Abstract
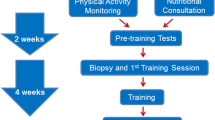
Adaptation to exercise training is a complex trait that may be influenced by genetic variants. We identified 36 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that had been previously associated with endurance or strength performance, exercise-related phenotypes or exercise intolerant disorders. A MassARRAY multiplex genotyping assay was designed to identify associations with these SNPs against collected endurance fitness phenotype parameters obtained from two exercise cohorts (Gene SMART study; n = 58 and Hawaiian Ironman Triathlon 2008; n = 115). These parameters included peak power output (PP), a time trial (TT), lactate threshold (LT), maximal oxygen uptake (VO2 max) in recreationally active individuals and a triathlon time-to-completion (Hawaiian Ironman Triathlon cohort only). A nominal significance threshold of α < 0.05 was used to identify 17 variants (11 in the Gene SMART population and six in the Hawaiian Ironman Triathlon cohort) which were significantly associated with performance gains in highly trained individuals. The variant rs1474347 located in Interleukin 6 (IL6) was the only variant with a false discovery rate < 0.05 and was found to be associated with gains in VO2 max (additional 4.016 mL/(kg min) for each G allele inherited) after training in the Gene SMART cohort. In summary, this study found further evidence to suggest that genetic variance can influence training response in a moderately trained cohort and provides an example of the potential application of genomic research in the assessment of exercise trait response.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analysed in this study will be provided by the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahmetov II, Fedotovskaya ON (2015) Current progress in sports genomics. Adv Clin Chem 70:247–314
Alves AJ, Goldhammer E, Ribeiro F, Eynon N, Cohen SBZ, Duarte JA, Viana JL, Sagiv M, Oliveira J (2013) GNAS A-1121G variant is associated with improved diastolic dysfunction in response to exercise training in heart failure patients. Int J Sports Med 34:274–280
Andrulionyte L, Kuulasmaa T, Chiasson JL, Laakso M, Group S-NS (2007) Single nucleotide polymorphisms of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha gene (PPARA) influence the conversion from impaired glucose tolerance to type 2 diabetes: the STOP-NIDDM trial. Diabetes 56:1181–1186
Arora P, Garcia-Bailo B, Dastani Z, Brenner D, Villegas A, Malik S, Spector TD, Richards B, El-Sohemy A, Karmali M, Badawi A (2011) Genetic polymorphisms of innate immunity-related inflammatory pathways and their association with factors related to type 2 diabetes. BMC Med Genet 12:95
Bonetti DL, Hopkins WG (2010) Variation in performance times of elite flat-water canoeists from race to race. Int J Sports Physiol Perform 5:210–217
Bouchard C (2011) Overcoming barriers to progress in exercise genomics. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 39:212–217
Brondani LA, Assmann TS, Duarte GC, Gross JL, Canani LH, Crispim D (2012) The role of theuncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) on the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 56:215–225
Brown BM, Rainey-Smith SR, Castalanelli N, Gordon N, Markovic S, Sohrabi HR, Weinborn M, Laws SM, Doecke J, Shen K, Martins RN, Peiffer JJ (2017) Study protocol of the Intense Physical Activity and Cognition study: The effect of high-intensity exercise training on cognitive function in older adults. Alzheimers Dement (N Y) 3:562–570
Burguete-Garcia AI, Martinez-Nava GA, Valladares-Salgado A, Bermudez Morales VH, Estrada-Velasco B, Wacher N, Peralta-Romero J, Garcia-Mena J, Parra E, Cruz M (2014) Association of beta1 and beta3 adrenergic receptors gene polymorphisms with insulin resistance and high lipid profiles related to type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Nutr Hosp 29:1327–1334
Buford TW, Roberts MD, Church TS (2013) Toward exercise as personalized medicine. Sports Med 43:157–165
Chathoth S, Ismail MH, Vatte C, Cyrus C, Al Ali Z, Ahmed KA, Acharya S, Al Barqi AM, Al Ali A (2018) Association of uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) gene polymorphism with obesity: a case-control study. BMC Med Genet 19:203
De Moor MH, Liu YJ, Boomsma DI, Li J, Hamilton JJ, Hottenga JJ, Levy S, Liu XG, Pei YF, Posthuma D, Recker RR, Sullivan PF, Wang L, Willemsen G, Yan H, De Geus EJ, Deng HW (2009) Genomewide association study of exercise behavior in Dutch and American adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41:1887–1895
Deeny SP, Poeppel D, Zimmerman JB, Roth SM, Brandauer J, Witkowski S, Hearn JW, Ludlow AT, Contreras-Vidal JL, Brandt J, Hatfield BD (2008) Exercise, APOE, and working memory: MEG and behavioral evidence for benefit of exercise in epsilon4 carriers. Biol Psychol 78:179–187
Doney AS, Fischer B, Lee SP, Morris AD, Leese G, Palmer CN (2005) Association of common variation in the PPARA gene with incident myocardial infarction in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a Go-DARTS study. Nucl Recept 3:4
Dong C, Zhou H, Shen C, Yu LG, Ding Y, Zhang YH, Guo ZR (2015) Role of peroxisome proliferatoractivated receptors gene polymorphisms in type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. World J Diabetes 6:654–661
den Hoed M, Brage S, Zhao JH, Westgate K, Nessa A, Ekelund U, Spector TD, Wareham NJ, Loos RJ (2013) Heritability of objectively assessed daily physical activity and sedentary behavior. Am J Clin Nutr 98:1317–1325
Ellis JA, Ong B (2017) The MassARRAY((R)) system for targeted SNP genotyping. Methods Mol Biol 1492:77–94
Evans D, Aberle J, Wendt D, Wolf A, Beisiegel U, Mann WA (2001) A polymorphism, L162V, in the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) gene is associated with lower body mass index in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Mol Med (Berl) 79:198–204
Flavell DM, Ireland H, Stephens JW, Hawe E, Acharya J, Mather H, Hurel SJ, Humphries SE (2005) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha gene variation influences age of onset and progression of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 54:582–586
Fredriksson J, Anevski D, Almgren P, Sjogren M, Lyssenko V, Carlson J, Isomaa B, Taskinen MR, Groop L, Orho-Melander M, Botnia Study G (2007) Variation in GYS1 interacts with exercise andgender to predict cardiovascular mortality. PLoS One 2:e285
Fuku N, Alis R, Yvert T, Zempo H, Naito H, Abe Y, Arai Y, Murakami H, Miyachi M, Pareja-Galeano H, Emanuele E, Hirose N, Lucia A (2016) Muscle-Related Polymorphisms (MSTN rs1805086 and ACTN3 rs1815739) Are Not Associated with Exceptional Longevity in Japanese Centenarians. PLoS One 11:e0166605
Galy O, Hue O, Chamari K, Boussana A, Chaouachi A, Prefaut C (2008) Influence of performance level on exercise-induced arterial hypoxemia during prolonged and successive exercise in triathletes. Int J Sports Physiol Perform 3:482–500
Garatachea N, Santiago C, Yvert T, Verde-Rello Z, Fiuza-Luces C, Santos-Lozano A, Gomez-Gallego F, Lucia A (2015) Genetic variants in the PPARD-PPARGC1A-NRF-TFAM mitochondriogenesis pathway are neither associated with muscle characteristics nor physical performance in elderly. Ricyde-Revista Internacional De Ciencias Del Deporte 11:196–208
Grealy R, Smith CL, Chen T, Hiller D, Haseler LJ, Griffiths LR (2013) The genetics of endurance: frequency of the ACTN3 R577X variant in Ironman World Championship athletes. J Sci Med Sport 16:365–371
Grealy R, Herruer J, Smith CL, Hiller D, Haseler LJ, Griffiths LR (2015) Evaluation of a 7-gene genetic profile for athletic endurance phenotype in ironman championship triathletes. PLoS ONE 10:e0145171
He Z, Hu Y, Feng L, Li Y, Liu G, Xi Y, Wen L, Lucia A (2008) NRF-1 genotypes and endurance exercise capacity in young Chinese men. British J of Sports Med 42(5):361–366
He ZH, Hu Y, Li YC, Gong LJ, Cieszczyk P, Maciejewska-Karlowska A, Leonska-Duniec A, Muniesa CA, Marin-Peiro M, Santiago C, Garatachea N, Eynon N, Lucia A (2015) PGC-related gene variants and elite endurance athletic status in a Chinese cohort: a functional study. Scand J Med Sci Sports 25:184–195
Hennis PJ, O'Doherty AF, Levett DZ, Grocott MP, Montgomery HM (2015) Genetic factors associated with exercise performance in atmospheric hypoxia. Sports Med 45:745–761
Houweling PJ, Papadimitriou ID, Seto JT, Perez LM, Coso JD, North KN, Lucia A, Eynon N (2018) Is evolutionary loss our gain? The role of ACTN3 p.Arg577Ter (R577X) genotype in athletic performance, ageing, and disease. Hum Mutat 39:1774–1787
Issurin VB (2017) Evidence-based prerequisites and precursors of athletic talent: a review. Sports Med 47:1993–2010
Jurinke C, van den Boom D, Cantor CR, Koster H (2002) Automated genotyping using the DNA MassArray technology. Methods Mol Biol 187:179–192
Karanikolou A, Wang G, Pitsiladis Y (2017) Letter to the editor: a genetic-based algorithm for personalized resistance training. Biol Sport 34:31–33
Liang KY, Mintun MA, Fagan AM, Goate AM, Bugg JM, Holtzman DM, Morris JC, Head D (2010) Exercise and Alzheimer's disease biomarkers in cognitively normal older adults. Ann Neurol 68:311–318
Lin Y, Gu SJ, Wu M, Chen Q, Zhou ZY, Yu H, Zhang LJ, Luo WS, Guo ZR (2012) Association between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors gene polymorphism and essential hypertension. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 33:597–601
Liu Y, Berthier-Schaad Y, Fallin MD, Fink NE, Tracy RP, Klag MJ, Smith MW, Coresh J (2006) IL-6 haplotypes, inflammation, and risk for cardiovascular disease in a multiethnic dialysis cohort. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:863–870
McCoy J, Bates M, Eggett C, Siervo M, Cassidy S, Newman J, Moore SA, Gorman G, Trenell MI, Velicki L, Seferovic PM, Cleland JGF, MacGowan GA, Turnbull DM, Jakovljevic DG (2017) Pathophysiology of exercise intolerance in chronic diseases: the role of diminished cardiac performance in mitochondrial and heart failure patients. Open Heart 4:e000632
Montani D, Girerd B, Gunther S, Riant F, Tournier-Lasserve E, Magy L, Maazi N, Guignabert C, Savale L, Sitbon O, Simonneau G, Soubrier F, Humbert M (2014) Pulmonary arterial hypertension in familial hemiplegic migraine with ATP1A2 channelopathy. Eur Respir J 43:641–643
Munoz-Canoves P, Scheele C, Pedersen BK, Serrano AL (2013) Interleukin-6 myokine signaling in skeletal muscle: a double-edged sword? FEBS J 280:4131–4148
Panicker V, Cluett C, Shields B, Murray A, Parnell KS, Perry JR, Weedon MN, Singleton A, Hernandez D, Evans J, Durant C, Ferrucci L, Melzer D, Saravanan P, Visser TJ, Ceresini G, Hattersley AT, Vaidya B, Dayan CM, Frayling TM (2008) A common variation in deiodinase 1 gene DIO1 is associated with the relative levels of free thyroxine and triiodothyronine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:3075–3081
Panoulas VF, Douglas KM, Smith JP, Taffe P, Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou A, Toms TE, Elisaf MS, Nightingale P, Kitas GD (2008) Polymorphisms of the endothelin-1 gene associate with hypertension in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Endothelium 15:203–212
Pitsiladis YP, Tanaka M, Eynon N, Bouchard C, North KN, Williams AG, Collins M, Moran CN, Britton SL, Fuku N, Ashley EA, Klissouras V, Lucia A, Ahmetov II, de Geus E, Alsayrafi M, Athlome Project C (2016) Athlome Project Consortium: a concerted effort to discover genomic and other “omic” markers of athletic performance. Physiol Genomics 48:183–190
Ramos AV, Bastos-Rodrigues L, Resende BA, Friedman E, Campanha-Versiani L, Miranda DM, Sarquis M, De Marco L (2012) The contribution of FTO and UCP-1 SNPs to extreme obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular risk in Brazilian individuals. BMC Med Genet 13:101
Rankinen T, Perusse L, Rauramaa R, Rivera MA, Wolfarth B, Bouchard C (2004) The human gene map for performance and health-related fitness phenotypes: the 2003 update. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36:1451–1469
Rankinen T, Church T, Rice T, Markward N, Leon AS, Rao DC, Skinner JS, Blair SN, Bouchard C (2007) Effect of endothelin 1 genotype on blood pressure is dependent on physical activity or fitness levels. Hypertension 50:1120–1125
Tejedor MT, Garcia-Sobreviela MP, Ledesma M, Arbones-Mainar JM (2014) The apolipoprotein E polymorphism rs7412 associates with body fatness independently of plasma lipids in middle aged men. PLoS One 9:e108605
Uthurralt J, Gordish-Dressman H, Bradbury M, Tesi-Rocha C, Devaney J, Harmon B, Reeves EK, Brandoli C, Hansen BC, Seip RL, Thompson PD, Price TB, Angelopoulos TJ, Clarkson PM, Moyna NM, Pescatello LS, Visich PS, Zoeller RF, Gordon PM, Hoffman EP (2007) PPARalpha L162V underlies variation in serum triglycerides and subcutaneous fat volume in young males. BMC Med Genet 8:55
Voisin S, Jacques M, Lucia A, Bishop DJ, Eynon N (2019) Statistical considerations for exercise protocols aimed at measuring trainability. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 47:37–45
Walsh S, Haddad CJ, Kostek MA, Angelopoulos TJ, Clarkson PM, Gordon PM, Moyna NM, Visich PS, Zoeller RF, Seip RL, Bilbie S, Thompson PD, Devaney J, Gordish-Dressman H, Hoffman EP, Price TB, Pescatello LS (2012) Leptin and leptin receptor genetic variants associate with habitual physical activity and the arm body composition response to resistance training. Gene 510:66–70
Woods D, Hickman M, Jamshidi Y, Brull D, Vassiliou V, Jones A, Humphries S, Montgomery H (2001) Elite swimmers and the D allele of the ACE I/D polymorphism. Hum Genet 108:230–232
Yan X, Eynon N, Papadimitriou ID, Kuang J, Munson F, Tirosh O, O’Keefe L, Griffiths LR, Ashton KJ, Byrne N, Pitsiladis YP, Bishop DJ (2017) The gene SMART study: method, study design, and preliminary findings. BMC Genomics 18:821
Yan X, Dvir N, Jacques M, Cavalcante L, Papadimitriou ID, Munson F, Kuang J, Garnham A, Landen S, Li J, O’Keefe L, Tirosh O, Bishop DJ, Voisin S, Eynon N (2018) ACE I/D gene variant predicts ACE enzyme content in blood but not the ACE, UCP2, and UCP3 protein content in human skeletal muscle in the Gene SMART study. J Appl Physiol 125:923–930
Zervou S, Whittington HJ, Ostrowski PJ, Cao F, Tyler J, Lake HA, Neubauer S, Lygate CA (2017) Increasing creatine kinase activity protects against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury but not against anthracycline toxicity in vitro. PLoS ONE 12:e0182994
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Cassie Albury for assistance with the molecular methods used in this manuscript.
Funding
This research was chiefly supported by the Commonwealth Collaborative Research Network funding to Bond University CRN-AESS. Mr. Nicholas Harvey was supported by a Ph.D. stipend also provided by Bond University CRN-AESS. This research was also supported by infrastructure purchased with Australian Government EIF Super Science Funds as part of the Therapeutic Innovation Australia—Queensland Node project (LRG). Nir Eynon is supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council, Australia (NHMRC CDF# APP1140644).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee (Gene SMART study: VU human research ethics committee: HRE13-233; QUT human research ethics committee: 1600000342; Hawaiian Ironman triathlon study: QUT Human Research Ethics Committee: 1300000499) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Communicated by Stefan Hohmann.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harvey, N.R., Voisin, S., Dunn, P.J. et al. Genetic variants associated with exercise performance in both moderately trained and highly trained individuals. Mol Genet Genomics 295, 515–523 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01639-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01639-8