Abstract
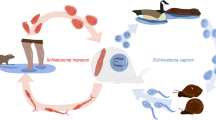
Toxocara tanuki is a common large roundworm in raccoon dogs. Experimental infection studies of T. tanuki in mice were conducted to clarify the distribution and infectivity of larvae in tissue. Groups of BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice (n = 5 mice/group) were each inoculated with 1000 embryonated T. tanuki eggs and necropsied at 7, 31, 91, and 182 days post inoculation (dpi). The number of larvae in the central nervous system, heart, lungs, kidneys, spleen, gastrointestinal tract, liver, and carcass was examined. Larvae obtained from the aforementioned mice on different days of the necropsy were orally inoculated into four groups of ICR mice (n = 6 mice/group) that were then necropsied at 21 dpi. Larvae were recovered from all mice. In the BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice, most of the larvae (> 88.7%) were recovered from the liver and the remainder from other tissues. The total number of larvae recovered from C57BL/6 mice was significantly higher than that from BALB/c mice, but no difference in the relative larval distribution within the viscera between the two mouse strains was observed. The mean recovery percentage of larvae from ICR mice infected with 182-day-old tissue larvae was 3.3%. Our findings showed that T. tanuki larvae migrated predominantly to the liver of mice and that the larvae maintained their infectivity for at least half a year.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data presented here are available upon request.
References
Akao N, Ohta N (2007) Toxocariasis in Japan. Parasitol Int 56:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2007.01.009
Alexander U, Lim CW, Kim B, Hong EJ, Kim HC, Park BK (2018) Morphological and molecular characterization of Toxocara tanuki (Nematoda: Ascaridae) from Korean raccoon dog, Nyctereutes procyonoides koreensis. Korean J Parasitol 56:567–575. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2018.56.6.567
Al-Sabi MNS, Chriél M, Jensen TH, Enemark HL (2013) Endoparasites of the raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides) and the red fox (Vulpes vulpes) in Denmark 2009–2012 - A comparative study. Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl 2:144–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijppaw.2013.04.001
Bekele F, Shumbej T (2019) Fruit and vegetable contamination with medically important helminths and protozoans in Tarcha town, Dawuro zone, South West Ethiopia. Res Rep Trop Med 10:19–23. https://doi.org/10.2147/rrtm.s205250
Fisher M (2003) Toxocara cati: an underestimated zoonotic agent. Trends Parasitol 19:167–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1471-4922(03)00027-8
Hamilton CM, Stafford P, Pinelli E, Holland CV (2006) A murine model for cerebral toxocariasis: characterization of host susceptibility and behaviour. Parasitology 132:791–801
Hoffmeister B, Glaeser S, Flick H, Pornschlegel S, Suttorp N, Bergmann F (2007) Cerebral toxocariasis after consumption of raw duck liver. Am J Trop Med Hyg 76:600–602. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.2007.76.600
Kłapeć T, Borecka A (2012) Contamination of vegetables, fruits and soil with geohelmints eggs on organic farms in Poland. Ann Agric Environ Med 19:421–425
Laurimaa L, Süld K, Davison J, Moks E, Valdmann H, Saarma U (2016) Alien species and their zoonotic parasites in native and introduced ranges: the raccoon dog example. Vet Parasitol 219:24–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2016.01.020
Matoba Y, Yamada D, Asano M et al (2006) Parasitic helminths from feral raccoons (Procyon lotor) in Japan. Helminthologia 43:139–146
Moorhouse DE (1982) Toxocariasis: a possible cause of the Palm Island mystery disease. Med J Aust 1:172–173
Morimatsu Y, Akao N, Akiyoshi H, Kawazu T, Okabe Y, Aizawa H (2006) Case reports: a familial case of visceral larva migrans after ingestion of raw chicken livers: appearance of specific antibody in broncho alveolar lavage fluid of the patients. Am J Trop Med Hyg 75:303–306. https://doi.org/10.4269/ajtmh.2006.75.303
Nagakura K, Tachbana H, Kaneda Y, Kato Y (1989) Toxocariasis possibly caused by ingesting raw chicken. J Infect Dis 160:735–736. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/160.4.735
Navajas M, Cotton D, Kreiter S, Gutierrez J (1992) Molecular approach in spider mites (Acari: Tetranychidae): preliminary data on ribosomal DNA sequences. Exp Appl Acarol 15:211–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01246563
Noh Y, Hong ST, Yun JY, Park HK, Oh JH, Kim YE, Jeon BS (2012) Meningitis by Toxocara canis after ingestion of raw ostrich liver. J Korean Med Sci 27:1105–1108. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.9.1105
Okada N, Ooi HK, Taira K (2021) Detection of larvae of Toxocara cati and T. tanuki from the muscles of free-ranging layer farm chickens. Parasitol Res 120:1737–1741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-021-07115-w
Okamoto T (1986) Experimental studies of visceral larva migrans with Toxocara tanuki Yamaguti, 1941. Jpn J Parasitol 35:355–364 (In Japanese with English summary)
Pitra C, Schwarz S, Fickel J (2010) Going west-invasion genetics of the alien raccoon dog Nyctereutes procynoides in Europe. Eur J Wildl Res 56:117–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-009-0283-2
Salem G, Schantz P (1992) Toxocaral visceral larva migrans after ingestion of raw lamb liver. Clin Infect Dis 15:743–744
Sato H, Inaba T, Ihama Y, Kamiya H (1999) Parasitological survey on wild carnivora in North-Western Tohoku, Japan. J Vet Med Sci 61:1023–1026. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.61.1023
Sato H, Suzuki K, Aoki M (2006) Nematodes from raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides viverrinus) introduced recently on Yakushima Island, Japan. J Vet Med Sci 68:693–700. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.68.693
Stürchler D, Weiss N, Gassner M (1990) Transmission of toxocariasis. J Infect Dis 162:571–571. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/162.2.571
Taira K, Permin A, Kapel CMO (2003) Establishment and migration pattern of Toxocara canis larvae in chickens. Parasitol Res 90:521–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-003-0894-6
Taira K, Saitoh Y, Kapel CMO (2011) Toxocara cati larvae persist and retain high infectivity in muscles of experimentally infected chickens. Vet Parasitol 180:287–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.03.020
Taira K, Yanagida T, Akazawa N, Saitoh Y (2013) High infectivity of Toxocara cati larvae from muscles of experimentally infected rats. Vet Parasitol 196:397–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2013.03.012
Uchida A, Uchida K, Kawakami Y, Murata Y (1999) Helminthological surveys of raccoon dogs captured in Tokyo and Kanagawa Prefectures. J Jpn Vet Med Assoc 52:715–721 (In Japanese with English summary)
Yoshikawa M, Koyama N, Hontsu S, Yamamoto Y, Ogawa S, Nakamura T, Mizuno Y, Miura S, Mikasa K, Kimura H (2010) Clinical analysis of eight patients with pulmonary toxocariasis. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi 48:351–356 (In Japanese with English summary)
Acknowledgements
We thanked Ms. Hiroka Kaneda for her technical assistance.
Funding
This study was partially supported by the Center for Human and Animal Symbiosis Science, Azabu University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NO and KT substantially contributed to the study conceptualization. NO and KT significantly contributed to data analysis and interpretation. NO, KT, and HKO contributed to the manuscript drafting. All authors critically reviewed and revised the manuscript draft and approved the final version for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study was carried out in accordance with the rules and regulations set by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Azabu University (Permit Number: 190220–4).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Una Ryan
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Okada, N., Ooi, HK. & Taira, K. Toxocara tanuki larval distribution in mice and the infectivity of tissue larvae. Parasitol Res 122, 1327–1332 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-023-07832-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-023-07832-4