Abstract
Purpose
c-MYC plays an important role in regulating cellular growth and apoptosis, and it is aberrantly expressed in many human malignancies. Although c-MYC has been extensively investigated in Burkitt lymphoma and diffuse large B cell lymphoma, little has been reported in anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL). The aim of this study was to investigate the expression and genetic alterations of c-MYC in primary systemic ALCL, characterize its clinicopathologic features and immunophenotypes, and discuss their implications in prognosis.
Methods
Tissue microarrays using samples from 85 ALCL patients were used to evaluate expression of c-MYC and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK). c-MYC and ALK genetic alterations were detected using fluorescence in situ hybridization. The Kaplan–Meier and multivariate Cox regression methods were used for survival analysis.
Results
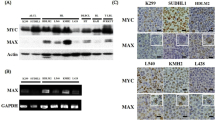
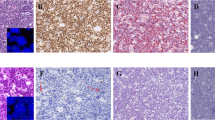
c-MYC was expressed in 24 of 85 samples (28.2%), and ALK was expressed in 54 (63.5%). c-MYC and ALK were co-expressed in 16 samples (18.8%). c-MYC expression and c-MYC and ALK co-expression increased with ALCL clinical stages and the International Prognostic Index (IPI) score (p < 0.05). Fifty of the samples (58.8%) had ALK rearrangement, and 18 (22.1%) had aneuploidy. c-MYC rearrangement was not detected, but aneuploidy was observed in 19 cases (22.4%). c-MYC aneuploidy was significantly different based on c-MYC expression and the IPI score (p < 0.05). c-MYC was a significant independent prognostic factor for progression-free survival and overall survival in patients with ALCL.
Conclusion
c-MYC protein expression and c-MYC aneuploidy could predict worse survival in patients with ALCL.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated that are relevant to the results presented in this article are included in this article. Other data that were not relevant for the results presented here are available from the corresponding author (ZW Chen) upon reasonable request.
References
Atsaves V, Tsesmetzis N, Chioureas D et al (2017) PD-L1 is commonly expressed and transcriptionally regulated by STAT3 and MYC in ALK-negative anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 31:1633–1637. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.103
Casey SC, Tong L, Li Y et al (2016) MYC regulates the antitumor immune response through CD47 and PD-L1. Science 352:227–231. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aac9935
Chen Z, Wang J, Zhang H et al (2012) Topo IIα gene alterations correlated with survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Eur J Clin Invest 42:310–320. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2362.2011.02585.x
Dang CV (2012) MYC on the path to cancer. Cell 149:22–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.003
Feldman AL, Dogan A, Smith DI et al (2011) Discovery of recurrent t(6;7)(p25.3;q32.3) translocations in ALK-negative anaplastic large cell lymphomas by massively parallel genomic sequencing. Blood 117:915–919. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-08-303305
Feldman AL, Vasmatzis G, Asmann YW et al (2013) Novel TRAF1-ALK fusion identified by deep RNA sequencing of anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 52:1097–1102. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.22104
Ferreri AJ, Govi S, Pileri SA et al (2013) Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK-negative. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 85:206–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2012.06.004
Helm F, Kammertoens T, Lehmann FM et al (2013) Targeting c-MYC with T-cells. PLoS ONE 8:e77375. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077375
Hermann M, Scholman HJ, Marafioti T et al (1997) Differential expression of apoptosis, Bcl-x and c-Myc in normal and malignant lymphoid tissues. Eur J Haematol 59:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0609.1997.tb00955.x
Kansal R, Sait SN, Block AW et al (2005) Extra copies of chromosome 2 are a recurring aberration in ALK-negative lymphomas with anaplastic morphology. Mod Pathol 18:235–243. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.3800299
Kinney MC, Higgins RA, Medina EA (2011) Anaplastic large cell lymphoma: twenty-five years of discovery. Arch Pathol Lab Med 135:19–43. https://doi.org/10.1043/2010-0507-RAR.1
Klapproth K, Wirth T (2010) Advances in the understanding of MYC-induced lymphomagenesis. Br J Haematol 149:484–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08159.x
Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR et al (2010) Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 363:1693–1703. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1006448
Liang X, Branchford B, Greffe B et al (2013) Dual ALK and MYC rearrangements leading to an aggressive variant of anaplastic large cell lymphoma. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 35:e209–e213. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPH.0b013e3182815046
Lyapichev KA, Tang G, Li S et al (2020) MYC expression is associated with older age, common morphology, increased MYC copy number, and poorer prognosis in patients with ALK+ anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Hum Pathol 108:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2020.11.002
Meyer N, Penn LZ (2008) Reflecting on 25 years with MYC. Nat Rev Cancer 8:976–990. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2231
Minoo P, Wang HY (2012) ALK-immunoreactive neoplasms. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 5:397–410
Moritake H, Shimonodan H, Marutsuka K et al (2011) C-MYC rearrangement may induce an aggressive phenotype in anaplastic lymphoma kinase positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma: Identification of a novel fusion gene ALO17/C-MYC. Am J Hematol 86:75–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.21887
Morris SW, Kirstein MN, Valentine MB et al (1994) Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science 263:1281–1284. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.8122112
Parrilla Castellar ER, Jaffe ES, Said JW et al (2014) ALK-negative anaplastic large cell lymphoma is a genetically heterogeneous disease with widely disparate clinical outcomes. Blood 124:1473–1480. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-04-571091
Perkins SL, Pickering D, Lowe EJ et al (2005) Childhood anaplastic large cell lymphoma has a high incidence of ALK gene rearrangement as determined by immunohistochemical staining and fluorescent in situ hybridisation: A genetic and pathological correlation. Br J Haematol 131:624–627. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05808.x
Piva R, Chiarle R, Manazza AD et al (2006) Ablation of oncogenic ALK is a viable therapeutic approach for anaplastic large-cell lymphomas. Blood 107:689–697. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-05-2125
Pulford K, Morris SW, Turturro F (2004) Anaplastic lymphoma kinase proteins in growth control and cancer. J Cell Physiol 199:330–358. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.10472
Raetz EA, Perkins SL, Carlson MA et al (2002) The nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase fusion protein induces c-Myc expression in pediatric anaplastic large cell lymphomas. Am J Pathol 161:875–883. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64248-4
Sibon D, Fournier M, Briere J et al (2012) Long-term outcome of adults with systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma treated within the Groupe d’Etude des Lymphomes de l’Adulte trials. J Clin Oncol 30:3939–3946. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2012.42.2345
Strippoli A, Cocomazzi A, Basso M et al (2020) c-MYC expression is a possible keystone in the colorectal cancer resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Cancers (basel) 12:E638. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12030638
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL et al (2016b) WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues, 4th edn. IARC, Lyon
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA et al (2016a) The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 127:2375–2390. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-01-643569
Tabbó F, Barreca A, Piva R et al (2012) ALK signaling and target therapy in anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Front Oncol 2:41. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2012.00041
Valera A, López-Guillermo A, Cardesa-Salzmann T et al (2013) MYC protein expression and genetic alterations have prognostic impact in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with immunochemotherapy. Haematologica 98:1554–1562. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2013.086173
Van Roosbroeck K, Cools J, Dierickx D et al (2010) ALK-positive large B-cell lymphomas with cryptic SEC31A-ALK and NPM1-ALK fusions. Haematologica 95:509–513. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2009.014761
Vasmatzis G, Johnson SH, Knudson RA et al (2012) Genome-wide analysis reveals recurrent structural abnormalities of TP63 and other p53-related genes in peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Blood 120:2280–2289. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-03-419937
Weilemann A, Grau M, Erdmann T et al (2015) Essential role of IRF4 and MYC signaling for survival of anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Blood 125:124–132. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-08-594507
Werner MT, Zhang Q, Wasik MA (2017) From pathology to precision medicine in anaplastic large cell lymphoma expressing anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK+ ALCL). Cancers (basel) 9:E138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9100138
Wu C, Zhang HF, Gupta N et al (2016) A positive feedback loop involving the Wnt/β-catenin/MYC/Sox2 axis defines a highly tumorigenic cell subpopulation in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma. J Hematol Oncol 9:120. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-016-0349-z
Zhang HW, Chen ZW, Li SH et al (2011) Clinical significance and prognosis of MYC translocation in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hematol Oncol 29:185–189. https://doi.org/10.1002/hon.991
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province (201801D121347, 201701D121165 and 2012011038-4) and the Intramural Research Program of Fenyang College of Shanxi Medical University (2016D10, 2016D12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.C. and F.C. designed the study. Z.C. and F.C. wrote the manuscript, and Z.C. revised the manuscript. Y.X. and Z.C. interpreted the results of the hematoxylin and eosin and immunochemical staining. F.C., Z.Z., and X.T. collected the clinical data and carried out immunochemical staining. F.C., Y.X., and S.L. performed TMA construction and FISH. F.C. and H.Z. were responsible for the statistical evaluation and analyzed data. All the authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Shanxi Tumor Hospital.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Chai, F., Xi, Y. et al. Aberrant expression and genetic alteration of c-MYC in anaplastic large cell lymphoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 148, 267–278 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03691-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-021-03691-7