Abstract
Purpose
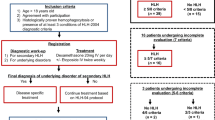
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), especially lymphoma-associated HLH (LA-HLH), is a refractory immune disorder with high mortality. There is still no consensus regarding the ideal treatment for LA-HLH.
Methods
We performed a prospective multicenter study (NCT 04077905) to explore the efficacy of a modified DEP regimen as induction therapy for LA-HLH. Twenty-eight patients from 6 clinical centers in China were enrolled between September 2019 and July 2021. We evaluated the efficacy of the modified DEP induction therapy 4 weeks after the initiation of treatment.
Results
The results showed that the overall response rate was 89.3% (25/28 patients), whereby 28.6% (8/28 patients) achieved a complete response and 60.7% (17/28 patients) were in partial response. Ferritin and soluble CD25 levels were decreased significantly 4 weeks after the modified DEP induction therapy (P = 0.001 and P = 0.00016, respectively), while platelet count and total bilirubin improved significantly (P = 0.004 and P = 0.001, respectively). The 1-year overall survival rate of all patients was 34.5%, with a median survival of 6.5 months (range 0.5–19 months). Patients with LA-HLH who underwent a stem cell transplantation had a significantly better prognosis than those not achieving complete response 4 weeks after modified DEP induction therapy (P = 0.034).
Conclusion
Our study suggests that the modified DEP regimen is a safe and effective induction therapy for LA-HLH. Timely stem cell transplantation can improve the prognosis of patients with LA-HLH.
Trail registry number
NCT 04077905. URL: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04077905?id=NCT04077905&draw=2&rank=1.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Han AR, Lee HR, Park BB, Hwang IG, Park S, Lee SC, Kim K, Lim HY, Ko YH, Kim SH, Kim WS (2007) Lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic syndrome: clinical features and treatment outcome. Ann Hematol 86:493–498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-007-0278-6
Henter JI, Horne A, Arico M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, Ladisch S, McClain K, Webb D, Winiarski J, Janka G (2007) HLH-2004: diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 48:124–131. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.21039
Henter JI, Samuelsson-Horne A, Arico M et al (2002) Treatment of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with HLH-94 immunochemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation. Blood 100:2367–2373. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2002-01-0172
Hue SS, Oon ML, Wang S, Tan SY, Ng SB (2020) Epstein-Barr virus-associated T- and NK-cell lymphoproliferative diseases: an update and diagnostic approach. Pathology 52:111–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pathol.2019.09.011
Huwyler J, Drewe J, Krähenbuhl S (2008) Tumor targeting using liposomal antineoplastic drugs. Int J Nanomed 3:21–29. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S1253
Janka GE (1983) Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Eur J Pediatr 140:221–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00443367
Jin Z, Wang Y, Wang J, Wu L, Pei R, Lai W, Wang Z (2018) Multivariate analysis of prognosis for patients with natural killer/T cell lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Hematology 23:228–234. https://doi.org/10.1080/10245332.2017.1385191
Kim WY, Montes-Mojarro IA, Fend F, Quintanilla-Martinez L (2019) Epstein–Barr virus-associated T and NK-cell lymphoproliferative diseases. Front Pediatr 7:71–71. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2019.00071
La Rosee P, Horne A, Hines M et al (2019) Recommendations for the management of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults. Blood 133:2465–2477. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2018894618
Lehmberg K, Nichols KE, Henter JI, Girschikofsky M, Greenwood T, Jordan M, Kumar A, Minkov M, La Rosée P, Weitzman S, Study Group on Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Subtypes of the Histiocyte Society (2015) Consensus recommendations for the diagnosis and management of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis associated with malignancies. Haematologica 100:997–1004. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2015.123562
Li F, Li P, Zhang R, Yang G, Ji D, Huang X, Xu Q, Wei Y, Rao J, Huang R, Chen G (2014) Identification of clinical features of lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic syndrome (LAHS): an analysis of 69 patients with hemophagocytic syndrome from a single-center in central region of China. Med Oncol 31:902. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0902-y
Liang JH, Wang L, Zhu HY, Qian J, Liao H, Wu JZ, Xia Y, Wu W, Cao L, Fan L, Li JY, Xu W (2020) Dose-adjusted EPOCH regimen as first-line treatment for non-Hodgkin lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a single-arm, open-label, phase II trial. Haematologica 105:e29–e32. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2019.220301
Lin CH, Shih YH, Chen TC, Chou CW, Hsu CY, Teng CJ (2021) A decade of lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: does the outcome improve? J Clin Med 10:5114. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10215114
Locatelli F, Jordan MB, Allen C et al (2020) Emapalumab in children with primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. N Engl J Med 382:1811–1822. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1911326
Marsh RA, Allen CE, McClain KL et al (2013) Salvage therapy of refractory hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with alemtuzumab. Pediatr Blood Cancer 60:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.24188
Meng G, Wang Y, Wang J, Wang Z (2021) The DEP regimen is superior to the HLH-1994 regimen as first-line therapy for lymphoma-associated haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Leuk Lymphoma 62:854–860. https://doi.org/10.1080/10428194.2020.1849671
Otrock ZK, Eby CS (2015) Clinical characteristics, prognostic factors, and outcomes of adult patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Am J Hematol 90:220–224. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.23911
Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zerón P, López-Guillermo A, Khamashta MA, Bosch X (2014) Adult haemophagocytic syndrome. Lancet 383:1503–1516. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(13)61048-x
Sano H, Kobayashi R, Tanaka J et al (2014) Risk factor analysis of non-Hodgkin lymphoma-associated haemophagocytic syndromes: a multicentre study. Br J Haematol 165:786–792. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.12823
Shin HJ, Chung JS, Lee JJ et al (2008) Treatment outcomes with CHOP chemotherapy in adult patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. J Korean Med Sci 23:439–444. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.3.439
Song Y, Wang J, Wang Y, Wu L, Wang Z (2021a) Requirement for containing etoposide in the initial treatment of lymphoma associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Cancer Biol Ther 22:598–606. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2021.1996139
Song Y, Yin Q, Wang J, Wang Z (2021b) Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients with lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Cell Transplant 30:9636897211057076. https://doi.org/10.1177/09636897211057077
Trottestam H, Horne A, Arico M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Gadner H, Imashuku S, Ladisch S, Webb D, Janka G, Henter JI, Histiocyte Society (2011) Chemoimmunotherapy for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: long-term results of the HLH-94 treatment protocol. Blood 118:4577–4584. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-06-356261
Wang J, Wang Y, Wu L, Wang X, Jin Z, Gao Z, Wang Z (2020) Ruxolitinib for refractory/relapsed hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Haematologica 105:e210–e212. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2019.222471
Wang Y, Huang W, Hu L, Cen X, Li L, Wang J, Shen J, Wei N, Wang Z (2015) Multicenter study of combination DEP regimen as a salvage therapy for adult refractory hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 126:2186–2192. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2015-05-644914
Wohlfarth P, Agis H, Gualdoni GA, Weber J, Staudinger T, Schellongowski P, Robak O (2019) Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist anakinra, intravenous immunoglobulin, and corticosteroids in the management of critically ill adult patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. J Intensive Care Med 34:723–731. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885066617711386
Zhou L, Liu Y, Wen Z et al (2020) Ruxolitinib combined with doxorubicin, etoposide, and dexamethasone for the treatment of the lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic syndrome. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 146:3063–3074. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03301-y
Zoref-Lorenz A, Murakami J, Hofstetter L et al (2022) An improved index for diagnosis and mortality prediction in malignancy-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Blood 139:1098–1110. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2021012764
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients who participated in this trial and the members of the Chinese Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Group.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81871633), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (no. 7181003), and Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals’ Ascent Plan (DFL20180101). The funding body did not contribute to this study with respect to the design, data analysis, and/or writing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by YP. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YP and all the authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Beijing Friendship Hospital.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all the participants.
Consent to publish
We obtained consent to publish from all the participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pi, Y., Wang, J., Zhou, H. et al. Modified DEP regimen as induction therapy for lymphoma-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a prospective, multicenter study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 3033–3041 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04157-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-022-04157-0