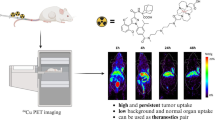
Abstract
Purpose
Nanobodies have become promising carriers due to excellent in vivo properties. Radiopharmaceutical therapy targeting programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) is an effective therapeutic strategy. Our study aimed to explore therapeutic efficacy of 131I labeled PD-L1 nanobody (Nb109) in non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) in vitro and in vivo.
Methods
131I-Nb109 was synthesized by chloramine-T method. We implemented stability analysis, SDS-PAGE and lipid-water partition coefficient test to assess its quality. Cell uptake assay and SPECT/CT scan were applied to evaluate its ability to target NSCLCs (H460 and A549). CCK8 assay and in vivo efficacy assay were conducted to estimate its therapeutic effect in H460 tumors. Damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) release in H460 cells incubated with 131I-Nb109 was investigated by western blot and ATP test kit.
Results
131I-Nb109 was hydrophilic with high labeling rate (69.51–98.06%), radiochemical purity (99.17% ± 0.76%) and stability. Cell uptake experiments showed that H460 cells (PD-L1 positive) compared with A549 cells (PD-L1 negative) had higher 131I-Nb109 uptake. SPECT/CT imaging revealed the accumulation of 131I-Nb109 in H460 tumor within 48 h. 131I-Nb109 inhibited H460 tumor growth without toxic side effects in contrast with control group. It also induced H460 cells to release DAMPs (adenosine triphosphate, high mobility group box 1, and heat shock protein 70).
Conclusion
131I-Nb109 had high stability, excellent ability to target and treatment PD-L1 positive tumors, and can improve tumor immunogenicity. The results of our study were expected to inspire the development of more novel radiopharmaceuticals to treat NSCLCs.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdel-Hameed ME, Farrag NS, Aglan H et al (2022) A new modality in targeted delivery of epirubicin for tumor theranosis based on PEGylated silver nanoparticles: Design, radiolabeling and bioevaluation. Int J Pharm 629:122358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.122358
Bannas P, Hambach J, Koch-Nolte F (2017) Nanobodies and nanobody-based human heavy chain antibodies as antitumor therapeutics. Front Immunol 8:1603. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01603
Carbone C, Piro G, Agostini A et al (2021) Intratumoral injection of TLR9 agonist promotes an immunopermissive microenvironment transition and causes cooperative antitumor activity in combination with anti-PD1 in pancreatic cancer. J Immunother Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2021-002876
Celikoglu F, Celikoglu SI, Goldberg EP (2008) Bronchoscopic intratumoral chemotherapy of lung cancer. Lung Cancer 61:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2008.03.009
Chen Y, Zhu S, Fu J et al (2022) Development of a radiolabeled site-specific single-domain antibody positron emission tomography probe for monitoring PD-L1 expression in cancer. J Pharm Anal 12:869–878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2022.09.001
Chitneni SK, Koumarianou E, Vaidyanathan G et al (2019) Observations on the effects of residualization and dehalogenation on the utility of N-succinimidyl ester acylation agents for radioiodination of the internalizing antibody trastuzumab. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213907
Christensen C, Kristensen LK, Alfsen MZ et al (2020) Quantitative PET imaging of PD-L1 expression in xenograft and syngeneic tumour models using a site-specifically labelled PD-L1 antibody. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 47:1302–1313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-019-04646-4
Dekempeneer Y, Caveliers V, Ooms M et al (2020) Therapeutic efficacy of (213)bi-labeled sdAbs in a preclinical model of ovarian cancer. Mol Pharm 17:3553–3566. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00580
Feng Y, Meshaw R, McDougald D et al (2022) Evaluation of an (131)I-labeled HER2-specific single domain antibody fragment for the radiopharmaceutical therapy of HER2-expressing cancers. Sci Rep 12:3020. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-07006-9
Feng Y, Meshaw R, Zhao XG et al (2023) Effective treatment of human breast carcinoma xenografts with single-dose (211)at-labeled anti-her2 single-domain antibody fragment. J Nucl Med 64:124–130. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.122.264071
Hohenforst-Schmidt W, Zarogoulidis P, Darwiche K et al (2013) Intratumoral chemotherapy for lung cancer: re-challenge current targeted therapies. Drug Des Devel Ther 7:571–583. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S46393
Hu B, Liu T, Li L et al (2022) IgG-binding nanobody capable of prolonging nanobody-based radiotracer plasma half-life and enhancing the efficacy of tumor-targeted radionuclide therapy. Bioconjug Chem 33:1328–1339. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.2c00209
Jneid B, Bochnakian A, Hoffmann C et al (2023) Selective STING stimulation in dendritic cells primes antitumor T cell responses. Sci Immunol 8:eabn6612. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.abn6612
Klawitter M, El-Ayoubi A, Buch J et al (2022) The oncolytic adenovirus XVir-N-31, in combination with the blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 axis, conveys abscopal effects in a humanized glioblastoma mouse model. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23179965
Kumar K (2022) Radioiodine labeling reagents and methods for new chemical entities and biomolecules. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 37:173–185. https://doi.org/10.1089/cbr.2021.0233
Kumar K, Woolum K (2021) A novel reagent for radioiodine labeling of new chemical entities (NCEs) and biomolecules. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144344
Larson SM, Carrasquillo JA, Cheung NK et al (2015) Radioimmunotherapy of human tumours. Nat Rev Cancer 15:347–360. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3925
Liu W, Zhang D, Feng Y et al (2015) Biodistribution and anti-tumor efficacy of intratumorally injected necrosis-avid theranostic agent radioiodinated hypericin in rodent tumor models. J Drug Target 23:371–379. https://doi.org/10.3109/1061186X.2014.1000337
Liu Q, Jiang L, Li K et al (2021) Immuno-PET imaging of (68)Ga-labeled nanobody Nb109 for dynamic monitoring the PD-L1 expression in cancers. Cancer Immunol Immunother 70:1721–1733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02818-y
Liu Q, Wang X, Yang Y et al (2022a) Immuno-PET imaging of PD-L1 expression in patient-derived lung cancer xenografts with [(68)Ga]Ga-NOTA-Nb109. Quant Imaging Med Surg 12:3300–3313. https://doi.org/10.21037/qims-21-991
Liu JQ, Zhang C, Zhang X et al (2022b) Intratumoral delivery of IL-12 and IL-27 mRNA using lipid nanoparticles for cancer immunotherapy. J Control Release 345:306–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.03.021
Liu T, Pei P, Shen W et al (2023a) Radiation-induced immunogenic cell death for cancer radioimmunotherapy. Small Methods. https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202201401
Liu Z, Chen H, Huang C et al (2023b) A Light-Responsive Injectable Hydrogel with Remodeling Tumor Microenvironment for Light-Activated Chemodynamic Therapy. Macromol Biosci 23:e2200329. https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.202200329
Luo H, Yang C, Kuang D et al (2022) Visualizing dynamic changes in PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung carcinoma with radiolabeled recombinant human PD-1. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 49:2735–2745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-022-05680-5
Lv G, Sun X, Qiu L et al (2020) PET imaging of tumor PD-L1 expression with a highly specific nonblocking single-domain antibody. J Nucl Med 61:117–122. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.119.226712
Ma H, Li F, Shen G et al (2021) Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of (131)I-labeled FAPI tracers for cancer theranostics. Mol Pharm 18:4179–4187. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.1c00566
Ma H, Li F, Shen G et al (2022) In vitro and in vivo evaluation of (211)At-labeled fibroblast activation protein inhibitor for glioma treatment. Bioorg Med Chem 55:116600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116600
Marti M, Merwaiss F, Butkovic A et al (2022) Production of potyvirus-derived nanoparticles decorated with a nanobody in biofactory plants. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 10:877363. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.877363
Mole RH (1953) Whole body irradiation; radiobiology or medicine? Br J Radiol 26:234–241. https://doi.org/10.1259/0007-1285-26-305-234
Piramoon M, Khodadust F, Hosseinimehr SJ (2021) Radiolabeled nanobodies for tumor targeting: from bioengineering to imaging and therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1875:188529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188529
Poletto G, Evangelista L, Venturini F et al (2022) Nanoparticles and radioisotopes: a long story in a nutshell. Pharmaceutics. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102024
Pruszynski M, Koumarianou E, Vaidyanathan G et al (2013) Targeting breast carcinoma with radioiodinated anti-HER2 Nanobody. Nucl Med Biol 40:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2012.08.008
Puttemans J, Dekempeneer Y, Eersels JL et al (2020) Preclinical targeted alpha- and beta(-)-radionuclide therapy in HER2-positive brain metastasis using camelid single-domain antibodies. Cancers (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12041017
Qi Z, Pei P, Zhang Y et al (2022) (131)I-alphaPD-L1 immobilized by bacterial cellulose for enhanced radio-immunotherapy of cancer. J Control Release 346:240–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.04.029
Shewaiter MA, Selim AA, Moustafa YM et al (2022) Radioiodinated acemetacin loaded niosomes as a dual anticancer therapy. Int J Pharm 628:122345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.122345
Su W, Chen C, Wang T et al (2020) Radionuclide-labeled gold nanoparticles for nuclei-targeting internal radio-immunity therapy. Mater Horiz 7:1115–1125. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9mh01725a
Sun Q, Li J, Ding Z et al (2023) Radiopharmaceuticals heat anti-tumor immunity. Theranostics 13:767–786. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.79806
Wu Y, Pfeifer AK, Myschetzky R et al (2013) Induction of anti-tumor immune responses by peptide receptor radionuclide therapy with (177)Lu-DOTATATE in a murine model of a human neuroendocrine tumor. Diagnostics (Basel) 3:344–355. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics3040344
Yang E, Liu Q, Huang G et al (2022) Engineering nanobodies for next-generation molecular imaging. Drug Discov Today 27:1622–1638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2022.03.013
Yang T, Peng L, Qiu J et al (2023) A radiohybrid theranostics ligand labeled with fluorine-18 and lutetium-177 for fibroblast activation protein-targeted imaging and radionuclide therapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-023-06169-5
Zhang Z, Liu X, Chen D et al (2022) Radiotherapy combined with immunotherapy: the dawn of cancer treatment. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7:258. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01102-y
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers [No.82071956] and [82272030]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MZ and FY contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by MZ, JZ and MY. The first draft of the manuscript was written by MZ and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
All animal studies and experimental procedures were approved by Animal Welfare Ethics Committee of Shanghai Tenth People’s Hospital with an approval number (ID: SHDSYY-2023–0746).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, M., Zhang, J., Yang, M. et al. In vitro and in vivo study on the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer with radionuclide labeled PD-L1 nanobody. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 8429–8442 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04793-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04793-0