Abstract
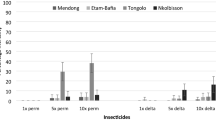
Resistance of mosquitoes to insecticides is a growing concern in India. Since only a few insecticides are used for public health and limited development of new molecules is expected in the next decade, maintaining the efficacy of control programs mostly relies on resistance management strategies. Developing such strategies requires a deep understanding of factors influencing resistance together with characterizing the mechanisms involved. Among factors likely to influence insecticide resistance in mosquitoes, agriculture and urbanization have been implicated but rarely studied in detail. In the present study, we evaluate the permethrin resistance and cross-resistance pattern of several insecticides in Culex quinquefasciatus mosquitoes. After 10 generation of selection with permethrin, the LC50 value for both larvae and adult Cx. quinquefasciatus was increased by 17.3- and 17.1-folds compared with susceptible strain. Detoxification enzyme profiles and native PAGE electrophoresis of esterase isoenzyme further revealed that esterase and CytP450 may be involved in permethrin resistance (PerRes) strain compared with susceptible strain. In addition to cross-resistance, study revealed that high resistance to cypermethrin (RR = 6.3, 8.8-folds). This study provided important information for understanding permethrin resistance and facilitating a better strategy for the management of resistance. These studies conclude that a strong foundation for further study of permethrin resistance mechanisms observed in Cx. quinquefasciatus mosquitoes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anspaugh DD, Rose LR, Koehler PG, Hodgson E, Roe RM (1994) Multiple mechanism of pyrethroid resistance in the German cockroach, Blattella germanica (L.). Pestic Biochem Physiol 50:138–148
Brogdon WG (1989) Biochemical resistance detection: an alternative to bioassay. Parasitol Today 5:56–60
CDC (2004) Evaluating mosquitoes for insecticide resistance-web based instruction. Centre for infectious disease, centre for disease control and prevention, (Accessed Oct 2004). www.cdc.gov/ncidod/wbt/resistance/toc.htm (2004)
Cheng Guilin LY, Yanchou J (1995) Cross resistant patterns of insecticide-selected strains of cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner). Res Pest Manag News 7:13–15
Feyereisen R (2005) Insect cytochrome P450. In Comprehensive Molecular Insect Science Edited by: Gilbert, L.I., Iatrou, K., Gill, S., Elsevier, Oxford pp. 1–77
Fonseca-González I, Cárdenas R, Quiñones ML, McAllister J, Brogdon WG (2009) Pyrethroid and organophosphates resistance in Anopheles (N.) nuneztovari Gabaldón populations from malaria endemic areas in Colombia. Parasitol Res 105:1399–1409
Grant DF, Dietze EC, Hammock BD (1991) Glutathione S-transferase isozyme in Aedes aegypti: purification, characterization, and isozyme specific regulation. Insect Biochem 4:511–523
Gubler D, Jeffery JAL, Thi Yen N, Nam VS, Nghia LT, Hoffmann AA, Kay BH, Ryan PA (2009) Characterizing the Aedes aegypti Population in a Vietnamese Village in Preparation for a Wolbachia-Based Mosquito Control Strategy to Eliminate Dengue. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 3;11: e-552
Gunning RV, Easton CS, Balfe M, Ferris IG (1991) Pyrethroid resistance mechanisms in Australian Helicoverpa armigera. Pestic Sci 33:473–490
Hansen IA, Marcombe S, Mathieu RB, Pocquet N, Riaz MA, Poupardin R, Sélior S, Darriet F, Reynaud S, Yébakima (2012) Insecticide resistance in the dengue vector Aedes aegypti from Martinique: distribution, mechanisms and relations with environmental factors. PLoS One 7;2: e30989
Hardstone MC, Leichter CA, Scott JG (2009) Multiplicative interaction between the two major mechanisms of Permethrin resistance, kdr and cytochrome P450-monooxygenase detoxification, in mosquitoes. J Evol Biol 22:416–423
Hemingway J, Hawkes NJ, McCarroll L, Ranson H (2004) The molecular basis of insecticide resistance in mosquitoes. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 34:653–665
Hemingway J, Beaty BJ, Rowland M, Scott TW, Sharp BL (2006) The Innovative Vector Control Consortium: improved control of mosquito-borne diseases. Trends Parasitol 22;7: 308–312
Hu Z, Du Y, Nomura Y, Dong KA (2011) Sodium channel mutation identified in Aedes aegypti selectively reduces cockroach sodium channel sensitivity to type I, but not type II pyrethroids. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 41(1):9–13
Kao CH, Hung CF, Sun CN (1989) Parathion and methyl parathion resistance in diamondback moth (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) larvae. J Econ Entomol 82:1299–1304
Kasai S, Shono T, Komagata O, Tsuda Y, Kobayashi M, Motoki M, Kashima I, Tanikawa T, Yoshida M, Tanaka I, Shinjo G, Hashimoto T, Ishikawa T, Takahashi T, Higa Y, Tomita T (2007) Insecticide resistance in potential vector mosquitoes for West Nile virus in Japan. J. Med. Entomol 44; 5: 822– 829
Koelle K, Gambhir M, Michael E (2008) Complex Ecological Dynamics and Eradicability of the Vector Borne Macroparasitic Disease, Lymphatic Filariasis. PLoS One 3;8: e-2874
Kranthi KR (2005) Insecticide resistance monitoring, mechanisms and management manual. Central Institute for Cotton Research. India pp. 78–82
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folins phenol reagent. J Bio Chem 193:265–275
Mebrahtu YB, Norem J, Taylor M (1997) Inheritance of larval resistance to permethrin in Aedes aegypti and association with sex ratio distortion and life history variation. Am J Trop Med Hyg 56:456–465
Miller TA (1998) Mechanisms of resistance to pyrethroid insecticides. Parasitol. Today 4; 7: s3–s7
Molyneux DH, Malecela MN (2011) Neglected tropical diseases and the millennium development goals: why the “other diseases” matter: reality versus rhetoric. Parasit Vect 4:234
Muthusamy R, Shivakumar MS (2014) Resistance selection and molecular mechanisms of cypermethrin resistance in red hairy caterpillar (Amsacta albistriga Walker). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol In Press
Muthusamy R, Shivakumar MS (2015) Effect of lambda cyhalothrin and temephos on detoxification enzyme systems in Cx. quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae). J Env Biol 36:235–239
Muthusamy R, Suganya R, Gowri M, Shivakumar M (2013) Biochemical mechanisms of organophosphate and pyrethroid resistance in red hairy caterpillar Amsacta albistriga (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). J Saudi Society of Agric Sci 12:47–52
Nardini L, Christian RN, Coetzer N, Ranson H, Coetzee M, Koekemoer L.L (2012) Detoxification enzymes associated with insecticide resistance in laboratory strains of Anopheles arabiensis of different geographic origin. Parasit. Vect 5; 1: 113
Nazni WA, Kamaludin MY, Lee HL, Rogayah T, Sa’diyah I (2000) Oxidase activity in relation to insecticide resistance in vectors of public health importance. Trop Biomed 17:69–79
Paeporn P, Supaphathom K, Srisawat R, Komalamisra N, Deesin V, Ya umphan P, Leeming Sawat S (2004) Biochemical detection of pyrethroid resistance mechanism in Aedes aegypti in Ratchaburi province. Thailand. Trop. Med 21; 2:145–151
Peng R, Maklokova VI, Chandrashekhar JH, Lan Q (2011). In vivo functional genomics studies of sterol carrier protein-2 gene in the yellow fever mosquito. PLoS One. 6; 3: e-18030
Powers AM, Soumahoro MK, Boelle PY, Gaüzere BA, Atsou K, Pelat C, Lambert B, La Ruche G, Gastellu-Etchegorry M, Renault P (2011) The Chikungunya Epidemic on La Réunion Island in 2005–2006: a cost-of-illness study. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis 5; 6: e1197
Ramkumar G, Karthi S, Muthusamy R, Natarajan D, Shivakumar MS (2015) Adulticidal and smoke toxicity of Cipadessa baccifera (Roth) plant extracts against Anopheles stephensi, Aedes aegypti, and Culex quinquefasciatus. Parasitol Res 114:167–173
Recep A, Sibel Y (2012) Inheritance and detoxification enzyme levels in Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae) strain selected with chlorpyrifos. J Pest Sci 83:85–93
Rodríguez MM, Bisset JA, Fernandez DM, Soca A (2000) Malathion resistance in Aedes aegypti and Culex quinquefasciatus after its use in Aedes aegypti control programs. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc 16; 4: 324–330
Rodríguez MM, Bisset JA, Fernandez DM (2007) Levels of insecticide resistance and resistance mechanisms in Aedes aegypti from some Latin American countries. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc 23; 4: 510–519
Sahgal AS, Kumar MKK (1994) Microplate assay of elevated esterase activity in individual pyrethroid-resistant mosquitoes. J Biosci 19:193–199
Scott JG, Liu N, Wen Z (1998) Insect cytochromes P450: diversity, insecticide resistance and tolerance to plant toxins. Comp Biochem Physiol C 121:147–155
Shankarganesh K, Walia S, Dhingra S, Subrahmanyam B, Ramesh Babu S (2012) Effect of dihydrodillapiole on pyrethroid resistance associated esterase inhibition in an Indian strain of Spodoptera litura (Fabricius), Pestic. Biochem Physiol 102:86–90
Somwang P, Yanola J, Suwan W, Walton C, Lumjuan N, Prapanthadara L (2011) Somboon L (2011) Enzymes-based resistant mechanism in pyrethroid resistant and susceptible Aedes aegypti strains from northern Thailand. Parasitol Res 109:531–537
Strode C, Wondji CS, David JP, Hawkes NJ, Lumjuan N, Parakrama NDR, Karunaratne SHP, Hemingway J, Black WC IV, Ranson H (2008) Genomic analysis of detoxification genes in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 38:113–123
Styer LM, Lim PY, Louie KL, Albright RG, Kramer LD, Bernard KA (2010) Mosquito saliva causes enhancement of West Nile virus infection in mice. J Virol 854:1517–1527
Swain V, Seth RK, Mohanty SS, Raghavendra K (2008) Effect of temperature on development, eclosion, longevity and survivorship of malathion-resistant and malathion-susceptible strain of Culex quinquefasciatus. Parasitol Res 103:299–303
Swain V, Seth RK, Raghavendra K, Mohanty SS (2009) Characterization of biochemical based insecticide resistance mechanism by thermal bioassay and the variation of esterase activity in Culex quinquefasciatus. Parasitol Res 104:1307–1313
Tan W, Wang X, Quan X, Gao H (2012) Cloning and overexpression of transferring gene from cypermethrin-resistant Culex pipiens pallens. Parasitol Res 110:939–959
Tikar N, Arkaja Kumar GBK, Prasad S (2009) Temephos-induced resistance in Aedes aegypti and its cross-resistance studies to certain insecticides from India. Parasitol Res 105:57–63
Urmila J, Vijayan VA (2009) Biochemical characterization of deltamethrin resistance in a laboratory-selected strain of Aedes aegypti. Parasitol Res 104:1431–1438
White MT, Griffin JT, Churcher TS, Ferguson NM, Basáñez MG, Ghani AC (2011) Modelling the impact of vector control interventions on Anopheles gambiae population dynamics. Parasit Vect 4:153
World Health Organization (1981) Instructions for determining the susceptibility or resistance of adult mosquitoes to organochlorine, organophosphate and carbamate insecticides, WHO/VBC/81.805, World Health Organization, Geneva
World Health Organization (2006) Pesticides and their application for the control of vectors and pests of public health importance, WHO/CDS/NTD/WHOPES/ GCDPP/2006
Xu Y, Yang M, Sun J, Qian J, Zhang D, Sun Y, Ma L, Zhu C (2008) Glycogen branching enzyme: a novel deltamethrin resistance-associated gene from Culex pipiens pallens. Parasitol Res 103; 2: 449–458
Acknowledgments
Infrastructural support provided by Department of Biotechnology, Periyar University, Salem, Tamil nadu, India is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramkumar, G., Shivakumar, M.S. Laboratory development of permethrin resistance and cross-resistance pattern of Culex quinquefasciatus to other insecticides. Parasitol Res 114, 2553–2560 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4459-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-015-4459-2