-resolution analysis of human segmental trisomies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:12031–12036
Krisher RL, Prather RS (2012) A role for the Warburg effect in preimplantation embryo development: metabolic modification to support rapid cell proliferation. Mol Reprod Dev 79:311–320
Lahn BT, Page DC (1997) Functional coherence of the human Y-chromosome. Science 278:675–680
Lander AD (2010) The edges of understanding. BMC Biol 8:40
Lehoczky JA, Innis JW (2008) Expanded HOXA13 polyalanine tracts in a monotreme. Evol Dev 10:433–438
Li W-H (1997) Molecular evolution. Sinauer, Sunderland
Li H-G, Ding X-F, Liao A-H, Kong X-B, Xiong C-L (2007) Expression of CatSper family transcripts in the mouse testis during post-natal development and human ejaculated spermatozoa: relationship to sperm motility. Mol Hum Reprod 13:299–306
Lim H, Ma L, Ma W-G, Maas RL, Dey SK (1999) Hoxa-10 regulates uterine stromal cell responsiveness to progesterone during implantation and decidualization in the mouse. Mol Endocrinol 13:1005–1017
Livernois A, Graves J, Waters P (2012) The origin and evolution of vertebrate sex chromosomes and dosage compensation. Heredity 108:50–58
Long M, Betran E, Thornton K, Wang W (2003) The origin of new genes: glimpses from the young and old. Nat Rev Genet 4:865–875
Lopes AS, Larsen LH, Ramsing N, Løvendahl P, Räty M, Peippo J, Greve T, Callesen H (2005) Respiration rates of individual bovine in vitro-produced embryos measured with a novel, non-invasive and highly sensitive microsensor system. Reproduction 130:669–679
Lupski JR (2007) Genomic rearrangements and sporadic disease. Nat Genet 39:S43–S47
Lynch VJ, Roth JJ, Takahashi K, Dunn CW, Nonaka DF, Stopper GF, Wagner GP (2004) Adaptive evolution of HoxA–11 and HoxA–13 at the origin of the uterus in mammals. Proc Biol Sci 271:2201-2207
Lynch VJ, Tanzer A, Wang Y, Leung FC, Gellersen B, Emera D, Wagner GP (2008) Adaptive changes in the transcription factor HoxA-11 are essential for the evolution of pregnancy in mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:14928–14933
Lyng R, Shur BD (2009) Mouse oviduct-specific glycoprotein is an egg-associated ZP3-independent sperm-adhesion ligand. J Cell Sci 122:3894–3906
Makalowski W, Boguski MS (1998) Evolutionary parameters of the transcribed mammalian genome: an analysis of 2820 orthologous rodent and human sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:9407–9412
Makino T, McLysaght A (2010) Ohnologs in the human genome are dosage balanced and frequently associated with disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:9270–9274
Merico A, Sulo P, Piškur J, Compagno C (2007) Fermentative lifestyle in yeasts belonging to the Saccharomyces complex. FEBS J 274:976–989
Metz EC, Robles-Sikisaka R, Vacquier VD (1998) Nonsynonymous substitution in abalone sperm fertilization genes exceeds substitution in introns and mitochondrial DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:10676–10681
Miller GT, Pitnick S (2002) Sperm-female coevolution in Drosophila. Science 298:1230–1233
Mortlock DP, Innis JW (1997) Mutation of HOXA13 in hand-foot-genital syndrome. Nat Genet 15:179–180
Mueller JL, Ravi Ram K, McGraw LA, Bloch Qazi MC, Siggia ED, Clark AG, Aquadro CF, Wolfner MF (2005) Cross-species comparison of Drosophila male accessory gland protein genes. Genetics 171:131–143
Muller HJ (1914) A gene for the fourth chromosome of Drosophila. J Exp Zool 17:325–336
Murphy WJ, Pearks Wilkerson AJ, Raudsepp T, Agarwala R, Schäffer AA, Stanyon R, Chowdhary BP (2006) Novel gene acquisition on carnivore Y chromosomes. PLoS Genet 2:e43
Nielsen R (2005) Molecular signatures of natural selection. Annu Rev Genet 39:197–218
Orth JD, Thiele I, Palsson BØ (2010) What is flux balance analysis? Nat Biotechnol 28:245–248
Ovádi J, Orosz F, Hollán S (2004) Functional aspects of cellular microcompartmentation in the development of neurodegeneration: mutation induced aberrant protein-protein associations. Mol Cell Biochem 256–257:83–93
Papp B, Pal C, Hurst LD (2003) Dosage sensitivity and the evolution of gene families in yeast. Nature 424:194–197
Parisi M, Nuttall R, Naiman D, Bouffard G, Malley J, Andrews J, Eastman S, Oliver B (2003) Paucity of genes on the Drosophila X chromosome showing male-biased expression. Science 299:697–700
Paterson S, Vogwill T, Buckling A, Benmayor R, Spiers AJ, Thomson NR, Quail M, Smith F, Walker D, Libberton B, Fenton A, Hall N, Brockhurst MA (2010) Antagonistic coevolution accelerates molecular evolution. Nature 464:275–278
Peirce E, Breed W (2001) A comparative study of sperm production in two species of Australian arid zone rodents (Pseudomys australis, Notomys alexis) with marked differences in testis size. Reproduction 121:239–247
Pérez-Bercoff Å, McLysaght A, Conant GC (2011) Patterns of indirect protein interactions suggest a spatial organization to metabolism. Mol BioSyst 7:3056–3064
Pfeiffer T, Schuster S (2005) Game-theoretical approaches to studying the evolution of biochemical systems. Trends Biochem Sci 30:20–25
Pfeiffer T, Schuster S, Bonhoeffer S (2001) Cooperation and competition in the evolution of ATP-producing pathways. Science 292:504–507
Piškur J, Rozpedowska E, Polakova S, Merico A, Compagno C (2006) How did Saccharomyces evolve to become a good brewer? Trends Genet 22:183–186
Podlaha O, Zhang J (2003) Positive selection on protein-length in the evolution of a primate sperm ion channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:12241–12246
Podlaha O, Webb DM, Tucker PK, Zhang J (2005) Positive selection for indel substitutions in the rodent sperm protein catsper1. Mol Biol Evol 22:1845–1852
Pronk JT, Yde Steensma H, Van Dijken JP (1996) Pyruvate metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 12:1607–1633
Ramm SA, Parker GA, Stockley P (2005) Sperm competition and the evolution of male reproductive anatomy in rodents. Proc Biol Sci 272:949–955
Ramm SA, Oliver PL, Ponting CP, Stockley P, Emes RD (2008) Sexual selection and the adaptive evolution of mammalian ejaculate proteins. Mol Biol Evol 25:207–219
Ranz JM, Castillo-Davis CI, Meiklejohn CD, Hartl DL (2003) Sex-dependent gene expression and evolution of the Drosophila transcriptome. Science 300:1742–1745
Redel BK, Brown AN, Spate LD, Whitworth KM, Green JA, Prather RS (2012) Glycolysis in preimplantation development is partially controlled by the Warburg effect. Mol Reprod Dev 79:262–271
Rice WR (1984) Sex chromosomes and the evolution of sexual dimorphism. Evolution 38:735–742
Sakagami N, Nishida K, Akiyama K, Abe H, Hoshi H, Suzuki C, Yoshioka K (2015) Relationships between oxygen consumption rate, viability, and subsequent development of in vivo-derived porcine embryos. Theriogenology 83:14–20
Satouh Y, Inoue N, Ikawa M, Okabe M (2012) Visualization of the moment of mouse sperm–egg fusion and dynamic localization of IZUMO1. J Cell Sci 125:4985–4990
Schulte-Hostedde AI, Millar JS (2004) Intraspecific variation of testis size and sperm length in the yellow-pine chipmunk (Tamias amoenus): implications for sperm competition and reproductive success. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 55:272–277
Scotti M (2012) Role of the homeodomain transcription factor Hoxa13 in embryonic development and formation of extra-embryonic structures. Thèses et mémoires électroniques de l’Université de Montréal. http://hdl.handle.net/1866/7053
Seshagiri PB, Bavister BD (1991) Glucose and phosphate inhibit respiration and oxidative metabolism in cultured hamster eight-cell embryos: evidence for the “Crabtree effect”. Mol Reprod Dev 30:105–111
Shaut CAE, Keene DR, Sorensen LK, Li DY, Stadler HS (2008) HOXA13 is essential for placental vascular patterning and labyrinth endothelial specification. PLoS Genet 4:e1000073
Shlomi T, Benyamini T, Gottlieb E, Sharan R, Ruppin E (2011) Genome-scale metabolic modeling elucidates the role of proliferative adaptation in causing the Warburg effect. PLoS Comput Biol 7:e1002018
Simmons LW, Fitzpatrick JL (2012) Sperm wars and the evolution of male fertility. Reproduction 144:519–534
Smith NGC, Eyre-Walker A (2002) Adaptive protein evolution in Drosophila. Nature 415:1022–1024
Sturmey R, Leese H (2003) Energy metabolism in pig oocytes and early embryos. Reproduction 126:197–204
Swanson WJ, Vacquier VD (2002) The rapid evolution of reproductive proteins. Nat Rev Genet 3:137–144
Swanson WJ, Yang Z, Wolfner MF, Aquadro CF (2001) Positive Darwinian selection drives the evolution of several female reproductive proteins in mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:2509–2514
Swanson WJ, Nielsen R, Yang Q (2003) Pervasive adaptive evolution in mammalian fertilization proteins. Mol Biol Evol 20:18–20
Thiele I, Swainston N, Fleming RM, Hoppe A, Sahoo S, Aurich MK et al (2013) A community-driven global reconstruction of human metabolism. Nat Biotechnol 31:419–425
Thompson JG, Partridge RJ, Houghton FD, Cox CI, Leese HJ (1996) Oxygen uptake and carbohydrate metabolism by in vitro derived bovine embryos. J Reprod Fertil 106:299–306
Torgerson DG, Kulathinal RJ, Singh RS (2002) Mammalian sperm proteins are rapidly evolving: evidence of positive selection in functionally diverse genes. Mol Biol Evol 19:1973–1980
Trimarchi JR, Liu L, Porterfield DM, Smith PJS, Keefe DL (2000) Oxidative phosphorylation-dependent and -independent oxygen consumption by individual preimplantation mouse embryos. Biol Reprod 62:1866–1874
Tsaur SC, Ting CT, Wu CI (1998) Positive selection driving the evolution of a gene of male reproduction, Acp26aa, of Drosophila. II. Divergence versus polymorphism. Mol Biol Evol 15:1040–1046
Turner LM, Hoekstra HE (2006) Adaptive evolution of fertilization proteins within a genus: variation in ZP2 and ZP3 in deer mice (Peromyscus). Mol Biol Evol 23:1656–1669
Turner LM, Hoekstra HE (2008a) Causes and consequences of the evolution of reproductive proteins. Int J Dev Biol 52:769–780
Turner LM, Hoekstra HE (2008b) Reproductive protein evolution within and between species: maintenance of divergent ZP3 alleles in Peromyscus. Mol Ecol 17:2616–2628
Utsunomiya T, Goto K, Nasu M, Kumasako Y, Araki Y, Yokoo T et al (2008) Evaluating the quality of human embryos with a measurement of oxygen consumption by scanning electrochemical microscopy. J Mamm Ova Res 25:2–7
van Hoek MJ, Hogeweg P (2009) Metabolic adaptation after whole genome duplication. Mol Biol Evol 26:2441–2453
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB (2009) Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 324:1029–1033
Varum S, Rodrigues AS, Moura MB, Momcilovic O, Easley CA 4th, Ramalho-Santos J, Van Houten B, Schatten G (2011) Energy metabolism in human pluripotent stem cells and their differentiated counterparts. PLoS ONE 6:e20914
Veitia RA, Bottani S, Birchler JA (2013) Gene dosage effects: nonlinearities, genetic interactions, and dosage compensation. Trends Genet 29:385–393
Vibranovski MD, Zhang Y, Long M (2009) General gene movement off the X chromosome in the Drosophila genus. Genome Res 19:897–903
Wagner GP (1989) The biological homology concept. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 20:51–69
Warburg O (1956) On the origin of cancer cells. Science 123:309–314
Warot X, Fromental-Ramain C, Fraulob V, Chambon P, Dollé P (1997) Gene dosage-dependent effects of the Hoxa-13 and Hoxd-13 mutations on morphogenesis of the terminal parts of the digestive and urogenital tracts. Development 124:4781–4791
Waters PD, Wallis MC, Graves JAM (2007) Mammalian sex—origin and evolution of the Y chromosome and SRY. Semin Cell Dev Biol 18:389–400
West GB, Brown JH, Enquist BJ (1999) The fourth dimension of life: fractal geometry and allometric scaling of organisms. Science 284:1677–1679
West GB, Woodruff WH, Brown JH (2002) Allometric scaling of metabolic rate from molecules and mitochondria to cells and mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99 (Suppl 1):2473–2478
Wildman DE, Chen C, Erez O, Grossman LI, Goodman M, Romero R (2006) Evolution of the mammalian placenta revealed by phylogenetic analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:3203–3208
Wiseman FK, Alford KA, Tybulewicz VL, Fisher EM (2009) Down syndrome—recent progress and future prospects. Hum Mol Genet 18:R75–R83
Wolfner MF (1997) Tokens of love: functions and regulation of Drosophila male accessory gland products. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 27:179–192
Wong A (2011) The molecular evolution of animal reproductive tract proteins: what have we learned from mating-system comparisons? Int J Evol Biol 2011:908735
Wong KHH, Wintch HD, Capecchi MR (2004) Hoxa11 regulates stromal cell death and proliferation during neonatal uterine development. Mol Endocrinol 18:184–193
Yang Z (1998) Likelihood ratio tests for detecting positive selection and application to primate lysozyme evolution. Mol Biol Evol 15:568–573
Yang Z, Nielsen R, Goldman N, Pedersen A-MK (2000a) Codon-substitution models for heterogeneous selection pressure at amino acid sites. Genetics 155:431–449
Yang Z, Swanson WJ, Vacquier VD (2000b) Maximum likelihood analysis of molecular adaptation in abalone sperm lysin reveals variable selective pressures among lineages and sites. Mol Biol Evol 17:1446–1455
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Bethany R. Mordhorst and Miranda L. Wilson contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mordhorst, B.R., Wilson, M.L. & Conant, G.C. Some assembly required: evolutionary and systems perspectives on the mammalian reproductive system. Cell Tissue Res 363, 267–278 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2257-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2257-x