Abstract
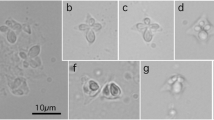
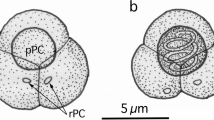
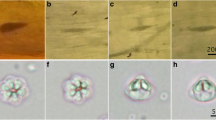
The myxosporean genus Unicapsula (Multivalvulida: Trilosporidae) is defined as having a spore with three unequal shell valves and polar capsules, of which one is prominent and the two other polar capsules are rudimentary. Genetic characterization of members of the genus, currently 11 nominal species, is, at present, unsatisfactory yet when comparing to the closely related genus Kudoa (Multivalvulida: Kudoidae). In the present study, we characterized long ribosomal RNA gene (rDNA) sequences of three Unicapsula spp., namely Unicapsula pyramidata, Unicapsula seriolae, and a novel myxosporean species, Unicapsula setoensis n. sp., from Asian fishes. Elongated plasmodia of U. pyramidata were found in the trunk muscle of Japanese threadfin breams, Nemipterus japonicus, fished off northern Vietnam in the South China Sea. Semitriangular spores, 5.5–6.4 μm in length and 5.6–9.6 μm in width, consisted of three shell valves with two caudal appendages, 7.2–7.4 μm in length. One prominent polar capsule, 2.0–2.4 μm in diameter, was located in the apical shell valve and two rudimentary polar capsules, 0.4–0.5 μm in diameter, in each caudal shell valve. Elongated plasmodia of U. seriolae were found in the trunk muscle of a greater yellowtail, Seriola dumerili, aquacultured in Japan. Semispherical spores, 5.9–7.4 μm in length and 6.3–7.4 μm in width, also consisted of three shell valves and one prominent polar capsule, 3.4–3.8 μm in diameter, with two rudimentary polar capsules, 0.7–1.0 μm in diameter. Plasmodia of U. setoensis n. sp. were found in the trunk muscle of yellowfin gobies, Acanthogobius flavimanus, fished off Hofu, Yamaguchi Prefecture, in the Inland Sea of Japan. Semispherical spores, 5.6–6.9 μm in diameter, displayed three shell valves and one prominent and two rudimentary polar capsules. The former functional polar capsule was 1.9–2.5 μm in diameter and extruded a 9.4–13.8-μm-long polar filament. Nearly the whole length of the 18S rDNA and more than 2,200 bp of the 28S rDNA of the three Unicapsula spp. were sequenced along with nucleotide sequences of the 5.8S rDNA and internal transcribed spacer-1 and spacer-2 of U. pyramidata and U. setoensis n. sp. Molecular genetic analyses supported the morphological species differentiation of U. pyramidata and U. seriolae, and the distinctness of U. setoensis n. sp. from hitherto known species.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alama-Bermejo G, Cuadrado M, Raga JA, Holzer AS (2009) Morphological and molecular redescription of the myxozoan Unicapsula pflugfelderi Schubert, Sprague & Reinboth 1975 from two teleost hosts in the Mediterranean. A review of the genus Unicapsula Davis 1924. J Fish Dis 32:335–350
Anisimova M, Gascuel O (2006) Approximate likelihood-ratio test for branches: a fast, accurate, and powerful alternative. Syst Biol 55:539–552
Baxa DV, Stover A, Clifford M, Kurobe T, The SJ, Moyle P, Hedrick RP (2013) Henneguya sp. in yellowfin goby Acanthogobius flavimanus from the San Francisco Estuary. SpringerPlus 2:420 [http://www.springerplus.com/content/2/1/420]
Bell JD, Steffe AS, Talbot RB (1987) The Oriental goby, Acanthogobius flavimanus, colonizes a third estuary in New Sourth Wales, Australia. Jpn J Ichthyol 34:227–230
Brittan MR, Albrecht AB, Hopkirk JB (1963) An Oriental goby collected in the San Joaquin River Delta near Stockton, California. Calif Fish Game 49:302–304
Dereeper A, Guignon V, Blanc G, Audic S, Buffet S, Chevenet F, Dufayard JF, Guindon S, Lefort V, Lescot M, Claverie J-M, Gascuel O (2008) Phylogeny.fr: robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res 36:465–469
Egusa S, Nakajima K (1980) Kudoa amamiensis n. sp. (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) found in cultured yellow-tails and wild daselfishes from Amami-Oshima and Okinawa, Japan. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 46:1193–1198
Eiras JC, Saraiva A, Cruz C (2014) Synopsis of the species of Kudoa Meglitsch, 1947 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Multivalvulida). Syst Parasitol 87:153–180
Grabner DS, Yokoyama H, Shirakashi S, Kinami R (2012) Diagnostic PCR assays to detect and differentiate Kudoa septempunctata, K. thyrsites and K. lateolabracis (Myxozoa, Multivalvulida) in muscle tissue of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Aquaculture 338–341:36–40
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704
Harada T, Kawai T, Sato H, Yokoyama H, Kumeda Y (2012a) Development of a quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay for detection of Kudoa septempunctata in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Int J Food Microbiol 155:161–167
Harada T, Kawai T, Jinnai M, Ohnishi T, Sugita-Konishi Y, Kumeda Y (2012b) Detection of Kudoa septempunctata 18S rDNA in patient fecal samples from novel foodborne outbreaks caused by consumption of raw olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). J Clin Microbiol 50:2964–2968
Hoshina T (1952) Notes on some myxosporidian parasites on fishes of Japan. J Tokyo Univ Fisheries 39:69–89
Jeon C-H, Wi S, Song J-Y, Choi H-S, Kim J-H (2014) Development of loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for detection of Kudoa septempunctata (Myxozoa: Multivalvulida) in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Parasitol Res. doi:10.1007/s00436-014-3821-0
Kawai T, Sekizuka T, Yahata Y, Kuroda M, Kumeda Y, Iijima Y, Kamata Y, Sugita-Konishi Y, Ohnishi T (2012) Identification of Kudoa septempunctata as the causative agent of novel food poisoning outbreaks in Japan by consumption of Paralichthys olivaceus in raw fish. Clin Infect Dis 54:1046–1052
Kent ML, Andree KB, Bartholomew JL, El-Matbouli M, Desser SS, Devlin RH, Feist SW, Hedrick RP, Hoffmann RW, Khattra J, Hallett SL, Lester RJG, Longshaw M, Palenzuela O, Siddall ME, Xiao C (2001) Recent advances in our knowledge of the Myxozoa. J Eukaryot Microbiol 48:395–413
Lester RJG (1982) Unicapsula seriolae n. sp. (Myxosporea, Multivalvulida) from Australian yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi. J Protozool 29:584–587
Li Y-C, Sato H, Tanaka S, Ohnishi T, Kamata Y, Sugita-Konishi Y (2013) Characterization of the ribosomal RNA gene of Kudoa neothunni (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) in tunas (Thunnus spp.) and Kudoa scomberi n. sp. in a chub mackerel (Scomber japonicus). Parasitol Res 112:1991–2003
Lom J, Dyková I (2006) Myxozoan genera: definition and notes on taxonomy, life-cycle terminology and pathogenic species. Folia Parasitol 53:1–36
Lom J, Noble ER (1984) Revised classification of the class Myxosporea Bütschli, 1881. Folia Parasitol 31:193–205
Matsukane Y, Sato H, Tanaka S, Kamata Y, Sugita-Konishi Y (2010) Kudoa septempunctata n. sp. (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida) from an aquacultured olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) imported from Korea. Parasitol Res 107:865–872
Matsukane Y, Sato H, Tanaka S, Kamata Y, Sugita-Konishi Y (2011) Kudoa iwatai and two novel Kudoa spp., K. trachuri n. sp. and K. thunni n. sp. (Myxosporea: Multivalvulida), from daily consumed marine fish in western Japan. Parasitol Res 108:913–926
Miller TL, Adlard RD (2013) Unicapsula species (Myxosporea: Trilosporidae) of Australian marine fishes, including the description of Unicapsula andersenae n. sp. in five teleost families off Queensland, Australia. Parasitol Res 112:2945–2957
Moran JDW, Whitaker DJ, Kent ML (1999) A review of the myxosporean genus Kudoa Meglitsch, 1947, and its impact on the international aquaculture industry and commercial fisheries. Aquaculture 172:163–196
Naidjenova NN, Zaika VE (1970) Three new genera of myxosporean parasites of fish from the Indian Ocean. Zool Zh 49:451–454 (in Russian with English summary)
Nakada M (2008) Capture-based aquaculture of yellowtail. In: Lovatelli A, Holthus PF (eds) Capture-based aquaculture: global overview. FAO Fisheries Technical Paper, No. 508. FAO, Rome, pp 199–215
Sato H (2011) Biology of the Myxozoa, a newly recognized parasitic pathogen causing food poisoning. Yamaguchi J Vet Med 38:1–26 (in Japanese with English summary)
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Whipps CM, Grossel G, Adlard RD, Yokoyama H, Bryant MS, Munday BL, Kent ML (2004) Phylogeny of the Multivalvulidae (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) based on comparative ribosomal DNA sequence analysis. J Parasitol 90:618–622
Yokoyama H (2003) A review: gaps in our knowledge on myxozoan parasites of fishes. Fish Pathol 38:125–136
Yokoyama H, Freeman MA, Yoshinaga T, Ogawa K (2004) Myxobolus buri, the myxosporean parasite causing scoliosis of yellowtail, is synonymous with Myxobolus acanthogobii infecting the brain of the yellowfin goby. Fisheries Sci 70:1036–1042
Yokoyama H, Abe N, Maehara T, Suzuki J (2014) First record of Unicapsula seriolae (Myxozoa: Multivalvulida) from the muscle of Malabar grouper Epinephelus malabaricus in Japan. Parasitol Int. doi:10.1016/j.parint.2014.03.002
Zhou LS, Li-Chan ECY (2009) Effect of Kudoa spores, endogenous protease activity and frozen storage on cooked texture of minced Pacific hake (Merluccius productus). Food Chem 11:1076–1082
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid (H25-shokuhin-ippan) from the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomochi, H., Li, YC., Tran, B.T. et al. Three Unicapsula species (Myxosporea: Trilosporidae) of Asian marine fishes, including the description of Unicapsula setoensis n. sp. in the yellowfin goby (Acanthogobius flavimanus) from the Inland Sea of Japan. Parasitol Res 113, 3807–3816 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4048-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-4048-9