Abstract
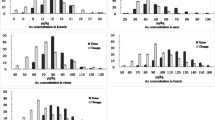
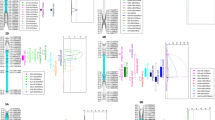
The heavy metals lead and cadmium have become important pollutants in the environment, which exert negative effects on plant morphology, growth and photosynthesis. It is particularly significant to uncover the genetic loci and the causal genes for lead and cadmium tolerance in plants. This study used an IBM Syn10 DH population to identify the quantitative trait loci (QTL) controlling maize seedling tolerance to lead and cadmium by linkage mapping. The broad-sense heritability of these seedling traits ranged from 65.8–97.3% and 32.0–98.8% under control (CK) and treatment (T) conditions, respectively. A total of 53 and 64 QTL were detected under CK and T conditions, respectively. Moreover, 42 QTL were identified using lead and cadmium tolerance coefficient (LCTC). Among these QTL, five and two major QTL that explained > 10% of phenotypic variation were identified under T condition and using LCTC, respectively. Furthermore, eight QTL were simultaneously identified by T and LCTC, explaining 5.23% to 9.21% of the phenotypic variations. Within these major and common QTL responsible for the combined heavy metal tolerance, four candidate genes (Zm00001d048759, Zm00001d004689, Zm00001d004843, Zm00001d033527) were previously reported to correlate with heavy metal transport and tolerance. These findings will contribute to functional gene identification and molecular marker-assisted breeding for improving heavy metal tolerance in maize.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Ghani AH, Sanchez DL, Kumar B, Lubberstedt T (2016) Paper roll culture and assessment of maize root parameters. Bio-Protoc 6(18):e1926
Alloway (2015) Heavy metals in soils. Mineral Mag 55(8):1318–1324
Austin DF, Lee M (1996) Genetic resolution and verification of quantitative trait loci for flowering and plant height with recombinant inbred lines of maize. Genome 39(5):957–968
Buckler ES, Holland JB, Bradbury PJ, Acharya CB, Brown PJ et al (2009) The genetic architecture of maize flowering time. Science 325(5941):714–718
Burton AL, Johnson JM, Foerster JM, Hirsch CN, Buell CR et al (2014) QTL mapping and phenotypic variation for root architectural traits in maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 127(11):2293–2311
Canadas EM, Ballesteros MV et al (2014) Does gypsum influence seed germination? Turk J Bot 38(1):141–147
Chen H, Zheng C, Wang S, Tu C (2000) Combined pollution and pollution index of heavy metals in red soil. Pedosphere 10(2):117–124
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138(3):963–971
Comas L, Becker S, Cruz VMV, Byrne PF, Dierig DA (2013) Root traits contributing to plant productivity under drought. Front Plant Sci 4:442
Courbot M, Willems G, Motte P, Arvidsson S, Roosens N et al (2007) A major quantitative trait locus for cadmium tolerance in Arabidopsis halleri colocalizes with HMA4, a gene encoding a heavy metal ATPase. Plant Physiol 144(2):1052–1065
Ding Y, Cao J, Ni L et al (2013) ZmCPK11 is involved in abscisic acid-induced antioxidant defence and functions upstream of ZmMPK5 in abscisic acid signalling in maize. J Exp Bot 4:871–884
Du H, Ning L, He B et al (2020) Cross-species root transcriptional network analysis highlights conserved modules in response to nitrate between maize and sorghum. Int J Mol Sci 21(4):1445
Dudley JW, Dijkhuizen A, Paul C, Coates ST, Rocheford TR (2004) Effects of random mating on marker–QTL associations in the cross of the Illinois high protein × Illinois low protein maize strains. Crop Sci 44(4):1419–1428
Dutilleul C, Jourdain A, Bourguignon J, Hugouvieux V (2008) The Arabidopsis putative selenium-binding protein family: expression study and characterization of SBP1 as a potential new player in cadmium detoxification processes. Plant Physiol 147(1):239–251
Fang F, Wang M, Zhu Q et al (2016) DkMYB6 is involved in persimmon fruit deastringency, via transcriptional activation on both DkPDC and DkERF. Postharvest Biol Technol 111:167–177
Fediuc E, Erdei L (2002) Physiological and biochemical aspects of cadmium toxicity and protective mechanisms induced in Phragmites australis and Typha latifolia. J Plant Physiol 159(3):265–271
Gall JE, Boyd RS, Rajakaruna N (2015) Transfer of heavy metals through terrestrial food webs: a review. Environ Monit Assess 187(4):1–21
Gao Q, Yang Z, Yong Z et al (2012) Characterization of an Abc1 kinase family gene OsABC1-2 conferring enhanced tolerance to dark-induced stress in rice. Gene 498(2):155–163
Gu C, Wen Y, Wu L et al (2020) Arsenite-induced transgenerational glycometabolism is associated with up-regulation of H3K4me2 via inhibiting spr-5 in caenorhabditis elegans. Toxicol Lett 326:11–17
Gui J, Zheng S, Chang L et al (2016) OsREM4.1 interacts with OsSERK1 to coordinate the interlinking between abscisic acid and brassinosteroid signaling in rice. Dev Cell 38(2):201–213
Hallauer AR, Carena MJ, Mirandailho JD (2010) Quantitative genetics in maize breeding, vol 6. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin
Hochholdinger F (2009) The maize root system: morphology, anatomy, and genetics[M]//Handbook of maize: its biology. Springer, New York, NY, pp 145–60
Hoopes GM, Hamilton JP, Wood JC et al (2019) An updated gene atlas for maize reveals organ‐specific and stress‐induced genes[J]. Plant J 97(6):1154–1167
Hoppe DC, McCully ME, Wenzel CL (1986) The nodal roots of Zea: their development in relation to structural features of the stem. Can J Bot 64(11):2524–2537
Huang CF, Yamaji N, Mitani N, Yano M, Nagamura Y et al (2009) A bacterial-type ABC transporter is involved in aluminum tolerance in rice. Plant Cell 21(2):655–667
Huisman MT, Chhatta AA, Tellingen OV et al (2005) MRP2 (ABCC2) transports taxanes and confers paclitaxel resistance and both processes are stimulated by probenecid. Int J Cancer 116(5):824–829
Jang MG, Kim YJ, Jang GH et al (2014) Ectopic overexpression of the aluminum-induced protein gene from Panax ginseng enhances heavy metal tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 119(1):95–106
Jansen C, Zhang Y, Liu H, Gonzalez-Portilla PJ, Lauter N et al (2015) Genetic and agronomic assessment of cob traits in corn under low and normal nitrogen management conditions. Theor Appl Genet 128(7):1231–1242
Kirch HH, Schlingensiepen SK et al (2005) Detailed expression analysis of selected genes of the aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) gene superfamily in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 57(3):315–332
Knapp SJ, Stroup WW, Ross WM (1985) Exact confidence intervals for heritability on a progeny mean basis 1. Crop Sci 25(1):192–194
Lagriffoul A, Mocquot B, Mench M, Vangronsveld J (1998) Cadmium toxicity effects on growth, mineral and chlorophyll contents, and activities of stress related enzymes in young maize plants (Zea mays L.). Plant Soil 200(2):241–250
Laurie S, Feeney KA, Maathuis F et al (2010) A role for HKT1 in sodium uptake by wheat roots. Plant J 32(2):139–149
Leene JV, Blomme J, Kulkarni SR et al (2016) Functional characterization of the Arabidopsis transcription factor bZIP29 reveals its role in leaf and root development. J Exp Bot 67(19):5825–5840
Li H, Liu C, Zhou L, Zhao Z, Li Y et al (2018a) Molecular and functional characterization of the magnesium transporter gene ZmMGT12 in maize. Gene 665:167–173
Li H, Liu C, Zhou L et al (2018b) Molecular and functional characterization of the magnesium transporter gene ZmMGT12 in maize[J]. Gene 665:167–173
Li S, Lin Y, Wang P et al (2018c) Histone acetylation cooperating with AREB1 transcription factor regulates drought response and tolerance in Populus trichocarpa. Plant Cell 31(3):437
Lima MDLA, de Souza CL, Bento DAV, De Souza AP, Carlini-Garcia LA (2006) Mapping QTL for grain yield and plant traits in a tropical maize population. Mol Breed 17(3):227–239
Liu Y, Wang L, Sun C, Zhang Z, Zheng Y et al (2014) Genetic analysis and major QTL detection for maize kernel size and weight in multi-environments. Theor Appl Genet 127(5):1019–1037
Liu YJ, Ji et al (2015) Arabidopsis AtbHLH112 regulates the expression of genes involved in abiotic stress tolerance by binding to their E-box and GCG-box motifs. New Phytol 207(3):692–709
Liu H, Zhang L, Wang J, Li C, Zeng X et al (2017a) Quantitative trait locus analysis for deep-sowing germination ability in the maize IBM Syn10 DH population. Front Plant Sci 8:813
Liu Q, Le L, Wang X et al (2017b) Comprehensive analysis of rice laccase gene (OsLAC) family and ectopic expression of OsLAC10 enhances tolerance to copper stress in Arabidopsis. Int J Mol Sci 18(2):209
Liu Q, Luo L, Wang X, Shen Z, Zheng L (2017c) Comprehensive analysis of rice laccase gene (OsLAC) family and ectopic expression of OsLAC10 enhances tolerance to copper stress in Arabidopsis. Int J Mol Sci 18(2):209
Ma L, Guan Z, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Zhang Y et al (2018) Identification of quantitative trait loci for leaf-related traits in an IBM Syn10 DH maize population across three environments. Plant Breed 137(2):127–138
Ma L, Qing C, Frei U, Shen Y, Lübberstedt T (2020) Association mapping for root system architecture traits under two nitrogen conditions in germplasm enhancement of maize doubled haploid lines. Crop J 8(2):213–226
Malamy JE (2005) Intrinsic and environmental response pathways that regulate root system architecture. Plant Cell Environ 28(1):67–77
McCouch S R, Xiao J (2019) From Malthus to molecular mapping: prospects for the utilization of genome analysis to enhance the world food supply[M]//Molecular dissection of complex traits. CRC Press pp 267–278
Miller L, Houghton JA (1945) The microKjeldahl determination of the nitrogen content of amino acids and proteins. J Biol Chem 169:373–383
Młodzińska E, Kłobus G, Christensen MD et al (2015) The plasma membrane H+-ATPase AHA2 contributes to the root architecture in response to different nitrogen supply. Physiol Plant 154(2):270–282
Nie S, Huang S, Zhang S et al (2013) Later Effects of Various Heavy Metal Stress on Maize Grain Yields in Wheat-Maize Rotation Systems [J][J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica 4
Ookawa T, Hobo T, Yano M, Murata K, Ando T et al (2010) New approach for rice improvement using a pleiotropic QTL gene for lodging resistance and yield. Nat Commun 1(1):1–11
Pace J, Lee N, Naik HS, Ganapathysubramanian B, Lübberstedt T (2014) Analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) seedling roots with the high-throughput image analysis tool ARIA (Automatic Root Image Analysis). PLoS ONE 9(9):108255
Pace J, Gardner C, Romay C, Ganapathysubramanian B, Lübberstedt T (2015) Genome-wide association analysis of seedling root development in maize (Zea mays L.). BMC Genom 16(1):47
Pál M, Horváth E, Janda T, Páldi E, Szalai G (2006) Physiological changes and defense mechanisms induced by cadmium stress in maize. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 169(2):239–246
Park Y, Xu ZY, Kim SY et al (2016) Spatial regulation of ABCG25, an ABA exporter, is an important component of the mechanism controlling cellular ABA levels. Plant Cell 28:2528
Peng H, He X, Gao J, Ma H, Zhang Z et al (2015) Transcriptomic changes during maize roots development responsive to Cadmium (Cd) pollution using comparative RNAseq-based approach. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 464(4):1040–1047
Rahman H, Ramanathan V, Nallathambi J et al (2016) Over-expression of a NAC 67 transcription factor from finger millet (Eleusine coracana L.) confers tolerance against salinity and drought stress in rice. BMC Biotechnol 16(1):7–20
Rana RM, Shinan D, Haijuan T, Fiaz A, Hongsheng Z (2012) Functional analysis of OsHSBP1 and OsHSBP2 revealed their involvement in the heat shock response in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Exp Bot 63(16):6003
Rauser WE (1987) Compartmental efflux analysis and removal of extracellular cadmium from roots. Plant Physiol 1:62–65
Sanchez DL, Liu S, Ibrahim R, Blanco M, Lübberstedt T (2018) Genome-wide association studies of doubled haploid exotic introgression lines for root system architecture traits in maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Sci 268:30–38
Sandalio LM, Dalurzo HC, Gomez M, Romero-Puertas MC, Del Rio LA (2001) Cadmium-induced changes in the growth and oxidative metabolism of pea plants. J Exp Bot 52(364):2115–2126
Sengar RS, Gautam M, Sengar RS, Garg SK, Sengar K et al (2008) Lead stress effects on physiobiochemical activities of higher plants. Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology, vol 196. Springer, New York, pp 73–93
Shen Y, Zhang Y, Chen J, Lin H, Zhao M et al (2013) Genome expression profile analysis reveals important transcripts in maize roots responding to the stress of heavy metal Pb. Physiol Plant 147(3):270–282
Shung CY, Sunter G (2007) AL1-dependent repression of transcription enhances expression of Tomato golden mosaic virus AL2 and AL3. Virology 364(1):112–122
Si L, Zhang J, Hussain A et al (2021) Accumulation and translocation of food chain in soil-mulberry (Morus alba L.)-silkworm (Bombyx mori) under single and combined stress of lead and cadmium. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208:111582
Tian XR , Wu H , Li J et al (2015) Heavy Metal Accumulation and Antioxidative System Responses of Plagiomnium acutum Under Combined Cadmium and Lead Stresses[J]. J Agro-Environ Sci 34(5):844–851
Tuberosa R, Salvi S, Sanguineti MC, Landi P, Maccaferri M et al (2002) Mapping QTLs regulating morpho-physiological traits and yield: case studies, shortcomings and perspectives in drought-stressed maize. Ann Bot 89(7):941–963
Villicaña C, Warner N et al (2016) Antiporter NHX2 differentially induced in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum natural genetic variant under salt stress. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 124(2):361–375
Virlouvet L (2011) Identification and characterization of genes involved in the variation of quantitative characteristics affected by drought in maize[D]. University of Paris Sud-Paris XI
Wang S, Basten C J, Zeng Z B (2005) Windows QTL cartographer version 2.5. Statistical genetics[J]
Wei Y, An Z, Zou Z et al (2015) The stress-responsive kinases MAPKAPK2/MAPKAPK3 activate starvation-induced autophagy through Beclin 1 phosphorylation. Elife 4:4
Williams CG, Goodman MM, Stuber CW (1995) Comparative recombination distances among Zea mays L. inbreds, wide crosses and interspecific hybrids. Genetics 141(4):1573–1581
Xia T, Xiao D et al (2012) Heterologous expression of ATG8c from soybean confers tolerance to nitrogen deficiency and increases yield in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 7(5):e37217
Xia X, Fan X, Wei J et al (2014) Rice nitrate transporter OsNPF2.4 functions in low-affinity acquisition and long-distance transport. J Exp Bot 66(1):317
Xia S, Deng R, Zhang Z, Liu C, Shi G (2016) Variations in the accumulation and translocation of cadmium among pak choi cultivars as related to root morphology. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(10):9832–9842
Xu MY, Rocha P, Man LW et al (2011) Rice gene OsDSR-1 promotes lateral root development in arabidopsis under high-potassium conditions. J Plant Biol 54(3):180–189
Ying C, Ruidong H, Wenchun J, Zhiqiang C (2005) Effect of heavy metal lead and cadmium on grain quality of maize. Yournal Shenyang Agric Univ 36(2):218–220
Young ND (1996) QTL mapping and quantitative disease resistance in plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol 34(1):479–501
Zhang J, Chen K, Pang Y, Naveed SA, Zhao X et al (2017) QTL mapping and candidate gene analysis of ferrous iron and zinc toxicity tolerance at seedling stage in rice by genome-wide association study. BMC Genomics 18(1):828
Zhang J, Zhu Q, Yu H, Li L, Zhang G et al (2019) Comprehensive analysis of the cadmium tolerance of abscisic acid-, stress-and ripening-induced proteins (ASRs) in maize. Int J Mol Sci 20(1):133
Zhao X, Cao Y, Li Y, Hu S, Pan G et al (2018a) Identification of QTL and candidate genes for Pb accumulation in maize at maturity stage. Maydica 61(2):9
Zhao X, Luo L, Cao Y, Liu Y, Li Y et al (2018b) Genome-wide association analysis and QTL mapping reveal the genetic control of cadmium accumulation in maize leaf. BMC Genomics 19(1):1–13
Zhao Z, Zhang H, Fu Z, Chen H, Lin Y et al (2018c) Genetic-based dissection of arsenic accumulation in maize using a genome-wide association analysis method. Plant Biotechnol J 16(5):1085–1093
Acknowledgements
The authors thank anonymous reviewers for their comments on the manuscript. We would like to thank Michael Lee (Iowa State University) for providing the IBMSyn10 DH population. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31871637 and 32001500).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YS, LM, GP and TL conceived and designed the experiments; FH and XZ performed the experiments; FH and PL analyzed the data; GY and CZ contributed reagents, materials and analysis tools, respectively; FH and YS wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Human or animal rights
This study does not include human or animal subjects.
Additional information
Communicated by Stefan Hohmann.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, F., Zhou, X., Liu, P. et al. Genetic dissection of maize seedling traits in an IBM Syn10 DH population under the combined stress of lead and cadmium. Mol Genet Genomics 296, 1057–1070 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-021-01800-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-021-01800-2