Abstract
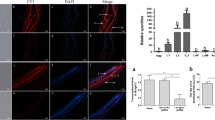
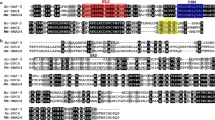
The components of the transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) signaling pathway in parasitic nematodes remain unknown. In this research, a type I receptor for TGF-β was isolated from the hookworm Ancylostoma caninum. The new gene was designated as Acdaf-1, a Caenorhabditis elegans daf-1 homolog. The full-length cDNA of Acdaf-1 encodes a 595-amino-acid protein with an NH2-terminal signal peptide. This protein has a cytoplasm tail (209-595aa region) which corresponds to the type 1a membrane topology. Between amino acid position 295–500, the protein contains the ATP binding site, substrate binding sites, and PKC-kinase-like domain. Real-time RT-PCR showed that the transcript was expressed in three main stages of A. caninum. It reached the maximal level in the female adult worm stage with lower transcript level in the first and second larvae (L1/L2) and intermediate level in L3 stages as well as in the male worms. After serum activation, the activity of Acdaf-1 was decreased in L3 larvae. These data implied that Acdaf-1 might relate to the infection ability of the larvae. Immunolocalization revealed that AcDAF-1 was present in eggs, intestine, and epidermis cells of larvae (L1, L2, and L3 stages) with strong signal in primordium of the gonads in L3 and was abundant in epidermis, intestine, and ovary of adult worm. These results suggested that Acdaf-1 might be involved in the interaction of the parasite and host relationship and provide a potential target for parasite control.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor-β
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- aa:
-
Amino acid
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription-PCR
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- CLM:
-
Cutaneous larvae migrans
- IPTG:
-
Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- ES:
-
Excretory/secretory
References
Allendorph GP, Vale WW, Choe S (2006) Structure of the ternary signaling complex of a TGF-beta superfamily member. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:7643–7648
Arasu P (2001) In vitro reactivation of Ancylostoma caninum tissue-arrested third-stage larvae by transforming growth factor-beta. J Parasitol 87:733–738
Barna J, Princz A, Kosztelnik M, Hargitai B, Takacs-Vellai K, Vellai T (2012) Heat shock factor-1 intertwines insulin/IGF-1, TGF-beta and cGMP signaling to control development and aging. BMC Dev Biol 12:32
Brand AM, Varghese G, Majewski W, Hawdon JM (2005) Identification of a DAF-7 ortholog from the hookworm Ancylostoma caninum. Int J Parasitol 35:1489–1498
Crook M (2014) The dauer hypothesis and the evolution of parasitism: 20 years on and still going strong. Int J Parasitol 44:1–8
Crook M, Grant WN (2013) Dominant negative mutations of Caenorhabditis elegans daf-7 confer a novel developmental phenotype. Dev Dyn 242:654–664
Crook M, Thompson FJ, Grant WN, Viney ME (2005) daf-7 and the development of Strongyloides ratti and Parastrongyloides trichosuri. Mol Biochem Parasitol 139:213–223
Estevez M, Attisano L, Wrana JL, Albert PS, Massague J, Riddle DL (1993) The daf-4 gene encodes a bone morphogenetic protein receptor controlling C. elegans dauer larva development. Nature 365:644–649
Fielenbach N, Antebi A (2008) C. elegans dauer formation and the molecular basis of plasticity. Genes Dev 22:2149–2165
Freitas TC, Arasu P (2005) Cloning and characterisation of genes encoding two transforming growth factor-beta-like ligands from the hookworm, Ancylostoma caninum. Int J Parasitol 35:1477–1487
Gallo M, Riddle DL (2009) Effects of a Caenorhabditis elegans dauer pheromone ascaroside on physiology and signal transduction pathways. J Chem Ecol 35:272–279
Georgi LL, Albert PS, Riddle DL (1990) daf-1, a C. elegans gene controlling dauer larva development, encodes a novel receptor protein kinase. Cell 61:635–645
Gerisch B, Weitzel C, Kober-Eisermann C, Rottiers V, Antebi A (2001) A hormonal signaling pathway influencing C. elegans metabolism, reproductive development, and life span. Dev Cell 1:841–851
Gilabert A, Curran DM, Harvey SC, Wasmuth JD (2016) Expanding the view on the evolution of the nematode dauer signalling pathways: refinement through gene gain and pathway co-option. BMC Genomics 17:476
Gumienny TL, Savage-Dunn C (2013) TGF-beta signaling in C. elegans. WormBook 1–34. https://doi.org/10.1895/wormbook.1.22.2
Gunther CV, Georgi LL, Riddle DL (2000) A Caenorhabditis elegans type I TGF beta receptor can function in the absence of type II kinase to promote larval development. Development 127:3337–3347
Gupta V, Harkin DP, Kawakubo H, Maheswaran S (2004) Transforming growth factor-beta superfamily: evaluation as breast cancer biomarkers and preventive agents. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 4:165–182
Huse M, Chen Y-G, Massagué J, Kuriyan J (1999) Crystal structure of the cytoplasmic domain of the type I TGF β receptor in complex with FKBP12. Cell 96:425–436
Inoue T, Thomas JH (2000a) Suppressors of transforming growth factor-beta pathway mutants in the Caenorhabditis elegans dauer formation pathway. Genetics 156:1035–1046
Inoue T, Thomas JH (2000b) Targets of TGF-beta signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans dauer formation. Dev Biol 217:192–204
Kiss JE, Gao X, Krepp JM, Hawdon JM (2009) Interaction of hookworm 14-3-3 with the forkhead transcription factor DAF-16 requires intact Akt phosphorylation sites. Parasit Vectors 2:21
Ludewig AH, Schroeder FC (2013) Ascaroside signaling in C. elegans. WormBook:1–22
Luo S, Kleemann GA, Ashraf JM, Shaw WM, Murphy CT (2010) TGF-beta and insulin signaling regulate reproductive aging via oocyte and germline quality maintenance. Cell 143:299–312
McGehee AM, Moss BJ, Juo P (2015) The DAF-7/TGF-beta signaling pathway regulates abundance of the Caenorhabditis elegans glutamate receptor GLR-1. Mol Cell Neurosci 67:66–74
Monsivais D, Matzuk MM, Pangas SA (2017) The TGF-beta family in the reproductive tract. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 9
Nielsen H, Engelbrecht J, Brunak S,von Heijne G (1997) Identification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic signal peptides and prediction of their cleavage sites. Protein Eng 10:1–6
Padgett RW (1999) TGFbeta signaling pathways and human diseases. Cancer Metastasis Rev 18:247–259
Padgett RW, Savage C, Das P (1997) Genetic and biochemical analysis of TGF beta signal transduction. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 8:1–9
Padgett RW, Das P, Krishna S (1998) TGF-beta signaling, Smads, and tumor suppressors. Bioessays 20:382–390
Patterson GI, Padgett RW (2000) TGF beta-related pathways. Roles in Caenorhabditis elegans development. Trends Genet 16:27–33
Rajan TV (1998) A hypothesis for the tissue specificity of nematode parasites. Exp Parasitol 89:140–142
Ren P, Lim CS, Johnsen R, Albert PS, Pilgrim D, Riddle DL (1996) Control of C. elegans larval development by neuronal expression of a TGF-beta homolog. Science 274:1389–1391
Savage-Dunn C (2005) TGF-beta signaling. WormBook 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1895/wormbook.1.22.2
Shaw WM, Luo S, Landis J, Ashraf J, Murphy CT (2007) The C. elegans TGF-beta Dauer pathway regulates longevity via insulin signaling. Curr Biol 17:1635–1645
Swofford DL (2002) PAUP*: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (* and other methods), 4.0b.10. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ(1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Viney ME (2009) How did parasitic worms evolve? BioEssays: news and reviews in molecular, cellular and developmental biology 31:496–499
Viney ME, Thompson FJ, Crook M (2005) TGF-beta and the evolution of nematode parasitism. Int J Parasitol 35:1473–1475
Yang Y, Wei H, Qin W, Zheng J (2009) Expression and characterization of aspartic protease gene in eggs and larvae stage of Ancylostoma caninum. Parasitol Res 104:1327–1333
Yang Y, Qin W, Wei H, Ying J, Zhen J (2011) Characterization of cathepsin B proteinase (AcCP-2) in eggs and larvae stages of hookworm Ancylostoma caninum. Exp Parasitol 129:215–220
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the China National Nature Science foundation (No. 30972181).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Section Editor: Xing-Quan Zhu
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Qiao, Y., Chen, J. et al. Gene structure and expression patterns of Acdaf-1, a TGF-β type I receptor in Ancylostoma caninum. Parasitol Res 118, 817–828 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-018-6142-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-018-6142-x