Abstract
Background
Radiation-induced oral mucositis (OM) largely impairs the quality of life (QoL) of patients with head and neck cancer (HNC). Few choices with limited efficacy are available to prevent this adverse effect. This randomized trial was conducted to compare the efficacy of benzydamine (standard) and a new combination (sumac and rose water) in preventing radiation-induced OM.
Methods
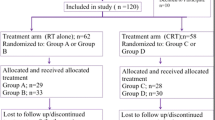
This was a phase II, triple-blind, active-controlled, randomized trial. The primary endpoint was OM, and the secondary endpoints were oral pain and QoL. Besides, the possible variables defining the outcomes were analyzed using the chi-squared test (univariate analysis) and binomial regression model (multivariate analysis).
Results
Sumac-rose group had fewer high-grade OM (33% vs. 63%, odds ratio [OR] 0.28, 95% confidence interval [CI 95%] 0.08–0.93, P = 0.03) and better QoL (P < 0.05). Multivariate analysis confirmed these findings. Sumac-rose rinsing could also postpone the start of oral pain (hazard ratio [HR] 0.02, CI 95% 0.001–0.32, P = 0.001) and high-grade OM (HR 0.28, P = 0.03) compared with benzydamine.
Conclusions
The sumac-rose group had a lower OM rate and grade and higher QoL than the benzydamine group. In addition, the experimental group developed high-grade OM and oral pain later during the radiotherapy course. Further studies need to be conducted to assess the role of sumac and rose water in reducing grade 3–4 mucositis in patients who undergo chemoradiation for head and neck cancer.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Gy:
-
Gray
- HG:
-
High grade
- HNC:
-
Head and neck cancer
- OM:
-
Oral mucositis
- OP:
-
Oral pain
- QoL:
-
Quality of life
- PFD:
-
Per fraction dose
- RIOM:
-
Radiation-induced oral mucositis
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RT:
-
Radiotherapy
- TD:
-
Total dose
References
Aghili MH (2011) Makhzan-AL Advieh The validation of European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire, Head and Neck Module (EORTC QLQ- H&N 35 [in Persian]. Tehran University of Medical Science Press, Berlin
Ameri A, Poshtmahi S, Heydarirad G et al (2021) Effect of Honey-Lemon Spray Versus Benzydamine Hydrochloride Spray on Radiation-Induced Acute Oral Mucositis in Head and Neck Cancer Patients: A Pilot, Randomized, Double-Blind, Active-Controlled Clinical Trial. J Altern Complement Med 27(3):255–262. https://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2020.0468
Ameri A, Norouzi S, Sourati A, Azghandi S, Novin K, Taghizadeh-Hesary F (2022) Randomized trial on acute toxicities of weekly vs three-weekly cisplatin-based chemoradiation in head and neck cancer. Cancer Rep (hoboken). 5(1):e1425. https://doi.org/10.1002/cnr2.1425
Ariyawardana A, Cheng KKF, Kandwal A et al (2019) Systematic review of anti-inflammatory agents for the management of oral mucositis in cancer patients and clinical practice guidelines. Support Care Cancer 27(10):3985–3995. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-019-04888-w
Bartley EJ, Fillingim RB (2013) Sex differences in pain: a brief review of clinical and experimental findings. Br J Anaesth 111(1):52–58. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aet127
Boskabady MH, Shafei MN, Saberi Z, Amini S (2011) Pharmacological effects of rosa damascena. Iran J Basic Med Sci 14(4):295–307
Dastan F, Ameri A, Dodge S, Hamidi Shishvan H, Pirsalehi A, Abbasinazari M (2020) Efficacy and safety of propolis mouthwash in management of radiotherapy induced oral mucositis; A randomized, double blind clinical trial. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 25(6):969–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rpor.2020.09.012
Hajibeygi R, Mirghazanfari SM, Pahlavani N et al (2022) Effect of a diet based on Iranian traditional medicine on inflammatory markers and clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients: a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. Eur J Integr Med. 55:102179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eujim.2022.102179
Han JH, Song JH, Kim YE, Lee YH, Lee JM, Lee JE (2018) Anti-aging effects of Rosa damascena extract containing low molecular glycoprotein. J Soc Cosmet Sci Korea 44(1):49–57. https://doi.org/10.15230/SCSK.2018.44.1.49
Isgrò C, Spagnuolo L, Pannucci E et al (2022) Rhus coriaria L. Extract: antioxidant effect and modulation of bioenergetic capacity in fibroblasts from Parkinson’s disease patients and THP-1 macrophages. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112774
Khalil M, Hayek S, Khalil N et al (2021) Role of Sumac (Rhus coriaria L.) in the management of metabolic syndrome and related disorders: focus on NAFLD-atherosclerosis interplay. J Funct Foods. 87:104811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2021.104811
Liu S, Zhao Q, Zheng Z et al (2021) Status of treatment and prophylaxis for radiation-induced oral mucositis in patients with head and neck cancer. Front Oncol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.642575
Martinelli G, Angarano M, Piazza S et al (2022) The nutraceutical properties of sumac (Rhus coriaria L.) against gastritis: antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activities in gastric epithelial cells infected with H. pylori. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091757
Mohammadi S, Zarei M, Zarei MM, Salehi I (2016) Effect of hydroalcoholic leaves extract of Rhus coriaria on pain in male rats. Anesth Pain Med 6(1):e32128. https://doi.org/10.5812/aapm.32128
Nicolatou-Galitis O, Bossi P, Orlandi E, René-Jean B (2021) The role of benzydamine in prevention and treatment of chemoradiotherapy-induced mucositis. Support Care Cancer 29(10):5701–5709. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-021-06048-5
Pulito C, Cristaudo A, Porta C et al (2020) Oral mucositis: the hidden side of cancer therapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 39(1):210. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-020-01715-7
Rakhsha A, Azghandi S, Ameri A, et al (2019) A report of delayed toxicities of intensity modulated radiation therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a single center cross-sectional study. 12(5):e91606. https://doi.org/10.5812/ijcm.91606
Sun Y, Ma N, Yi J, Zhou L, Cai S (2021) Gastroprotective effect and mechanisms of Chinese sumac fruits (Rhus chinensis Mill.) on ethanol-induced gastric ulcers in mice. Food Funct 12(24):12565–12579. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1fo02864b
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Taghizadeh-Hesary F, Akbari H, Bahadori M, Behnam B (2022) Targeted anti-mitochondrial therapy: the future of oncology. Genes (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101728
Taghizadeh-Hesary F, Houshyari M, Farhadi M (2023) Mitochondrial metabolism: a predictive biomarker of radiotherapy efficacy and toxicity. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04592-7
Funding
Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: AA, GhH, Methodology: AA, FTH, Software: SP, FTH, Validation: AA, Formal analysis: SP, FTH, Investigation: SP, FT, PA, Resources: AA, GhH, Data Curation: SP, Writing-original draft: SP, AB, FTH, Writing-review & editing: AA, FTH, Visualization: RC, Supervision: AA, GhH, Project administration: AA, GhC, Funding acquisition: N/A.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ameri, A., Heydarirad, G., Choopani, R. et al. Sumac-rose water mouthwash versus benzydamine to prevent radiation-induced oral mucositis in head and neck cancers: a phase II randomized trial. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 7427–7439 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04687-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-04687-1