Abstract
Purpose
Radiotherapy is an integral treatment for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); however, radiation-induced toxicities such as radiation pneumonitis (RP) present a considerable challenge. Herein, we aimed to evaluate the potential of salivary metabolomics as an independent risk factor for predicting RP.
Methods
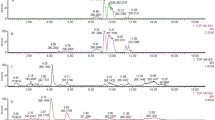
This study included 62 consecutive patients with NSCLC who underwent thoracic radiotherapy at Tokyo Medical University between September 2016 and December 2018. The median age of the patients was 75 years (range: 41–89), comprising 47 (75.8%) males and 15 (24.2%) females. Patients with stage I NSCLC received 75 Gy in 30 fractions, whereas those with stage II and III NSCLC received 66 Gy in 33 fractions. Saliva samples were collected before treatment and at 2 weeks, 1 month, 3 months, and 1 year after initiating radiotherapy. Clinical RP was defined as grade 2 according to the Common Toxicity Criteria for Adverse Events. Salivary metabolomics were analyzed using capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. Salivary metabolites were evaluated as potential predictors of RP.
Results
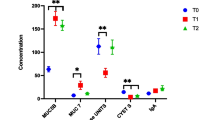
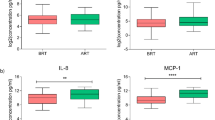
Clinical RP was observed in 11 patients (17.7%); no RP-related deaths were observed. Clinical RP developed at a median of 4 months (range: 2–6 months) after initiating radiotherapy. Three metabolites, butyrate, propionate, and hexanoate, collected before radiotherapy exhibited predictive ability for clinical RP. Multivariate logistic analysis indicated butyrate (P = 0.033) as a predictive factor, along with the previously known factor of lung volume irradiated with > 20 Gy (P = 0.045).
Conclusion
Salivary metabolite butyrate was an independent risk factor for clinical RP.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Research data are not available at this time. The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Arpaia N, Campbell C, Fan X et al (2013) Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature 504:451–455. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12726
Arroyo-Hernández M, Maldonado F, Lozano-Ruiz F, Muñoz-Montaño W, Nuñez-Baez M, Arrieta O (2021) Radiation-induced lung injury: current evidence. BMC Pulm Med 21:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-020-01376-4
Asai Y, Itoi T, Sugimoto M et al (2018) Elevated polyamines in saliva of pancreatic cancer. Cancers (Basel) 10:43. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10020043
Carter CL, Jones JW, Farese AM, MacVittie TJ, Kane MA (2017) Lipidomic dysregulation within the lung parenchyma following whole-thorax lung irradiation: markers of injury, inflammation and fibrosis detected by MALDI-MSI. Sci Rep 7:10343. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10396-w
Chun SG, Hu C, Choy H et al (2017) Impact of intensity-modulated radiation therapy technique for locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a secondary analysis of the NRG oncology RTOG 0617 randomized clinical trial. J Clin Oncol 35:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.69.1378
Dallinga JW, Robroeks CM, van Berkel JJ et al (2010) Volatile organic compounds in exhaled breath as a diagnostic tool for asthma in children. Clin Exp Allergy 40:68–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2222.2009.03343.x
Dallmann R, Viola AU, Tarokh L, Cajochen C, Brown SA (2012) The human circadian metabolome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:2625–2629. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1114410109
Hanania AN, Mainwaring W, Ghebre YT, Hanania NA, Ludwig M (2019) Radiation-induced lung injury: assessment and management. Chest 156:150–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2019.03.033
Itonaga T, Mikami R, Nakayama H et al (2019) Phase II study of compensator-based non-coplanar intensity-modulated radiotherapy for stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. J Radiat Res 60:387–393. https://doi.org/10.1093/jrr/rrz009
Jelonek K, Pietrowska M, Widlak P (2017) Systemic effects of ionizing radiation at the proteome and metabolome levels in the blood of cancer patients treated with radiotherapy: the influence of inflammation and radiation toxicity. Int J Radiat Biol 93:683–696. https://doi.org/10.1080/09553002.2017.1304590
Liu Y, Wang W, Shiue K et al (2021) Risk factors for symptomatic radiation pneumonitis after stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol 156:231–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2020.10.015
Luna JM, Chao HH, Diffenderfer ES et al (2019) Predicting radiation pneumonitis in locally advanced stage II–III non-small cell lung cancer using machine learning. Radiother Oncol 133:106–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2019.01.003
National Cancer Center Japan (2023) Cancer statistics in Japan 2023. https://ganjoho.jp/public/qa_links/report/statistics/2023_en.html, Accessed Aug 14, 2023
Nose D, Sugimoto M, Muta T, Miura SI (2023) Salivary polyamines help detect high-risk patients with pancreatic cancer: a prospective validation study. Int J Mol Sci 24:2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032998
Palma DA, Senan S, Tsujino K et al (2013) Predicting radiation pneumonitis after chemoradiation therapy for lung cancer: an international individual patient data meta-analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85:444–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.04.043
Pang Z, Chong J, Zhou G et al (2021) MetaboAnalyst 5.0: narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Res 49:W388–W396. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab382
Silwood CJ, Lynch E, Claxson AW, Grootveld MC (2002) 1H and (13)C NMR spectroscopic analysis of human saliva. J Dent Res 81:422–427. https://doi.org/10.1177/154405910208100613
Spigel DR, Faivre-Finn C, Gray JE et al (2022) Five-year survival outcomes from the PACIFIC trial: durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 40:1301–1311. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.21.01308
Sugimoto M, Wong DT, Hirayama A, Soga T, Tomita M (2010) Capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry-based saliva metabolomics identified oral, breast and pancreatic cancer-specific profiles. Metabolomics 6:78–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-009-0178-y
Sugimoto M, Kawakami M, Robert M, Soga T, Tomita M (2012) Bioinformatics tools for mass spectroscopy-based metabolomic data processing and analysis. Curr Bioinform 7:96–108. https://doi.org/10.2174/157489312799304431
Sugimoto M, Ota S, Kaneko M, Enomoto A, Soga T (2020) Quantification of salivary charged metabolites using capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight-mass spectrometry. Bio Protoc 10:e3797. https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.3797
Takeda I, Stretch C, Barnaby P et al (2009) Understanding the human salivary metabolome. NMR Biomed 22:577–584. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1369
Tandberg DJ, Tong BC, Ackerson BG, Kelsey CR (2018) Surgery versus stereotactic body radiation therapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: a comprehensive review. Cancer 124:667–678. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.31196
Tomita A, Mori M, Hiwatari K et al (2018) Effect of storage conditions on salivary polyamines quantified via liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Sci Rep 8:12075. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30482-x
Utada M, Yonehara S, Ozasa K (2019) Historical changes in histological diagnosis of lung cancer. J Epidemiol 29:238–240. https://doi.org/10.2188/jea.JE20180037
Vicente E, Vujaskovic Z, Jackson IL (2020) A systematic review of metabolomic and lipidomic candidates for biomarkers in radiation injury. Metabolites 10:259. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10060259
Yang S, Yao Y, Dong Y et al (2021) Prediction of radiation pneumonitis using genome-scale flux analysis of RNA-seq derived from peripheral blood. Front Med (lausanne) 8:715961. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.715961
Yatsuoka W, Ueno T, Miyano K et al (2019) Metabolomic profiling reveals salivary hypotaurine as a potential early detection marker for medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. PLoS ONE 14:e0220712. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0220712
Yatsuoka W, Ueno T, Miyano K et al (2021) Time-course of salivary metabolomic profiles during radiation therapy for head and neck cancer. J Clin Med 10:2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10122631
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Kaneko, S. Ota, and A. Enomoto for their help with the sample measurements. This study was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (grant numbers JP19K08106, JP16K10404, and JP22H00595).
Funding
This study was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (grant numbers JP19K08106, JP16K10404, and JP22H00595).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conception and design of the study. Material preparation and data collection were performed by SS. Analysis was performed by MS and KT. The first draft of the manuscript was written by SS and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
The Ethics Committee of Tokyo Medical University Hospital granted permission to conduct a cohort study to investigate radiation pneumonitis using salivary metabolomics to treat lung cancer (SH4092).
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants of this study.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shiraishi, S., Sugimoto, M. & Tokuuye, K. Salivary metabolites as novel independent predictors of radiation pneumonitis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 17559–17566 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05479-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05479-3