Abstract
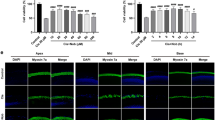
This study aimed to investigate the protective effects of PPARγ/CPT-1 regulation on cisplatin-induced cochlear hair cell injury. The viability, apoptosis and mitochondrial membrane potential of cisplatin-induced HEI-OC1 cells were determined by CCK-8 assay, TUNEL and JC-1 staining, respectively. The oxidative stress and lipid metabolism were detected by the assay kits of MDA, ROS, SOD, CAT, TG and FFA. The transfection efficiency of overexpression (OV)-PPARG and OV-CPT1A was examined by RT-qPCR and the expressions of apoptosis- and lipid metabolism-related proteins were detected by western blot. As a result, cisplatin with varying concentrations (5, 10, 30 μM) suppressed the viability, promoted the apoptosis and hindered the mitochondrial function of HEI-OC1 cells, accompanied with up-regulated expressions of Bax and cleaved caspase-3 and down-regulated expression of Bcl-2. The oxidative stress was aggravated and lipid metabolism was inhibited by cisplatin (5, 10, 30 μM) induction, evidenced by the increased levels of MDA, ROS, TG, FFA and the decreased levels of SOD and CAT. Overexpression of PPARG or CPT1A could improve the viability, mitochondrial function, lipid metabolism and suppress the oxidative stress and apoptosis of cisplatin-induced HEI-OC1 cells. In conclusion, up-regulation of PPARG or CPT1A ameliorated cochlear hair cell injury by improving cellular lipid metabolism and inhibiting oxidative stress.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Change history
18 April 2023
Figure 1 has been updated.
25 April 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-023-02017-1
References
Aboonabi A, Aboonabi A (2020) Anthocyanins reduce inflammation and improve glucose and lipid metabolism associated with inhibiting nuclear factor-kappaB activation and increasing PPAR-γ gene expression in metabolic syndrome subjects. Free Radic Biol Med 150:30–39
Bock FJ, Tait SWG (2020) Mitochondria as multifaceted regulators of cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21:85–100
Brock PR, Maibach R, Childs M et al (2018) Sodium thiosulfate for protection from cisplatin-induced hearing loss. N Engl J Med 378:2376–2385
Buendia I, Michalska P, Navarro E, Gameiro I, Egea J, León R (2016) Nrf2-ARE pathway: an emerging target against oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol Ther 157:84–104
Calder PC (2013) Long chain fatty acids and gene expression in inflammation and immunity. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 16:425–433
Clerici WJ, Dimartino DL, Prasad MR (1995) Direct effects of reactive oxygen species on cochlear outer hair cell shape in vitro. Hear Res 84:30–40
Djordjević VB (2004) Free radicals in cell biology. Int Rev Cytol 237:57–89
Du Z, Yang Y, Hu Y et al (2012) A long-term high-fat diet increases oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and apoptosis in the inner ear of D-galactose-induced aging rats. Hear Res 287:15–24
Fetoni AR, Sergi B, Ferraresi A, Paludetti G, Troiani D (2004) Protective effects of alpha-tocopherol and tiopronin against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Acta Otolaryngol 124:421–426
Fischel-Ghodsian N, Kopke RD, Ge X (2004) Mitochondrial dysfunction in hearing loss. Mitochondrion 4:675–694
Fu X, Wan P, Li P et al (2021) Mechanism and prevention of ototoxicity induced by aminoglycosides. Front Cell Neurosci 15:692762
Gagnon F, Aïssi D, Carrié A, Morange PE, Trégouët DA (2014) Robust validation of methylation levels association at CPT1A locus with lipid plasma levels. J Lipid Res 55:1189–1191
Gao X, Li K, Hui X et al (2011) Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1A prevents fatty acid-induced adipocyte dysfunction through suppression of c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Biochem J 435:723–732
Gao Y, She R, Sha W (2017) Gestational diabetes mellitus is associated with decreased adipose and placenta peroxisome proliferator-activator receptor γ expression in a Chinese population. Oncotarget 8:113928–113937
Gentilin E, Simoni E, Candito M, Cazzador D, Astolfi L (2019) Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: updates on molecular targets. Trends Mol Med 25:1123–1132
Guan Y (2002) Targeting peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) in kidney and urologic disease. Minerva Urol Nefrol 54:65–79
Hsiao PJ, Chiou HC, Jiang HJ, Lee MY, Hsieh TJ, Kuo KK (2017) Pioglitazone enhances cytosolic lipolysis, β-oxidation and autophagy to ameliorate hepatic steatosis. Sci Rep 7:9030
Im GJ, Chang J, Lee S et al (2015) Protective role of edaravone against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in an auditory cell line. Hear Res 330:113–118
Kamogashira T, Fujimoto C, Yamasoba T (2015) Reactive oxygen species, apoptosis, and mitochondrial dysfunction in hearing loss. Biomed Res Int 2015:617207
Karasawa T, Steyger PS (2015) An integrated view of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. Toxicol Lett 237:219–227
Kim HJ, Lee JH, Kim SJ et al (2010) Roles of NADPH oxidases in cisplatin-induced reactive oxygen species generation and ototoxicity. J Neurosci 30:3933–3946
Le Q, Tabuchi K, Warabi E, Hara A (2017) The role of peroxiredoxin I in cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Auris Nasus Larynx 44:205–212
Leal J, Ades AE, Wordsworth S, Dezateux C (2014) Regional differences in the frequency of the c.985A>G ACADM mutation: findings from a meta-regression of genotyping and screening studies. Clin Genet 85:253–259
Liu H, Giffen KP, Chen L et al (2022) Molecular and cytological profiling of biological aging of mouse cochlear inner and outer hair cells. Cell Rep 39:110665
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Ma J, Guo J, Chen H et al (2022) Isoflavones from Sojae semen praeparatum regulate lipid metabolism in atherosclerotic mice through PPARγ/LXRα/ABCA1 signaling pathway. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae 28:110–118
Mukherjea D, Jajoo S, Kaur T, Sheehan KE, Ramkumar V, Rybak LP (2010) Transtympanic administration of short interfering (si)RNA for the NOX3 isoform of NADPH oxidase protects against cisplatin-induced hearing loss in the rat. Antioxid Redox Signal 13:589–598
Natarajan V, Chawla R, Mah T et al (2020) Mitochondrial dysfunction in age-related metabolic disorders. Proteomics 20:e1800404
Previati M, Lanzoni I, Corbacella E et al (2004) RNA expression induced by cisplatin in an organ of Corti-derived immortalized cell line. Hear Res 196:8–18
Rajput K, Edwards L, Brock P, Abiodun A, Simpkin P, Al-Malky G (2020) Ototoxicity-induced hearing loss and quality of life in survivors of paediatric cancer. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 138:110401
Rottenberg S, Disler C, Perego P (2021) The rediscovery of platinum-based cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 21:37–50
Rybak LP, Whitworth C, Somani S (1999) Application of antioxidants and other agents to prevent cisplatin ototoxicity. Laryngoscope 109:1740–1744
Salehi P, Zallocchi M, Vijayakumar S et al (2022) In silico transcriptomics identifies FDA-approved drugs and biological pathways for protection against cisplatin-induced hearing loss. bioRxiv 2022.2001.2026.477836
Seok J, Jung HS, Park S, Lee JO, Kim CJ, Kim GJ (2020) Alteration of fatty acid oxidation by increased CPT1A on replicative senescence of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther 11:1
Singh SP, Schragenheim J, Cao J, Falck JR, Abraham NG, Bellner L (2016) PGC-1 alpha regulates HO-1 expression, mitochondrial dynamics and biogenesis: role of epoxyeicosatrienoic acid. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 125:8–18
Spoendlin H (1971) Primary structural changes in the organ of Corti after acoustic overstimulation. Acta Otolaryngol 71:166–176
Stefanovic-Racic M, Perdomo G, Mantell BS, Sipula IJ, Brown NF, O’Doherty RM (2008) A moderate increase in carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a activity is sufficient to substantially reduce hepatic triglyceride levels. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 294:E969-977
Tang LQ, Chen DP, Guo L et al (2018) Concurrent chemoradiotherapy with nedaplatin versus cisplatin in stage II-IVB nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an open-label, non-inferiority, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 19:461–473
Van De Water TR, Lallemend F, Eshraghi AA et al (2004) Caspases, the enemy within, and their role in oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of inner ear sensory cells. Otol Neurotol 25:627–632
Villani V, Zucchella C, Cristalli G et al (2016) Vitamin E neuroprotection against cisplatin ototoxicity: preliminary results from a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Head Neck 38(Suppl 1):E2118-2121
Wang Q, Li C, Zhang Q et al (2016) The effect of Chinese herbs and its effective components on coronary heart disease through PPARs-PGC1α pathway. BMC Complement Altern Med 16:514
Wang S, Zhu X, Xiong L, Ren J (2017) Ablation of Akt2 prevents paraquat-induced myocardial mitochondrial injury and contractile dysfunction: role of Nrf2. Toxicol Lett 269:1–14
Wu F, Xiong H, Sha S (2020) Noise-induced loss of sensory hair cells is mediated by ROS/AMPKα pathway. Redox Biol 29:101406
Yu HH, Seo SJ, Kim YH et al (2006) Protective effect of Rehmannia glutinosa on the cisplatin-induced damage of HEI-OC1 auditory cells through scavenging free radicals. J Ethnopharmacol 107:383–388
Yu HH, Jung SY, Shin MK, Park R, So HS, You YO (2010) Pueraria thunbergiana inhibits cisplatin-induced damage of HEI-OC1 auditory cells through scavenging free radicals. Phytother Res 24:834–839
Yu J, Wang Y, Liu P, Li Q, Sun Y, Kong W (2014) Mitochondrial DNA common deletion increases susceptibility to noise-induced hearing loss in a mimetic aging rat model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 453:515–520
Zhang L, Du Z, Gong S (2021) Mitochondrial dysfunction and sirtuins: important targets in hearing loss. Neural Plast 2021:1–10
Zhu RZ, Li BS, Gao SS, Seo JH, Choi BM (2021) Luteolin inhibits H(2)O(2)-induced cellular senescence via modulation of SIRT1 and p53. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 25:297–305
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XDM: designed and conceived the study. XN and PH: conducted the experiments. JL, ZC, TZ, BL, XIM and QW: helped them to collect and analyze the data. XN and PH: drafted the manuscript which was polished by XDM. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Martine Collart.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, X., Han, P., Liu, J. et al. Regulation of PPARγ/CPT-1 expression ameliorates cochlear hair cell injury by regulating cellular lipid metabolism and oxidative stress. Mol Genet Genomics 298, 473–483 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-023-01993-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-023-01993-8