Abstract
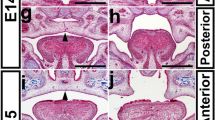
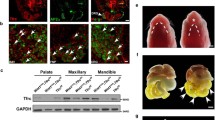
Cleft palate is among the most common craniofacial congenital anomalies. Up to 30 % of patients with cleft palate also have associated cardiac and vascular defects. VEGFa, a critical growth factor involved in multiple developmental processes including angiogenesis and ossification, is also required for palate development. Conditional deletion of VEGFa in cranial neural crest (CNC) cells using Wnt1-Cre (VEGFaCKO) resulted in cleft palate in mice. The phenotype included reduced proliferation of cells within the palatal shelves, abnormal palatal shelf elongation and elevation, and the inability to undergo fusion. Vascularization of the VEGFaCKO palatal shelves was greatly reduced, suggesting a non-cell autonomous role of VEGFa signaling from the CNC-derived cells to the endothelium during vessel formation. Defective vascular development was coupled with deficient intramembranous ossification of maxillary and palatal mesenchyme. In vitro assessment of CNC-derived palatal mesenchymal cells from VEGFaCKO mice demonstrated normal ossification after BMP2 stimulation, suggesting that inadequate expression of Bmp2 in VEGFaCKO mice was, in part, responsible for reduced ossification. Taken together, these data demonstrate that VEGFa produced in the CNC-derived mesenchyme drives proliferation, vascularization, and ossification, all of which are critical for palate development.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baek JA, Lan Y, Liu H, Maltby KM, Mishina Y, Jiang R (2011) Bmpr1a signaling plays critical roles in palatal shelf growth and palatal bone formation. Dev Biol 350:520–531
Chai Y, Maxson RE Jr (2006) Recent advances in craniofacial morphogenesis. Dev Dyn 235:2353–2375
Chen G, Deng C, Li YP (2012) TGF-beta and BMP signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int J Biol Sci 8:272–288
Chua CC, Hamdy RC, Chua BH (2000) Mechanism of transforming growth factor-beta1-induced expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in murine osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1497:69–76
Cohen SR, Corrigan M, Wilmot J, Trotman CA (1995) Cumulative operative procedures in patients aged 14 years and older with unilateral or bilateral cleft lip and palate. Plast Reconstr Surg 96:267–271
Cucina A, Borrelli V, Randone B, Coluccia P, Sapienza P, Cavallaro A (2003) Vascular endothelial growth factor increases the migration and proliferation of smooth muscle cells through the mediation of growth factors released by endothelial cells. J Surg Res 109:16–23
Dickson MC, Martin JS, Cousins FM, Kulkarni AB, Karlsson S, Akhurst RJ (1995) Defective haematopoiesis and vasculogenesis in transforming growth factor-beta 1 knock out mice. Development 121:1845–1854
Doetschman T, Georgieva T, Li H, Reed TD, Grisham C, Friel J, Estabrook MA, Gard C, Sanford LP, Azhar M (2012) Generation of mice with a conditional allele for the transforming growth factor beta3 gene. Genesis 50:59–66
Dudas M, Kim J, Li WY, Nagy A, Larsson J, Karlsson S, Chai Y, Kaartinen V (2006) Epithelial and ectomesenchymal role of the type I TGF-beta receptor ALK5 during facial morphogenesis and palatal fusion. Dev Biol 296:298–314
Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J (2003) The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med 9:669–676
Fiedler J, Roderer G, Gunther KP, Brenner RE (2002) BMP-2, BMP-4, and PDGF-bb stimulate chemotactic migration of primary human mesenchymal progenitor cells. J Cell Biochem 87:305–312
Fiedler J, Leucht F, Waltenberger J, Dehio C, Brenner RE (2005) VEGF-A and PlGF-1 stimulate chemotactic migration of human mesenchymal progenitor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334:561–568
Fromigue O, Marie PJ, Lomri A (1998) Bone morphogenetic protein-2 and transforming growth factor-beta2 interact to modulate human bone marrow stromal cell proliferation and differentiation. J Cell Biochem 68:411–426
Gerber HP, Hillan KJ, Ryan AM, Kowalski J, Keller GA, Rangell L, Wright BD, Radtke F, Aguet M, Ferrara N (1999) VEGF is required for growth and survival in neonatal mice. Development 126:1149–1159
Gerhardt H, Golding M, Fruttiger M, Ruhrberg C, Lundkvist A, Abramsson A, Jeltsch M, Mitchell C, Alitalo K, Shima D et al (2003) VEGF guides angiogenic sprouting utilizing endothelial tip cell filopodia. J Cell Biol 161:1163–1177
Goudy S, Law A, Sanchez G, Baldwin HS, Brown C (2010) Tbx1 is necessary for palatal elongation and elevation. Mech Dev 127:292–300
Gritli-Linde A (2007) Molecular control of secondary palate development. Dev Biol 301:309–326
Grosskreutz CL, Anand-Apte B, Duplaa C, Quinn TP, Terman BI, Zetter B, D’Amore PA (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor-induced migration of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro. Microvasc Res 58:128–136
Haigh JJ (2008) Role of VEGF in organogenesis. Organogenesis 4:247–256
Hill CR, Sanchez NS, Love JD, Arrieta JA, Hong CC, Brown CB, Austin AF, Barnett JV (2012) BMP2 signals loss of epithelial character in epicardial cells but requires the Type III TGFbeta receptor to promote invasion. Cell Signal 24:1012–1022
Hill CR, Yuasa M, Schoenecker J, Goudy SL (2014) Jagged1 is essential for osteoblast development during maxillary ossification. Bone 62:10–21
Holderfield MT, Hughes CC (2008) Crosstalk between vascular endothelial growth factor, notch, and transforming growth factor-beta in vascular morphogenesis. Circ Res 102:637–652
Humphreys R, Zheng W, Prince LS, Qu X, Brown C, Loomes K, Huppert SS, Baldwin S, Goudy S (2012) Cranial neural crest ablation of Jagged1 recapitulates the craniofacial phenotype of Alagille syndrome patients. Hum Mol Genet 21:1374–1383
Ito Y, Yeo JY, Chytil A, Han J, Bringas P Jr, Nakajima A, Shuler CF, Moses HL, Chai Y (2003) Conditional inactivation of Tgfbr2 in cranial neural crest causes cleft palate and calvaria defects. Development 130:5269–5280
Iwata J, Hacia JG, Suzuki A, Sanchez-Lara PA, Urata M, Chai Y (2012) Modulation of noncanonical TGF-beta signaling prevents cleft palate in Tgfbr2 mutant mice. J Clin Invest 122:873–885
Kuroda S, Sumner DR, Virdi AS (2012) Effects of TGF-beta1 and VEGF-A transgenes on the osteogenic potential of bone marrow stromal cells in vitro and in vivo. J Tissue Eng 3:2041731412459745
Larsson J, Goumans MJ, Sjostrand LJ, van Rooijen MA, Ward D, Leveen P, Xu X, ten Dijke P, Mummery CL, Karlsson S (2001) Abnormal angiogenesis but intact hematopoietic potential in TGF-beta type I receptor-deficient mice. EMBO J 20:1663–1673
Li L, Wang Y, Lin M, Yuan G, Yang G, Zheng Y, Chen Y (2013) Augmented BMPRIA-mediated BMP signaling in cranial neural crest lineage leads to cleft palate formation and delayed tooth differentiation. PLoS ONE 8:e66107
Liu D, Wang J, Kinzel B, Mueller M, Mao X, Valdez R, Liu Y, Li E (2007) Dosage-dependent requirement of BMP type II receptor for maintenance of vascular integrity. Blood 110:1502–1510
Loeys BL, Chen J, Neptune ER, Judge DP, Podowski M, Holm T, Meyers J, Leitch CC, Katsanis N, Sharifi N et al (2005) A syndrome of altered cardiovascular, craniofacial, neurocognitive and skeletal development caused by mutations in TGFBR1 or TGFBR2. Nat Genet 37:275–281
Maes C, Carmeliet P, Moermans K, Stockmans I, Smets N, Collen D, Bouillon R, Carmeliet G (2002) Impaired angiogenesis and endochondral bone formation in mice lacking the vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms VEGF164 and VEGF188. Mech Dev 111:61–73
Maes C, Goossens S, Bartunkova S, Drogat B, Coenegrachts L, Stockmans I, Moermans K, Nyabi O, Haigh K, Naessens M et al (2010) Increased skeletal VEGF enhances beta-catenin activity and results in excessively ossified bones. EMBO J 29:424–441
Matsubara H, Hogan DE, Morgan EF, Mortlock DP, Einhorn TA, Gerstenfeld LC (2012) Vascular tissues are a primary source of BMP2 expression during bone formation induced by distraction osteogenesis. Bone 51:168–180
Mayr-Wohlfart U, Waltenberger J, Hausser H, Kessler S, Gunther KP, Dehio C, Puhl W, Brenner RE (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates chemotactic migration of primary human osteoblasts. Bone 30:472–477
Mizutani J, Tokuda H, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Kato K, Kondo A, Natsume H, Kozawa O, Otsuka T (2012) Involvement of AMP-activated protein kinase in TGF-beta-stimulated VEGF synthesis in osteoblasts. Int J Mol Med 29:550–556
Murray JC, Schutte BC (2004) Cleft palate: players, pathways, and pursuits. J Clin Invest 113:1676–1678
Oshima M, Oshima H, Taketo MM (1996) TGF-beta receptor type II deficiency results in defects of yolk sac hematopoiesis and vasculogenesis. Dev Biol 179:297–302
Owusu JA, Liu M, Sidman JD, Scott AR (2013) Does the type of cleft palate contribute to the need for secondary surgery? A national perspective. Laryngoscope 123:2387–2391
Rice R, Spencer-Dene B, Connor EC, Gritli-Linde A, McMahon AP, Dickson C, Thesleff I, Rice DP (2004) Disruption of Fgf10/Fgfr2b-coordinated epithelial-mesenchymal interactions causes cleft palate. J Clin Invest 113:1692–1700
Ruhrberg C, Gerhardt H, Golding M, Watson R, Ioannidou S, Fujisawa H, Betsholtz C, Shima DT (2002) Spatially restricted patterning cues provided by heparin-binding VEGF-A control blood vessel branching morphogenesis. Genes Dev 16:2684–2698
Sanford LP, Ormsby I, Gittenberger-de Groot AC, Sariola H, Friedman R, Boivin GP, Cardell EL, Doetschman T (1997) TGFbeta2 knockout mice have multiple developmental defects that are non-overlapping with other TGFbeta knockout phenotypes. Development 124:2659–2670
Schutte BC, Murray JC (1999) The many faces and factors of orofacial clefts. Hum Mol Genet 8:1853–1859
Song X, Liu S, Qu X, Hu Y, Zhang X, Wang T, Wei F (2011) BMP2 and VEGF promote angiogenesis but retard terminal differentiation of osteoblasts in bone regeneration by up-regulating Id1. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 43:796–804
Stalmans I, Lambrechts D, De Smet F, Jansen S, Wang J, Maity S, Kneer P, von der Ohe M, Swillen A, Maes C et al (2003) VEGF: a modifier of the del22q11 (DiGeorge) syndrome? Nat Med 9:173–182
Wyse RK, Mars M, al-Mahdawi S, Russell-Eggitt IM, Blake KD (1990) Congenital heart anomalies in patients with clefts of the lip and/or palate. Cleft Palate J 27:258–264, discussion 264–255
Yoshida T, Vivatbutsiri P, Morriss-Kay G, Saga Y, Iseki S (2008) Cell lineage in mammalian craniofacial mesenchyme. Mech Dev 125:797–808
Zelzer E, Olsen BR (2005) Multiple roles of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in skeletal development, growth, and repair. Curr Top Dev Biol 65:169–187
Zelzer E, McLean W, Ng YS, Fukai N, Reginato AM, Lovejoy S, D’Amore PA, Olsen BR (2002) Skeletal defects in VEGF(120/120) mice reveal multiple roles for VEGF in skeletogenesis. Development 129:1893–1904
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 4507 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hill, C., Jacobs, B., Kennedy, L. et al. Cranial neural crest deletion of VEGFa causes cleft palate with aberrant vascular and bone development. Cell Tissue Res 361, 711–722 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2150-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-015-2150-7