Abstract
Objectives
The project is designed to compare the clinical efficacy and adverse events resulting from immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) plus chemotherapy and chemotherapy alone in patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Methods
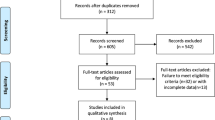
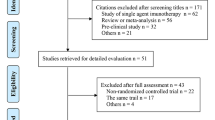
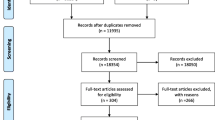
PubMed Database and ClinicalTrials.gov were both searched to identify randomized controlled clinical trials for assessing ICIs in all-stage SCLC. After screening in strict accordance with the inclusion and exclusion criteria, eligible studies were evaluated in regard to the population, intervention, comparator, outcome as well as study design (PICOS) pattern. Furthermore, primary endpoints of these randomized controlled trials (RCTs) included overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS) and complete/objective response rate (CRR/ORR). Statistical analyses were realized via Review Manager Version 5.3 Software.
Results
Compared with the chemotherapy alone group, the ICIs plus chemotherapy group significantly improved with respect to such indicators as OS (hazard ratio (HR) = 0.82, 95% CI 0.74–0.90, P < 0.0001), PFS (HR = 0.80, 95% CI 0.74–0.87, P < 0.00001) and ORR (64.7% versus 59.1%). According to the safety analysis, the incidence of treatment-related adverse events (trAEs) at all grades was higher in ICIs plus chemotherapy group (OR = 1.59, 95% CI 1.20–2.10, P = 0.001), bearing no statistical significance at grade 3 or above (OR = 1.21, 95% CI 0.99–1.49, P = 0.07).
Conclusions
The combination of ICIs and chemotherapy witnessed better anti-neoplastic efficacy for SCLC. Moreover, the incidence of trAEs at all grades was elevated in ICIs plus chemotherapy group, with little discrepancy in both groups at grade 3 or above.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data available from authors upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ICIs:
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
- SCLC:
-
Small cell lung cancer
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- RCTs:
-
Randomized controlled trials
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- CRR/ORR:
-
Complete/objective response rate
- HR:
-
Hazard ratio
- 95%CI:
-
95% Credible intervals
- trAEs:
-
Treatment-related adverse events
- CTLA-4:
-
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4
- PD-1:
-
Programmed death-1
- PD-L1:
-
Programmed cell death-ligand 1
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global Cancer statistics Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Buchbinder EI, Desai A (2016) CTLA-4 and PD-1 pathways: similarities, differences, and implications of their inhibition. Am J Clin Oncol 39(1):98–106. https://doi.org/10.1097/COC.0000000000000239
Calles A, Aguado G, Sandoval C, Álvarez R (2019) The role of immunotherapy in small cell lung cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 21(8):961–976. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-018-02011-9
Chen L (2004) Co-inhibitory molecules of the B7-CD28 family in the control of T-cell immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 4(5):336–347. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1349
Facchinetti F, Di Maio M, Tiseo M (2020) Adding PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors to chemotherapy for the first-line treatment of extensive stage small cell lung cancer (SCLC): a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Cancers (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092645
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M et al (2015) Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136(5):E359–E386. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29210
Fife BT, Bluestone JA (2008) Control of peripheral T-cell tolerance and autoimmunity via the CTLA-4 and PD-1 pathways. Immunol Rev 224:166–182. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00662.x
Goldman JW, Dvorkin M, Chen Y, Reinmuth N, Hotta K, Trukhin D et al (2021) Durvalumab, with or without tremelimumab, plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide alone in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): updated results from a randomised, controlled, open-label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol 22(1):51–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(20)30539-8
Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D, Read W, Tierney R, Vlahiotis A et al (2006) Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the united states over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J Clin Oncol 24(28):4539–4544. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2005.04.4859
Govindan R, Ding L, Griffith M, Subramanian J, Dees ND, Kanchi KL et al (2012) Genomic landscape of non-small cell lung cancer in smokers and never-smokers. Cell 150(6):1121–1134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.024
Horn L, Mansfield AS, Szczęsna A, Havel L, Krzakowski M, Hochmair MJ et al (2018) First-line atezolizumab plus chemotherapy in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 379(23):2220–2229. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1809064
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH (2008) PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 26:677–704. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090331
Leal T, Wang Y, Dowlati A, Lewis DA, Chen Y, Mohindra AR et al (2020) Randomized Phase II Clinical Trial of Cisplatin/Carboplatin and Etoposide (CE) Alone or in Combination with Nivolumab as Frontline Therapy for Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer (ES-SCLC): ECOG-ACRIN EA5161. J Clin Oncol 38(15):9000–9000. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2020.38.15_suppl.9000
List M, Jamous F, Gupta A, Huntington M (2015) Anti-Hu positive antibodies and small cell carcinoma: a single center review. S D Med 68(6):251 (253–5)
Liu SV, Camidge DR, Gettinger SN, Giaccone G, Heist RS, Hodi FS et al (2018) Long-term survival follow-up of atezolizumab in combination with platinum-based doublet chemotherapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Cancer 101:114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2018.06.033
Liu SV, Reck M, Mansfield AS, Mok T, Scherpereel A, Reinmuth N et al (2021) Updated overall survival and PD-L1 subgroup analysis of patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer treated with atezolizumab, carboplatin, and etoposide (IMpower133). J Clin Oncol 39(6):619–630. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.20.01055
Naidoo J, Page DB, Li BT, Connell LC, Schindler K, Lacouture ME et al (2015) Toxicities of the anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 immune checkpoint antibodies. Ann Oncol 26(12):2375–2391. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdv383
Oronsky B, Reid TR, Oronsky A, Carter CA (2017) What’s new in SCLC? a review. Neoplasia 19(10):842–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2017.07.007
Paz-Ares L, Dvorkin M, Chen Y, Reinmuth N, Hotta K, Trukhin D et al (2019) Durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): a randomised, controlled, open-label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 394(10212):1929–1939. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(19)32222-6
Paz-Ares LG, Dvorkin M, Chen Y, Reinmuth N, Hotta K, Trukhin D et al (2020) Durvalumab ± Tremelimumab + platinum-etoposide in first-line extensive-stage SCLC (ES-SCLC): updated results from the Phase III CASPIAN Study. J Clin Oncol 38(15):9002–9002. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2020.38.15_suppl.9002
Reck M, Bondarenko I, Luft A, Serwatowski P, Barlesi F, Chacko R et al (2013) Lpilimumab in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin as first-line therapy in extensive-disease-small-cell lung cancer: results from a randomized, double-blind, multicenter Phase 2 Trial. Ann Oncol 24(1):75–83. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mds213
Reck M, Luft A, Szczesna A, Havel L, Kim S-W, Akerley W et al (2016) Phase III randomized trial of lpilimumab plus etoposide and platinum versus placebo plus etoposide and platinum in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 34(31):3740–3748. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.67.6601
Rudin CM, Awad MM, Navarro A, Gottfried M, Peters S, Csőszi T et al (2020a) KEYNOTE-604: Pembrolizumab (Pembro) or Placebo Plus Etoposide and Platinum (EP) as First-Line Therapy for Extensive-Stage (ES) Small-Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC). J Clin Oncol 38(15):9001–9001. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2020.38.15_suppl.9001
Rudin CM, Awad MM, Navarro A, Gottfried M, Peters S, Csőszi T et al (2020b) Pembrolizumab or placebo plus etoposide and platinum as first-line therapy for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: randomized, double-blind, Phase III KEYNOTE-604 Study. J Clin Oncol 38(21):2369–2379. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.20.00793
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2017) Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin 67(1):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21387
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2019) Cancer Statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 69(1):7–34. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21551
Smith RA, Andrews KS, Brooks D, Fedewa SA, Manassaram-Baptiste D, Saslow D et al (2019) Cancer Screening in the United States, 2019: a review of Current American Cancer Society Guidelines and Current Issues in Cancer Screening. CA Cancer J Clin 69(3):184–210. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21557
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Nicholson AG, Yatabe Y, Austin JHM, Beasley MB et al (2015) The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Genetic, Clinical and Radiologic Advances Since the 2004 Classification. J Thorac Oncol 10(9):1243–1260. https://doi.org/10.1097/jto.0000000000000630
Wang S, Tang J, Sun T, Zheng X, Li J, Sun H et al (2017) Survival changes in patients with small cell lung cancer and disparities between different sexes, socioeconomic statuses and ages. Sci Rep 7(1):1339. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01571-0
Winston W, Tan M, FACP (2021) Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC). https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/280104-overview#a5. Accessed Mar 23 2021.
Yangqiu Li Y-LW (2016) Immunotherapy for small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(16)30159-0
Zhang S, Li S, Cheng Y (2020) Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone as first-line treatment for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorac Cancer 11(12):3536–3546. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.13698
Zimmerman S, Das A, Wang S, Julian R, Gandhi L, Wolf J (2019) 2017–2018 scientific advances in thoracic oncology: small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 14(5):768–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2019.01.022
Funding
No fund or specific grant received from any public, commercial or non-profit institutions in connection to this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XX contributed to the conception and design of the study, administrative support, data interpretation, and manuscript writing. YZ participated in data acquisition, statistical analysis, data interpretation as well as manuscript writing. QW was in charge of statistical analysis, data interpretation, and manuscript writing. SW was responsible for data interpretation and manuscript writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Ethical statement
Neither ethical approval nor patient consent is required as all analyses herein are based on previous published studies.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, Y., Wu, Q., Wu, S. et al. Comparing strategy of immune checkpoint inhibitors plus chemotherapy with chemotherapy alone for small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis based on six RCTs incorporating 2800 participants. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 148, 2465–2474 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03798-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03798-x