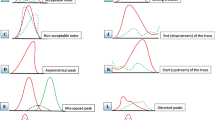
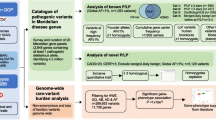
Abstract
Recently, the American College of Medical Genetics (ACMG) recommended the return of actionable secondary findings detected from clinical sequencing. The reported frequency of secondary findings in Asian populations were highly variable and it is unclear whether the uniformity in coverage offered by whole-genome sequencing (WGS) may impact the estimate. In this analysis, we aimed to refine the rate of secondary findings on East Asians through a large-scale WGS study. We classified 1256 protein-altering or splicing variants of the 59 actionable genes detected from WGS of 954 East Asians in strict accordance with the ACMG and the Association for Molecular Pathology guidelines. A total of 21 pathogenic or likely pathogenic variants were detected in 24 of the 954 East Asian genomes with an estimate of 2.5% of East Asians carrying actionable variants. Although the overall estimate of secondary findings was consistent with those reported for non-East Asian ethnicities, genetic and allelic heterogeneity was observed. WGS offers a wider breadth of coverage over WES, which highlights the need to further investigate the variable sensitivity of WES and WGS in the detection of secondary findings. Identifying secondary findings in populations underrepresented in previous genetic literature might improve variant interpretation and has a profound impact on local decision-making with regard to the cost-effectiveness of returning the secondary findings from clinical sequencing.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amendola LM, Dorschner MO, Robertson PD, Salama JS, Hart R, Shirts BH, Murray ML, Tokita MJ, Gallego CJ, Kim DS, Bennett JT, Crosslin DR, Ranchalis J, Jones KL, Rosenthal EA, Jarvik ER, Itsara A, Turner EH, Herman DS, Schleit J, Burt A, Jamal SM, Abrudan JL, Johnson AD, Conlin LK, Dulik MC, Santani A, Metterville DR, Kelly M, Foreman AK, Lee K, Taylor KD, Guo X, Crooks K, Kiedrowski LA, Raffel LJ, Gordon O, Machini K, Desnick RJ, Biesecker LG, Lubitz SA, Mulchandani S, Cooper GM, Joffe S, Richards CS, Yang Y, Rotter JI, Rich SS, O’Donnell CJ, Berg JS, Spinner NB, Evans JP, Fullerton SM, Leppig KA, Bennett RL, Bird T, Sybert VP, Grady WM, Tabor HK, Kim JH, Bamshad MJ, Wilfond B, Motulsky AG, Scott CR, Pritchard CC, Walsh TD, Burke W, Raskind WH, Byers P, Hisama FM, Rehm H, Nickerson DA, Jarvik GP (2015) Actionable exomic incidental findings in 6503 participants: challenges of variant classification. Genome Res 25(3):305–315
Chiou KR, Charng MJ (2016) Genetic diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia in Han Chinese. J Clin Lipidol 10(3):490–496
DePristo MA, Banks E, Poplin R, Garimella KV, Maguire JR, Hartl C, Philippakis AA, del Angel G, Rivas MA, Hanna M, McKenna A, Fennell TJ, Kernytsky AM, Sivachenko AY, Cibulskis K, Gabriel SB, Altshuler D, Daly MJ (2011) A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat Genet 43(5):491–498
Dewey FE, Murray MF, Overton JD, Habegger L, Leader JB, Fetterolf SN, O’Dushlaine C, Van Hout CV, Staples J, Gonzaga-Jauregui C, Metpally R, Pendergrass SA, Giovanni MA, Kirchner HL, Balasubramanian S, Abul-Husn NS, Hartzel DN, Lavage DR, Kost KA, Packer JS, Lopez AE, Penn J, Mukherjee S, Gosalia N, Kanagaraj M, Li AH, Mitnaul LJ, Adams LJ, Person TN, Praveen K, Marcketta A, Lebo MS, Austin-Tse CA, Mason-Suares HM, Bruse S, Mellis S, Phillips R, Stahl N, Murphy A, Economides A, Skelding KA, Still CD, Elmore JR, Borecki IB, Yancopoulos GD, Davis FD, Faucett WA, Gottesman O, Ritchie MD, Shuldiner AR, Reid JG, Ledbetter DH, Baras A, Carey DJ (2016) Distribution and clinical impact of functional variants in 50,726 whole-exome sequences from the DiscovEHR study. Science 354(6319):aaf6814
Green RC, Berg JS, Grody WW, Kalia SS, Korf BR, Martin CL, McGuire AL, Nussbaum RL, O’Daniel JM, Ormond KE, Rehm HL, Watson MS, Williams MS, Biesecker LG, G. American College of Medical and Genomics, (2013) ACMG recommendations for reporting of incidental findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing. Genet Med 15(7):565–574
Jamuar SS, Kuan JL, Brett M, Tiang Z, Tan WL, Lim JY, Liew WK, Javed A, Liew WK, Law HY, Tan ES, Lai A, Ng I, Teo YY, Venkatesh B, Reversade B, Tan EC, Foo R (2016) Incidentalome from genomic sequencing: a barrier to personalized medicine? EBioMedicine 5:211–216
Jang MA, Lee SH, Kim N, Ki CS (2015) Frequency and spectrum of actionable pathogenic secondary findings in 196 Korean exomes. Genet Med 17(12):1007–1011
Kalia SS, Adelman K, Bale SJ, Chung WK, Eng C, Evans JP, Herman GE, Hufnagel SB, Klein TE, Korf BR, McKelvey KD, Ormond KE, Richards CS, Vlangos CN, Watson M, Martin CL, Miller DT (2017) Recommendations for reporting of secondary findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing, 2016 update (ACMG SF v2.0): a policy statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Genet Med 19(2):249–255
Kwak SH, Chae J, Choi S, Kim MJ, Choi M, Chae JH, Cho EH, Hwang TJ, Jang SS, Kim JI, Park KS, Bang YJ (2017) Findings of a 1303 Korean whole-exome sequencing study. Exp Mol Med 49(7):e356
Kwong A, Ng EK, Wong CL, Law FB, Au T, Wong HN, Kurian AW, West DW, Ford JM, Ma ES (2012) Identification of BRCA1/2 founder mutations in Southern Chinese breast cancer patients using gene sequencing and high resolution DNA melting analysis. PLoS One 7(9):e43994
Li M, Li J, Li MJ, Pan Z, Hsu JS, Liu DJ, Zhan X, Wang J, Song Y, Sham PC (2017) Robust and rapid algorithms facilitate large-scale whole genome sequencing downstream analysis in an integrative framework. Nucleic Acids Res 45(9):e75
Lionel AC, Costain G, Monfared N, Walker S, Reuter MS, Hosseini SM, Thiruvahindrapuram B, Merico D, Jobling R, Nalpathamkalam T, Pellecchia G, Sung WWL, Wang Z, Bikangaga P, Boelman C, Carter MT, Cordeiro D, Cytrynbaum C, Dell SD, Dhir P, Dowling JJ, Heon E, Hewson S, Hiraki L, Inbar-Feigenberg M, Klatt R, Kronick J, Laxer RM, Licht C, MacDonald H, Mercimek-Andrews S, Mendoza-Londono R, Piscione T, Schneider R, Schulze A, Silverman E, Siriwardena K, Snead OC, Sondheimer N, Sutherland J, Vincent A, Wasserman JD, Weksberg R, Shuman C, Carew C, Szego MJ, Hayeems RZ, Basran R, Stavropoulos DJ, Ray PN, Bowdin S, Meyn MS, Cohn RD, Scherer SW, Marshall CR (2017) Improved diagnostic yield compared with targeted gene sequencing panels suggests a role for whole-genome sequencing as a first-tier genetic test. Genet Med
Meienberg J, Zerjavic K, Keller I, Okoniewski M, Patrignani A, Ludin K, Xu Z, Steinmann B, Carrel T, Rothlisberger B, Schlapbach R, Bruggmann R, Matyas G (2015) New insights into the performance of human whole-exome capture platforms. Nucleic Acids Res 43(11):e76
Meienberg J, Bruggmann R, Oexle K, Matyas G (2016) Clinical sequencing: is WGS the better WES? Hum Genet 135(3):359–362
Natarajan P, Gold NB, Bick AG, McLaughlin H, Kraft P, Rehm HL, Peloso GM, Wilson JG, Correa A, Seidman JG, Seidman CE, Kathiresan S, Green RC (2016) Aggregate penetrance of genomic variants for actionable disorders in European and African Americans. Sci Transl Med 8(364):364ra151
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, Voelkerding K, Rehm HL, Committee ALQA (2015) Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med 17(5):405–424
Stavropoulos DJ, Merico D, Jobling R, Bowdin S, Monfared N, Thiruvahindrapuram B, Nalpathamkalam T, Pellecchia G, Yuen RKC, Szego MJ, Hayeems RZ, Shaul RZ, Brudno M, Girdea M, Frey B, Alipanahi B, Ahmed S, Babul-Hirji R, Porras RB, Carter MB, Chad L, Chaudhry A, Chitayat D, Doust SJ, Cytrynbaum C, Dupuis L, Ejaz R, Fishman L, Guerin A, Hashemi B, Helal M, Hewson S, Inbar-Feigenberg M, Kannu P, Karp N, Kim R, Kronick J, Liston E, MacDonald H, Mercimek-Mahmutoglu S, Mendoza-Londono R, Nasr E, Nimmo G, N. Parkinson, N. Quercia, J. Raiman, M. Roifman, A. Schulze, A. Shugar, C. Shuman, P. Sinajon, K. Siriwardena, R. Weksberg, G. Yoon, C. Carew, R. Erickson, R. A. Leach, R. Klein, P. N. Ray, M. S. Meyn, S. W. Scherer, R. D. Cohn and C. R. Marshall (2016). “Whole Genome Sequencing Expands Diagnostic Utility and Improves Clinical Management in Pediatric Medicine. NPJ Genom Med 1
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by: Theme-based Research scheme T12C-714/14-R to P.T., Human Medical Research Fund (HMRF) 02131866 and 01121516 to M.M.G.B and 0451966 to C.S.T. and Seed Fund for Basic Research of The University of Hong Kong 201606159005 to C.S.T.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, C.Sm., Dattani, S., So, Mt. et al. Actionable secondary findings from whole-genome sequencing of 954 East Asians. Hum Genet 137, 31–37 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-017-1852-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-017-1852-1