Abstract
Purpose
The impact of myeloid sarcoma (MS) on clinical outcome of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients remains controversial. Moreover, little is known about the role of stem cell transplantation (SCT) in such patients.
Methods
Clinical data of patients with AML under 18 years of age were retrieved from the TARGET dataset. We analyzed the prevalence, clinical profile, molecular characteristics, and prognosis of MS in these patients.
Results
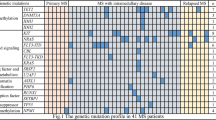
Among 884 pediatric patients with AML, the frequency of MS was 12.3%. Pediatric AML with MS was associated with age under 1-year, abnormal cytogenetics, and KMT2A rearrangement. Moreover, MS was associated with a low complete remission rate, high induction death, poor 5-year EFS, and OS. KMT2A rearrangement had a negative impact on clinical outcome in AML patients with MS. In addition, SCT had no significant effect on the survival of AML patients with MS. Multivariate analysis revealed that MS was an unfavorable prognostic factor in pediatric AML in terms of EFS (Hazard ratio 1.670, P < 0.001) and OS (Hazard ratio 1.623, P = 0.004).
Conclusions
The presence of MS at diagnosis of pediatric AML is associated with poor clinical outcomes, particularly when associated with KMT2A rearrangements. Moreover, pediatric patients with AML and MS may not benefit from SCT.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the TARGET website: https://ocg.cancer.gov/programs/target/data-matrix.
References
Almond LM, Charalampakis M, Ford SJ, Gourevitch D, Desai A (2017) Myeloid sarcoma: presentation diagnosis, and treatment. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 17:263–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clml.2017.02.027
Balgobind BV et al (2009) Novel prognostic subgroups in childhood 11q23/MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia: results of an international retrospective study. Blood 114:2489–2496. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-04-215152
Bisschop MM, Revesz T, Bierings M, van Weerden JF, van Wering ER, Hahlen K, van der Does-van den Berg A (2001) Extramedullary infiltrates at diagnosis have no prognostic significance in children with acute myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia 15:46–49
Bolouri H et al (2018) The molecular landscape of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia reveals recurrent structural alterations and age-specific mutational interactions. Nat Med 24:103–112. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4439
Bourlon C et al (2017) Extramedullary disease at diagnosis of AML does not influence outcome of patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant in CR1. Eur J Haematol 99:234–239. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejh.12909
Byrd JC et al (1997) Extramedullary leukemia adversely affects hematologic complete remission rate and overall survival in patients with t(8;21)(q22;q22): results from Cancer and Leukemia Group B 8461. J Clin Oncol 15:466–475. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.1997.15.2.466
Campidelli C, Agostinelli C, Stitson R, Pileri SA (2009) Myeloid sarcoma: extramedullary manifestation of myeloid disorders. Am J Clin Pathol 132:426–437. https://doi.org/10.1309/AJCP1ZA7HYZKAZHS
Cavdar AO et al (1989) High risk subgroup of acute myelomonocytic leukemia (AMML) with orbito-ocular granulocytic sarcoma (OOGS) in Turkish children. Retrospective analysis of clinical, hematological, ultrastructural and therapeutical findings of thirty-three OOGS. Acta Haematol 81:80–85. https://doi.org/10.1159/000205531
Chevallier P, Labopin M, Cornelissen J, Socie G, Rocha V, Mohty M, EBMT Ao (2011) Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for isolated and leukemic myeloid sarcoma in adults: a report from the Acute Leukemia Working Party of the European group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Haematologica 96:1391–1394. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2011.041418
Dusenbery KE et al (2003) Extramedullary leukemia in children with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia: a report from the Children's Cancer Group. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 25:760–768
El Jamal SM et al (2019) Myeloid sarcoma of the testis in children: clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical characteristics with KMT2A (MLL) gene rearrangement correlation. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAI.0000000000000783
Felice MS et al (2000) Good outcome of children with acute myeloid leukemia and t(8;21)(q22;q22), even when associated with granulocytic sarcoma: a report from a single institution in Argentina. Cancer 88:1939–1944
Gamis AS et al (2014) Gemtuzumab ozogamicin in children and adolescents with de novo acute myeloid leukemia improves event-free survival by reducing relapse risk: results from the randomized phase III Children's Oncology Group trial AAML0531. J Clin Oncol 32:3021–3032. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.55.3628
Ganzel C et al (2016) Extramedullary disease in adult acute myeloid leukemia is common but lacks independent significance: analysis of patients in ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group Trials, 1980–2008. J Clin Oncol 34:3544–3553. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2016.67.5892
Goyal SD et al (2015) Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant for AML: no impact of pre-transplant extramedullary disease on outcome. Bone Marrow Transplant 50:1057–1062. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.82
Gozdasoglu S, Yavuz G, Unal E, Tacyldz N, Cavdar AO (2002) Orbital granulocytic sarcoma and AML with poor prognosis in Turkish children. Leukemia 16:962. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402449 (author reply 963)
Johansson B et al (2000) Granulocytic sarcomas in body cavities in childhood acute myeloid leukemias with 11q23/MLL rearrangements. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 27:136–142
Johnston DL, Alonzo TA, Gerbing RB, Lange BJ, Woods WG (2010) The presence of central nervous system disease at diagnosis in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia does not affect survival: a Children's Oncology Group study. Pediatr Blood Cancer 55:414–420. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.22511
Johnston DL, Alonzo TA, Gerbing RB, Lange BJ, Woods WG (2012) Superior outcome of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients with orbital and CNS myeloid sarcoma: a report from the Children's Oncology Group. Pediatr Blood Cancer 58:519–524. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.23201
Kaur V, Swami A, Alapat D, Abdallah AO, Motwani P, Hutchins LF, Jethava Y (2018) Clinical characteristics, molecular profile and outcomes of myeloid sarcoma: a single institution experience over 13 years. Hematology 23:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/10245332.2017.1333275
Klco JM et al (2011) State of the art in myeloid sarcoma. Int J Lab Hematol 33:555–565. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-553X.2011.01361.x
Kobayashi R, Tawa A, Hanada R, Horibe K, Tsuchida M, Tsukimoto I, Japanese childhood AMLcsg (2007) Extramedullary infiltration at diagnosis and prognosis in children with acute myelogenous leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer 48:393–398. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.20824
Lazzarotto D et al (2017) Clinical outcome of myeloid sarcoma in adult patients and effect of allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Results from a multicenter survey. Leuk Res 53:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2016.12.003
Magdy M, Abdel Karim N, Eldessouki I, Gaber O, Rahouma M, Ghareeb M (2019) Myeloid sarcoma. Oncol Res Treat 42:224–229. https://doi.org/10.1159/000497210
Park KU, Lee DS, Lee HS, Kim CJ, Cho HI (2001) Granulocytic sarcoma in MLL-positive infant acute myelogenous leukemia: fluorescence in situ hybridization study of childhood acute myelogenous leukemia for detecting MLL rearrangement. Am J Pathol 159:2011–2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63052-0
Pieters R et al (2019) Outcome of infants younger than 1 year with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with the interfant-06 protocol: results from an international phase III randomized study. J Clin Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.00261
Pileri SA et al (2007) Myeloid sarcoma: clinico-pathologic, phenotypic and cytogenetic analysis of 92 adult patients. Leukemia 21:340–350. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404491
Pramanik R, Tyagi A, Chopra A, Kumar A, Vishnubhatla S, Bakhshi S (2018) Myeloid sarcoma predicts superior outcome in pediatric AML; can cytogenetics solve the puzzle? Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 18:e249–e254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clml.2018.03.013
Samborska M, Derwich K, Skalska-Sadowska J, Kurzawa P, Wachowiak J (2016) Myeloid sarcoma in children—diagnostic and therapeutic difficulties. Contemp Oncol (Pozn) 20:444–448. https://doi.org/10.5114/wo.2016.65602
Shimizu H et al (2012) Clinical significance of granulocytic sarcoma in adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Sci 103:1513–1517. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02324.x
Stove HK et al (2017) Extramedullary leukemia in children with acute myeloid leukemia: a population-based cohort study from the Nordic Society of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology (NOPHO). Pediatr Blood Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.26520
Wilson CS, Medeiros LJ (2015) Extramedullary manifestations of myeloid neoplasms. Am J Clin Pathol 144:219–239. https://doi.org/10.1309/AJCPO58YWIBUBESX
Winters AC, Bernt KM (2017) MLL-rearranged leukemias—an update on science and clinical approaches. Front Pediatr 5:4. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2017.00004
Yilmaz AF, Saydam G, Sahin F, Baran Y (2013) Granulocytic sarcoma: a systematic review. Am J Blood Res 3:265–270
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all study participants and the TARGET group for making these data publicly available.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81570140 to J.P. Fang), Guangdong Science and Technology Department (2017B030314026), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (2018A030313680 to L.H. Xu) and the China Scholarship Council [201806385032 to L.H. Xu].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, LH., Wang, Y., Chen, ZY. et al. Myeloid sarcoma is associated with poor clinical outcome in pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 146, 1011–1020 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03128-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03128-7