Abstract
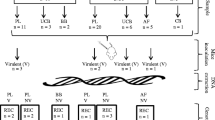
Advances in molecular epidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii are hampered by technical and cost-associated hurdles underlying the acquisition of genomic data from parasites. In order to implement an enhanced genotyping approach for molecular surveillance of T. gondii, we applied a multi-locus amplicon-based sequencing strategy to samples associated with human infection. This approach, targeting genome-dispersed polymorphic loci potentially involved in adaptation and virulence, genetically discriminated almost all 68 studied strains and revealed a scenario of marked genomic mosaicism. Two-thirds (n = 43) of all strains were classified as recombinant, although recombination seemed to be linked to the classical archetypal lineage. While 92% of the Sag2 archetype I strains revealed genetic mosaicism, only 45% of Sag2 archetype II strains were identified as recombinant. Contrarily to the virulence-associated archetype I, most type II strains (regardless of their recombination background) were non-virulent in mouse. Besides Sag2, some of the newly studied loci (namely the type I/I-like alleles of Sag1, B17, PK1, and Sag3 and type III/III-like alleles of TgM-A) constitute promising candidates to rapidly infer T. gondii mouse virulence. Our successful attempt to capture microsatellite length variation launches good perspectives for the straightforward transition from the laborious intensive historical method to more informative next-generation sequencing (NGS)/bioinformatics-based methodologies. Overall, while T. gondii whole-genome sequencing will be hardly feasible in most laboratories, this study shows that a discrete loci panel has the potential to improve the molecular epidemiology of T. gondii towards a better monitoring of circulating genotypes with clinical importance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajzenberg D, Dumètre A, Dardé ML (2005) Multiplex PCR for typing strains of Toxoplasma gondii. J Clin Microbiol 43:1940–1943. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.43.4.1940-1943.2005
Ajzenberg D, Pelloux H, Quinio D, Thulliez P, Cuisenier B, Desbois N, Aubert D, Robert-Gangneux F, Pratlong F, Kauffmann-Lacroix C, Nevez G, Delhaes L, Rabodonirina M, Dardé M, Duhamel C, Totet A, Gay-Andrieu F, Dalle F, Bessières M, Yera H, Villena I, Menotti J, Duong TH, Marty P, Bougnoux M, Franck J, Paris L, Pujol S, Bonnabau H, Carme B, Flori P, Filisetti D (2009) Genotype of 88 Toxoplasma gondii Isolates Associated with Toxoplasmosis in Immunocompromised Patients and Correlation with Clinical Findings. J Infect Dis 199:1155–1167. https://doi.org/10.1086/597477
Ajzenberg D, Collinet F, Mercier A, Vignoles P, Dardé ML (2010) Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii isolates with 15 microsatellite markers in a single multiplex PCR assay. J Clin Microbiol 48:4641–4645. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01152-10
Borges V, Pinheiro M, Pechirra P, Guiomar R, Gomes JP (2018) INSaFLU: an automated open web-based bioinformatics suite “from-reads” for influenza whole-genome-sequencing-based surveillance. Genome Med 10:46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-018-0555-0
Bossi P, Bricaire F (2004) Severe acute disseminated toxoplasmosis. Lancet (London, England) 364:579. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16841-4
Boyle JP, Rajasekar B, Saeij JPJ, Ajioka JW, Berriman M, Paulsen I, Roos DS, Sibley LD, White MW, Boothroyd JC (2006) Just one cross appears capable of dramatically altering the population biology of a eukaryotic pathogen like Toxoplasma gondii. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:10514–10519. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0510319103
Carriço JA, Silva-Costa C, Melo-Cristino J, Pinto FR, de Lencastre H, Almeida JS, Ramirez M (2006) Illustration of a common framework for relating multiple typing methods by application to macrolide-resistant Streptococcus pyogenes. J Clin Microbiol 44:2524–2532. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.02536-05
Dardé ML (2008) Toxoplasma gondii , “new” genotypes and virulence. Parasite 15:366–371. https://doi.org/10.1051/parasite/2008153366
de Melo Ferreira A, Vitor RWA, Gazzinelli RT, Melo MN (2006) Genetic analysis of natural recombinant Brazilian Toxoplasma gondii strains by multilocus PCR–RFLP. Infect Genet Evol 6:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEEGID.2004.12.004
Dubey JP, Jones JL (2008) Toxoplasma gondii infection in humans and animals in the United States. Int J Parasitol 38:1257–1278. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJPARA.2008.03.007
Dubey JP, López-Torres HY, Sundar N, Velmurugan GV, Ajzenberg D, Kwok OCH, Hill R, Dardé ML, Su C (2007) Mouse-virulent Toxoplasma gondii isolated from feral cats on Mona Island, Puerto Rico. J Parasitol 93:1365–1369. https://doi.org/10.1645/GE-1409.1
Dubey JP, Rajendran C, Ferreira LR, Martins J, Kwok OCH, Hill DE, Villena I, Zhou H, Su C, Jones JL (2011) High prevalence and genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii isolated from goats, from a retail meat store, destined for human consumption in the USA. Int J Parasitol 41:827–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2011.03.006
Dubey JP, Hill DE, Rozeboom DW, Rajendran C, Choudhary S, Ferreira LR, Kwok OCH, Su C (2012) High prevalence and genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii isolated from organic pigs in northern USA. Vet Parasitol 188:14–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.03.008
Eldeek H, Ahmad A, El-Mokhtar M, Abdel Kader A, AM M, Mounib M (2017) Toxoplasma genotyping in congenital toxoplasmosis in Upper Egypt: evidence of type I strain. Parasitol Res 9:2393–2406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5541-8
Fazaeli A, Ebrahimzadeh A (2007) A new perspective on and re-assessment of SAG2 locus as the tool for genetic analysis of Toxoplasma gondii isolates. Parasitol Res 101:99–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0449-8
Ferreira IMR, Vidal JE, de Mattos C d CB, de Mattos LC, Qu D, Su C, Pereira-Chioccola VL (2011) Toxoplasma gondii isolates: Multilocus RFLP–PCR genotyping from human patients in Sao Paulo State, Brazil identified distinct genotypes. Exp Parasitol 129:190–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EXPPARA.2011.06.002
Gajria B, Bahl A, Brestelli J, Dommer J, Fischer S, Gao X, Heiges M, Iodice J, Kissinger JC, Mackey AJ, Pinney DF, Roos DS, Stoeckert CJ, Wang H, Brunk BP (2008) ToxoDB: an integrated Toxoplasma gondii database resource. Nucleic Acids Res 36:D553–D556. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm981
Gelanew T, Hailu A, Scho’nian G, Lewis MD, Miles MA, Yeo M (2014) Multilocus sequence and microsatellite identification of intra-specific hybrids and ancestor-like donors among natural ethiopian isolates of leishmania donovani. Int J Parasitol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2014.05.008
Grigg ME, Sundar N (2009) Sexual recombination punctuated by outbreaks and clonal expansions predicts Toxoplasma gondii population genetics. Int J Parasitol 39:925–933. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJPARA.2009.02.005
Grigg ME, Ganatra J, Boothroyd JC, Margolis TP (2001) Unusual abundance of atypical strains associated with human ocular Toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis 184:633–639. https://doi.org/10.1086/322800
Herrmann DC, Pantchev N, Vrhovec GG, Barutzki D, Wilking H, Fröhlich A, Lüder CGK, Conraths FJ, Schares G (2010) Atypical Toxoplasma gondii genotypes identified in oocysts shed by cats in Germany. Int J Parasitol 40:285–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2009.08.001
Herrmann DC, Conraths FJ, Pantchev N, Vrhovec MG, Schares G, Maksimov A, Bärwald A (2012) Toxoplasma gondii sexual cross in a single naturally infected feline host: Generation of highly mouse-virulent and avirulent clones, genotypically different from clonal types I, II and III. Vet Res 43:39. https://doi.org/10.1186/1297-9716-43-39
Herrmann DC, Wibbelt G, Götz M, Conraths FJ, Schares G (2013) Genetic characterisation of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from European beavers (Castor fiber) and European wildcats (Felis silvestris silvestris). Vet Parasitol 191:108–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.VETPAR.2012.08.026
Hosseini SA, Amouei A, Sharif M, Sarvi S, Galal L, Javidnia J, Pagheh AS, Gholami S, Mizani A, Daryani A (2019) Human toxoplasmosis: a systematic review for genetic diversity of Toxoplasma gondii in clinical samples. Epidemiol Infect 147:e36. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268818002947
Howe DK, Honoré S, Derouin F, Sibley LD (1997) Determination of genotypes of Toxoplasma gondii strains isolated from patients with toxoplasmosis. J Clin Microbiol 35:1411–1414
Khan A, Taylor S, Su C, Mackey AJ, Boyle J, Cole R, Glover D, Tang K, Paulsen IT, Berriman M, Boothroyd JC, Pfefferkorn ER, Dubey JP, Ajioka JW, Roos DS, Wootton JC, Sibley LD (2005a) Composite genome map and recombination parameters derived from three archetypal lineages of Toxoplasma gondii. Nucleic Acids Res 33:2980–2992. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki604
Khan A, Su C, German M, Storch GA, Clifford DB, Sibley LD (2005b) Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii Strains from Immunocompromised Patients Reveals High Prevalence of Type I Strains. J Clin Microbiol 43:5881–5887. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.43.12.5881-5887.2005
Khan A, Fux B, Su C, Dubey JP, Darde ML, Ajioka JW, Rosenthal BM, Sibley LD (2007) Recent transcontinental sweep of Toxoplasma gondii driven by a single monomorphic chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:14872–14877. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0702356104
Lauron EJ, Tolia NH, Jimah JR, Khan A, Wang Q, Behnke MS, Sibley LD (2015) Rhoptry proteins ROP5 and ROP18 are major murine virulence factors in genetically divergent South American strains of Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS Genet 11:e1005434. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005434
Lehmann T, Marcet PL, Graham DH, Dahl ER, Dubey JP (2006) Globalization and the population structure of Toxoplasma gondii. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:11423–11428. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0601438103
Lorenzi H, Khan A, Behnke MS, Namasivayam S, Swapna LS, Hadjithomas M, Karamycheva S, Pinney D, Brunk BP, Ajioka JW, Ajzenberg D, Boothroyd JC, Boyle JP, Dardé ML, Diaz-Miranda MA, Dubey JP, Fritz HM, Gennari SM, Gregory BD, Kim K, Saeij JPJ, Su C, White MW, Zhu XQ, Howe DK, Rosenthal BM, Grigg ME, Parkinson J, Liu L, Kissinger JC, Roos DS, Sibley LD (2016) Local admixture of amplified and diversified secreted pathogenesis determinants shapes mosaic Toxoplasma gondii genomes. Nat Commun 7:13. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10147
Minot S, Melo MB, Li F, Lu D, Niedelman W, Levine SS, Saeij JPJ (2012) Admixture and recombination among Toxoplasma gondii lineages explain global genome diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:13458–13463. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1117047109
Pena HFJ, Gennari SM, Dubey JP, Su C (2008) Population structure and mouse-virulence of Toxoplasma gondii in Brazil. Int J Parasitol 38:561–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2007.09.004
Pinto M, Borges V, Antelo M, Pinheiro M, Nunes A, Azevedo J, Borrego MJ, Mendonça J, Carpinteiro D, Vieira L, Gomes JP (2016) Genome-scale analysis of the non-cultivable Treponema pallidum reveals extensive within-patient genetic variation. Nat Microbiol 2:16190. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.190
Robertson LJ, Clark CG, Debenham JJ, Dubey JP, Kváč M, Li J, Ponce-Gordo F, Ryan U, Schares G, Su C, Tsaousis AD (2019) Are molecular tools clarifying or confusing our understanding of the public health threat from zoonotic enteric protozoa in wildlife? Int J Parasitol. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJPPAW.2019.01.010
Rosenthal B, Ajioka J (2012) Population genetics, diversity, and spread of virulence in Toxoplasma gondii. In Sibley LD, Howlett BJ, Heitman J. Evolution of virulence in eukaryotic microbes. Wiley-Blackwell. (pp 231–235). https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118308165.ch24
Sibley LD, Ajioka JW (2008) Population Structure of Toxoplasma gondii: Clonal Expansion Driven by Infrequent Recombination and Selective Sweeps. Annu Rev Microbiol 62:329–351. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.62.081307.162925
Sibley LD, Boothroyd JC (1992) Construction of a molecular karyotype for Toxoplasma gondii. Mol Biochem Parasitol 51:291–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-6851(92)90079-Y
Sibley LD, Khan A, Ajioka JW, Rosenthal BM (2009) Genetic diversity of Toxoplasma gondii in animals and humans. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 364:2749–2761. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2009.0087
Su C, Evans D, Cole RH, Kissinger JC, Ajioka JW, Sibley LD (2003) Recent Expansion of Toxoplasma Through Enhanced Oral Transmission. Science 299:414–416. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1078035
Su C, Shwab EK, Zhou P, Zhu XQ, Dubey JP (2010) Moving towards an integrated approach to molecular detection and identification of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitology 137:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182009991065
Su C, Dubey JP, Ajzenberg D, Khan A, Ajioka JW, Rosenthal BM, Majumdar D, Darde M-L, Zhu X-Q, Sibley LD, Zhou P (2012) Globally diverse Toxoplasma gondii isolates comprise six major clades originating from a small number of distinct ancestral lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:5844–5849. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1203190109
Talundzic E, Ndiaye YD, Deme AB, Olsen C, Patel DS, Biliya S, Daniels R, Vannberg FO, Volkman SK, Udhayakumar V, Ndiaye D (2017) Molecular epidemiology of Plasmodium falciparum kelch13 mutations in senegal determined by using targeted amplicon deep sequencing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 61:e02116–e02116. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.02116-16
Van der Woude MW, Baumler AJ (2004) Phase and antigenic variation in bacteria. Clin Microbiol Rev 17:581–611. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.17.3.581-611.2004
Vijaykumar BR, Kant RS, Rajendran C, Lekshmi SU, Keerthana S, Mahadevan A, Shankar SK, Jayshree RS (2018) Restriction fragment length polymorphism-based genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii from autopsy-proven cases of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated cerebral toxoplasmosis. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 21:250–255. https://doi.org/10.4103/aian.AIAN_358_17
Vilares A, Gargaté MJ, Ferreira I, Martins S, Júlio C, Waap H, Ângelo H, Gomes JP (2014) Isolation and molecular characterization of Toxoplasma gondii isolated from pigeons and stray cats in Lisbon, Portugal. Vet Parasitol 205:506–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2014.08.006
Vilares A, Gargaté MJ, Ferreira I, Martins S, Gomes JP (2017) Molecular and virulence characterization of Toxoplasma gondii isolated from humans in Portugal. Parasitol Res 116:979–985. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5374-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Section Editor: Xing-Quan Zhu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vilares, A., Borges, V., Sampaio, D. et al. Towards a rapid sequencing-based molecular surveillance and mosaicism investigation of Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitol Res 119, 587–599 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-019-06523-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-019-06523-3