Abstract
Background
RRx-001, a minimally toxic next-generation checkpoint inhibitor that targets myeloid suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment, has also been shown to protect normal tissues from the cytotoxic effects of chemotherapy and radiation. The following experiments were carried out to determine whether the cytoprotective functions of RRx-001 in normal cells were operative in tumor cells.
Design
The effects of RRx-001 on normal cells, and ovarian cancer A2780 and UWB1 cells were evaluated with a colony-forming assay. Western blot densitometry was used to measure Nrf2 nuclear translocation in Caco2 cells after exposure to RRx-001. Following incubation with RRx-001, levels of the antioxidant, NQO1, were determined in Caco2 cells by measuring absorbance over 300 min at 440 nm. RRx-001-mediated cytotoxicity in HCT-116 colorectal cancer cells was evaluated with an MTT assay. In addition, the effect of RRx-001 incubation on the protein expression of Nrf2, PARP, cleaved PARP, procaspases 3, 8, and 9, Bcl-2, and Bax in HCT-116 colorectal cells was determined by western blot analysis.
Results
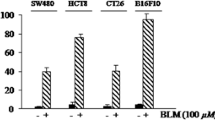
RRx-001 is demonstrated to induce Nrf2 in normal tissues, mediating protection, and to downregulate the Nrf2-controlled antiapoptotic target gene, B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) in tumors, mediating cytotoxicity.
Conclusion
Through Nrf2 induction in normal cells and inhibition of Bcl-2 in tumor cells, RRx-001 selectively protects normal cells against lethality in normal cells, but induces apoptosis in tumor cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cabrales P, Caroen S, Oronsky A, Carter C, Trepel J, Summers T et al (2017) The macrophage stimulating anti-cancer agent, RRx-001, protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Expert Rev Hematol. 10(6):575–582
Das D, Tian Z, Ray A, Ravillah D, Song Y, Richardson P, Oronsky B, Scicinski J, Chauhan D, Anderson K (2014) Anti-myeloma activity of a novel free radical inducer RRx-001. Blood 124(21):4712
Das DS, Ray A, Das A et al (2016) A novel hypoxia-selective epigenetic agent RRx-001 triggers apoptosis and overcomes drug resistance in multiple myeloma cells. Leukemia 30(11):2187–2197. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2016.96
Goel A, Aggarwal BB (2010) Curcumin, the golden spice from Indian saffron, is a chemosensitizer and radiosensitizer for tumors and chemoprotector and radioprotector for normal organs. Nutr Cancer 62(7):919–930
Grossman R, Ram Z (2013) The dark side of Nrf2. World Neurosurg. 80(3–4):284–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2011.09.055 (Epub 2012 Dec 12)
Hemann M, Lowe S (2006) The p53–Bcl-2 connection. Cell Death Differ 13(8):1256–1259
Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Ishii T, O’Connor T, Yamamoto M (2003) Keap1 regulates both cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling and degradation of Nrf2 in response to electrophiles. Genes Cells 8(4):379–391
Koukourakis MI (2003) Amifostine: is there evidence of tumor protection? Semin Oncol 30(6 Suppl 18):18–30
Lind C, Cadenas E, Hochstein P, Ernster L (1990) DT-diaphorase: purification, properties, and function. Methods Enzymol 186:287–301
Ning S, Bednarski M, Oronsky B, Scicinski J, Saul G, Knox SJ (2012) Dinitroazetidines are a novel class of anticancer agents and hypoxia-activated radiation sensitizers developed from highly energetic materials. Cancer Res 72(10):2600–2608
Ning S, Sekar TV, Scicinski J et al (2015) Nrf2 activity as a potential biomarker for the pan-epigenetic anticancer agent, RRx-001. Oncotarget 6(25):21547–21556
Niture SK, Jaiswal AK (2012) Nrf2 protein up-regulates antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 and prevents cellular apoptosis. J Biol Chem 287(13):9873–9886
O’Connell MA, Hayes JD (2015) The Keap1/Nrf2 pathway in health and disease: from the bench to the clinic. Biochem Soc Trans 43(4):687–689
Oronsky B, Paulmurugan R, Foygel K, Scicinski J, Knox SJ, Peehl D et al (2017a) RRx-001: a systemically non-toxic M2-to-M1 macrophage stimulating and prosensitizing agent in Phase II clinical trials. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 26(1):109–119
Oronsky B, Reid TR, Larson C, Carter CA, Brzezniak CE, Oronsky A, Cabrales P (2017b) RRx-001 protects against cisplatin-induced toxicities. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 143(9):1671–1677
Raghunand N, Scicinski J, Guntle GP et al (2017) Magnetic resonance imaging of RRx-001 pharmacodynamics in preclinical tumors. Oncotarget 8(60):102511–102520
Rojo de la Vega M, Chapman E, Zhang DD (2018) NRF2 and the hallmarks of cancer. Cancer Cell 34(1):21–43
Vomund S, Schäfer A, Parnham MJ, Brüne B, von Knethen A (2017) Nrf2, the master regulator of anti-oxidative responses. Int J Mol Sci 18(12):2772
Zhao H, Ning S, Scicinski J, Oronsky B, Knox SJ, Peehl DM (2015) Epigenetic effects of RRx-001: a possible unifying mechanism of anticancer activity. Oncotarget. 6(41):43172–43181
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines were followed.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oronsky, B., Scribner, C., Aggarwal, R. et al. RRx-001 protects normal tissues but not tumors via Nrf2 induction and Bcl-2 inhibition. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 145, 2045–2050 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02958-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02958-4