Abstract
Background
Skin cutaneous melanoma (SKCM) is a highly aggressive disease with a poor prognosis for advanced tumors. Anoikis is a caspase-dependent cell death process triggered by extracellular matrix (ECM) detachment, rectifies detachment-induced metabolic defects that compromise cell survival, recent study revealed the crucial role of anoikis for cancer cells to survive during metastasis. However, limited research focused on the role of anoikis in SKCM.
Methods
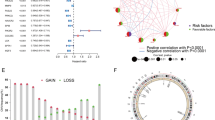
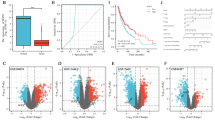
Our study utilized the 27 anoikis-related genes (ARGs) to divide SKCM patients into two clusters, and obtain differentially expressed genes (DEGs) for each cluster. These DEGs were used in stepwise Cox regression analysis to develop a prediction model for SKCM patients consisting of nine ARGs, called the anoikis-related signature (ARS). Subsequently, we used the risk scores calculated from the ARS to divide SKCM patients into two groups and explored differences in immune microenvironment, immune checkpoint reactivity, and drug sensitivity between the groups.
Results
Nine ARGs were identified to stratify SKCM patients into two risk groups, patients in the high-risk group had a poor prognosis and suppressed immune cell infiltration. Moreover, higher expression of immune checkpoint molecules and a greater sensitivity to immunotherapy and chemotherapy drugs were observed in the low-risk group. Finally, all of the ARS hub genes were found to be upregulated in SKCM tissues and cell lines.
Conclusion
A novel ARGs signature was identified for predicting the prognosis of SKCM. Based on the immune landscape associated with ARS discovered in our study, targeting ARS hub genes may be a promising treatment for SKCM.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
No sequencing was performed in this study, the datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the TCGA database (https://www.cancer.gov/ccg/research/genome-sequencing/tcga) and GEO database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/).
References
Bakir B, Chiarella AM, Pitarresi JR, Rustgi AK (2020) EMT, MET, plasticity, and tumor metastasis. Trends Cell Biol 30:764–776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2020.07.003
Blumenthal RD, Hansen HJ, Goldenberg DM (2005) Inhibition of adhesion, invasion, and metastasis by antibodies targeting CEACAM6 (NCA-90) and CEACAM5 (Carcinoembryonic Antigen). Cancer Res 65:8809–8817. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0420
Buchheit CL, Weigel KJ, Schafer ZT (2014) Cancer cell survival during detachment from the ECM: multiple barriers to tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 14:632–641. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3789
Cai J, Wei S, Wang B, Huang Y, Tang J, Lu Y et al (2013) Cloning and expression analysis of nonspecific cytotoxic cell receptor 1 (Ls-NCCRP1) from red snapper (Lutjanus sanguineus). Mar Genom 11:39–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2013.07.001
Chang C-C, Yang M-H, Lin B-R, Chen S-T, Pan S-H, Hsiao M et al (2013) CCN2 inhibits lung cancer metastasis through promoting DAPK-dependent anoikis and inducing EGFR degradation. Cell Death Differ 20:443–455. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.136
Charoentong P, Finotello F, Angelova M, Mayer C, Efremova M, Rieder D, Hackl H, Trajanoski Z (2017) Pan-cancer immunogenomic analyses reveal genotype-immunophenotype relationships and predictors of response to checkpoint blockade. Cell Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.019
Chen B-S, Xu Z-X, Xu X, Cai Y, Han Y-L, Wang J et al (2002) RhCG is downregulated in oesophageal squamous cell carcinomas, but expressed in multiple squamous epithelia. Eur J Cancer 38:1927–1936. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-8049(02)00190-9
Chiarugi P, Giannoni E (2008) Anoikis: A necessary death program for anchorage-dependent cells. Biochem Pharmacol 76:1352–1364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2008.07.023
Di Tucci C, Capone C, Galati G, Iacobelli V, Schiavi MC, Di Donato V et al (2019) Immunotherapy in endometrial cancer: new scenarios on the horizon. J Gynecol Oncol 30:e46. https://doi.org/10.3802/jgo.2019.30.e46
Gajiwala KS, Feng J, Ferre R, Ryan K, Brodsky O, Weinrich S et al (2013) Insights into the aberrant activity of mutant EGFR kinase domain and drug recognition. Structure 21:209–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2012.11.014
Gallimore A, Glithero A, Godkin A, Tissot AC, Plückthun A, Elliott T et al (1998) Induction and exhaustion of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes visualized using soluble tetrameric major histocompatibility complex class I-peptide complexes. J Exp Med 187:1383–1393. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.187.9.1383
Gilmore AP (2005) Anoikis. Cell Death Differ 12(Suppl 2):1473–1477. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401723
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R, Guinney J (2013) GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinformatics 14:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-7
Koufaris C, Kirmizis A (2020) N-terminal acetyltransferases are cancer-essential genes prevalently upregulated in tumours. Cancers (basel) 12:2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092631
Kroesen M, Büll C, Gielen PR, Brok IC, Armandari I, Wassink M et al (2016) Anti-GD2 mAb and vorinostat synergize in the treatment of neuroblastoma. Oncoimmunology 5:e1164919. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2016.1164919
Laikova KV, Oberemok VV, Krasnodubets AM, Gal’chinsky NV, Useinov RZ, Novikov IA et al (2019) Advances in the understanding of skin cancer: ultraviolet radiation, mutations, and antisense oligonucleotides as anticancer drugs. Molecules 24:1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24081516
Lee O-J, Son S-M, Hong KP, Lee Y-M, Kim M-Y, Choi J-W et al (2015) CEACAM6 as detected by the AP11 antibody is a marker notable for mucin-producing adenocarcinomas. Virchows Arch 466:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-014-1688-1
Li S, Zhang J, Qian S, Wu X, Sun L, Ling T et al (2021) S100A8 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis under TGF-β/USF2 axis in colorectal cancer. Cancer Commun (lond) 41:154–170. https://doi.org/10.1002/cac2.12130
Liu L, Lin J, He H (2019) Identification of potential crucial genes associated with the pathogenesis and prognosis of endometrial cancer. Front Genet 10:373. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00373
Liu H, Xu R, Gao C, Zhu T, Liu L, Yang Y et al (2021) Metabolic molecule PLA2G2D is a potential prognostic biomarker correlating with immune cell infiltration and the expression of immune checkpoint genes in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Front Oncol 11:755668. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.755668
Liu Y, Zhang Q, Xing B, Luo N, Gao R, Yu K et al (2022) Immune phenotypic linkage between colorectal cancer and liver metastasis. Cancer Cell 40:424-437.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2022.02.013
Ma H-L, Yu S-J, Chen J, Ding X-F, Chen G, Liang Y et al (2020) CA8 promotes RCC proliferation and migration though its expression level is lower in tumor compared to adjacent normal tissue. Biomed Pharmacother 121:109578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109578
Melanoma of the Skin - Cancer Stat Facts (n.d.). SEER. Available at: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/melan.html. Accessed 16 Jan 2023
Mendoza-Naranjo A, El-Naggar A, Wai DH, Mistry P, Lazic N, Ayala FRR et al (2013) ERBB4 confers metastatic capacity in Ewing sarcoma. EMBO Mol Med 5:1019–1034. https://doi.org/10.1002/emmm.201202343
Ming X-Y, Zhang X, Cao T-T, Zhang L-Y, Qi J-L, Kam N-W et al (2018) RHCG suppresses tumorigenicity and metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via inhibiting NF-κB signaling and MMP1 expression. Theranostics 8:185–198. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.21383
Misawa K, Kanazawa T, Imai A, Endo S, Mochizuki D, Fukushima H et al (2014) Prognostic value of type XXII and XXIV collagen mRNA expression in head and neck cancer patients. Mol Clin Oncol 2:285–291. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2013.233
Miwa T, Kanda M, Koike M, Iwata N, Tanaka H, Umeda S et al (2017) Identification of NCCRP1 as an epigenetically regulated tumor suppressor and biomarker for malignant phenotypes of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Oncol Lett 14:4822–4828. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.6753
Orillion A, Hashimoto A, Damayanti N, Shen L, Adelaiye-Ogala R, Arisa S et al (2017) Entinostat neutralizes myeloid-derived suppressor cells and enhances the antitumor effect of PD-1 inhibition in murine models of lung and renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 23:5187–5201. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0741
Pang ALY, Clark J, Chan W-Y, Rennert OM (2011) Expression of human NAA11 (ARD1B) gene is tissue-specific and is regulated by DNA methylation. Epigenetics 6:1391–1399. https://doi.org/10.4161/epi.6.11.18125
Paoli P, Giannoni E, Chiarugi P (2013) Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Mol Cell Res 1833:3481–3498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.06.026
Real FX, Rettig WJ, Chesa PG, Melamed MR, Old LJ, Mendelsohn J (1986) Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor in human cultured cells and tissues: relationship to cell lineage and stage of differentiation. Cancer Res 46:4726–4731
Sun Z, Zhao Y, Wei Y, Ding X, Tan C, Wang C (2022) Identification and validation of an anoikis-associated gene signature to predict clinical character, stemness, IDH mutation, and immune filtration in glioblastoma. Front Immunol 13:939523. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.939523
Tsao H (2001) Genetics of nonmelanoma skin cancer. Arch Dermatol 137:1486–1492. https://doi.org/10.1001/archderm.137.11.1486
Vickers AJ, Cronin AM, Elkin EB, Gonen M (2008) Extensions to decision curve analysis, a novel method for evaluating diagnostic tests, prediction models and molecular markers. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6947-8-53
Viloria-Petit AM, Kerbel RS (2004) Acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors: mechanisms and prevention strategies. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:914–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2003.09.091
Wang T-K, Lin Y-M, Lo C-M, Tang C-H, Teng C-LJ, Chao W-T et al (2016) Oncogenic roles of carbonic anhydrase 8 in human osteosarcoma cells. Tumour Biol 37:7989–8005. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4661-y
Wu S-G, Shih J-Y (2018) Management of acquired resistance to EGFR TKI-targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer 17:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0777-1
Ye H, Yu T, Temam S, Ziober BL, Wang J, Schwartz JL et al (2008) Transcriptomic dissection of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Genomics 9:69. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-69
Yu Y, Song Y, Cheng L, Chen L, Liu B, Lu D et al (2022) CircCEMIP promotes anoikis-resistance by enhancing protective autophagy in prostate cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 41:188. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-022-02381-7
Zajac AJ, Blattman JN, Murali-Krishna K, Sourdive DJ, Suresh M, Altman JD et al (1998) Viral immune evasion due to persistence of activated T cells without effector function. J Exp Med 188:2205–2213. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.188.12.2205
Zaremba A, Zimmer L, Griewank KG, Ugurel S, Roesch A, Schadendorf D et al (2020) Immunotherapy for malignant melanoma. Internist (berl) 61:669–675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00108-020-00812-1
Zeng D, Ye Z, Shen R, Yu G, Wu J, Xiong Y et al (2021) IOBR: multi-omics immuno-oncology biological research to decode tumor microenvironment and signatures. Front Immunol 12:687975. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.687975
Zhang H-F, Hughes CS, Li W, He J-Z, Surdez D, El-Naggar AM et al (2021) Proteomic screens for suppressors of anoikis identify IL1RAP as a promising surface target in Ewing sarcoma. Cancer Discov 11:2884–2903. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1690
Zhou J, Qian W, Huang C, Mai C, Lai Y, Lin Z et al (2022) Combined targeting of KRT23 and NCCRP1 as a potential novel therapeutic approach for the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Gland Surg 11:1673–1682. https://doi.org/10.21037/gs-22-486
Funding
The Wisdom Accumulation and Talent Cultivation Project of the Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University (YX202201); Outstanding Youth Project of Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2022JJ20093); Youth Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (82202391). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by ZY and DW. The first and revised draft of the manuscript was written by XL and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Central South University (Date2023.03.06/No快23128). And informed consent has been obtained from all subjects and/or their legal guardians.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, Z., Wang, D. & Li, X. A promising anoikis-related prognostic signature predicts prognosis of skin cutaneous melanoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 17757–17770 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05468-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05468-6