Abstract
Purpose
Bi-specific antibody (BsAb) is an emerging novel format of antibody. We aimed to develop the natural killer (NK) cell receptor NK group 2, member D (NKG2D)-mediated, immune surveillance system. In this system, the NKG2D ligand MHC class I-related chain A (MICA) was fused with BsAb, which targeted a cluster of differentiation 24 (CD24), a tumor-initiating cell marker that is over-expressed on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods
The Homo MICA extracellular domains (hMICA) were fused to the end of the heavy chain of cG7 with the flexible pentapeptide (Gly-Gly-Gly-Gly-Ser; G4S), which formed the cG7-MICA that was further identified using sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE) and western blotting (WB). The targeting specificity was characterized using the Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) technology and a flow cytometry assay. Furthermore, the design of BsAb cG7-MICA that targeted CD24 and NKG2D was proven to enhance antibody-dependent, cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) in vitro by the CytoTox 96 Nonradioactive Cytotoxicity assay. Degranulation and a cytokine production assay of NK cells demonstrated that NK cells were activated effectively by cG7-MICA. Further, in HCC-bearing nude mice, the anti-tumor effects of cG7-MICA combined with sorafenib were verified again.
Results
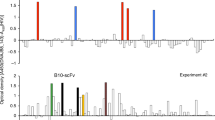
We purified cG7-MICA successfully, and it has a high affinity. In vivo, cG7-MICA recruited NK cells to the tumor site and improved the anti-tumor efficacy of sorafenib. cG7-MICA also activated NK cells to release interferon γ (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), and it increased the CD107a expression on the surface of the NK cells in vitro.
Conclusion
NK cells play a major role in the natural, innate immune system, and they have the function of identifying and killing target cells. cG7-MICA remodels the function of MICA molecules to activate NK cells, which provides a possible strategy for HCC-targeting immunotherapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambade A, Mulherkar R (2008) Adoptive T cell transfer augments IL-2 mediated tumor regression in a HNSCC xenograft nude mouse model. Cancer Lett 272(2):316–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2008.07.023
Arai S, Meagher R, Swearingen M, Myint H, Rich E, Martinson J, Klingemann H (2008) Infusion of the allogeneic cell line NK-92 in patients with advanced renal cell cancer or or melanoma: a phase I trial. Cytotherapy 10(6): 625–632. https://doi.org/10.1080/14653240802301872
Budzynski W, Radzikowski C (1994) Cytotoxic cells in immunodeficient athymic mice. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 16:319–346. https://doi.org/10.3109/08923979409007097
Chen ZG, Wang T, Tu XJ, Xie W, He H, Wang M, Zhang J (2017) Antibody-based targeting of CD24 enhances antitumor effect of cetuximab via attenuating phosphorylation of Src/STAT3. Biomed Pharmacother 90:427–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.03.094
Claire G, Larbouret C, Cesson V, Donda A, Held W, Mach J-P, Pelegrin A Robert B, (2005) MHC Class I-related chain A conjugated to antitumor antibodies can sensitize tumor cells to specific lysis by natural killer cells. Clin Cancer Res 11(20):7516–7522. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0872
Fathy AH, Bashandy AM, Bashandy SA, Mansour AM, Elsadek B (2017) Sequential analysis and staging of a diethylnitrosamine induced hepatocellular carcinoma in male Wistar albino rat model. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 95:1462–1472. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2017-0413
Geary CD, Sun JC (2017) Memory responses of natural killer cells. Semin Immunol 31:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2017.08.012
Huang LR, Hsu HC (1995) Cloning and expression of CD24 gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma A potential early tumor marker gene correlates with p53 mutation and tumor differentiation. Can Res 55:4717–4721
Lee TK, Castilho A, Cheung VC, Tang KH, Ma S, Ng IO (2011) CD24(+) liver tumor-initiating cells drive self-renewal and tumor initiation through STAT3-mediated NANOG regulation. Cell Stem Cell 9(1):50–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2011.06.005
Li D, Wang W (2017) Booming cancer immunotherapy fighting tumors. Sci China Life Sci 12:1445–1449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-017-9208-1
Lin S, Hoffmann K, Gao C, Petrulionis M, Herr I, Schemmer P (2017) Melatonin promotes sorafenib induced apoptosis through synergistic activation of JNK/c-jun pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Pineal Res 62(3):12398–12420. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12398
Lucas AF de, Tay RE, Pan D, Adrienne M, Luoma, Kai W, Wucherpfennig. (2018)Antibody-mediated inhibition of MICA and MICB shedding promotes NK cell–driven tumor immunity. Science 359:1537–1542. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao0505
Malmberg KJ, Carlsten M, Björklund A, Sohlberg E, Bryceson YT, Ljunggren HG (2017) Natural killer cell-mediated immunosurveillance of human cancer. Semin Immunol 31:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2017.08.002
Nausch N, Cerwenka A (2008) NKG2D ligands in tumor immunity. Oncogene 27(45):5944–5958. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.272
Peng H, Sun R (2017) Liver-resident NK cells and their potential functions. Cell Mol Immunol 14:890–894.w33. https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2017.72
Qiu L, Tang Q, Li G, Chen K (2017) Long non-coding RNAs as biomarkers and therapeutic targets: recent insights into hepatocellular carcinoma. Life Sci 191:273–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.10.007
Rothe A, Jachimowicz RD, Borchmann S, Madlener M, Keßler J, Reiners KS, Sauer M, Hansen HP, Ullrich RT, Chatterjee S, Borchmann P, Yazaki P, Koslowsky TC, Engert A, Heukamp LC, Hallek M, Strandmann EP von (2014) The bispecific immunoligand ULBP2-aCEA redirects natural killer cells to tumor cells and reveals potent anti-tumor activity against colon carcinoma. Int J Cancer 134(12):2829–2840. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28609
Shruthi K, Makol A, Anuradha C (2018) Sorafenib response in hepatocellular carcinoma: microRNAs as tuning forks. Hepatol Res 48:5–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/hepr.12991
Spear P, Wu MR, Sentman ML, Sentman CL (2013) NKG2D ligands as therapeutic targets. Cancer Immun 13(2):8–21
Tai WT, Cheng AL, Shiau CW, Huang HP, Huang JW, Chen PJ, Chen KF (2011) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is a major kinase-independent target of sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 55(5):1041–1048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2011.01.047
Tian Z (2017) NK cells and Immunotherapy. Semin Immunol 31:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2017.09.008
Turcios L, Vilchez V, Acosta LF, Poyil P, Butterfield DA, Mitov M, Marti F, Gedaly R (2017) Sorafenib and FH535 in combination act synergistically on hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting cell bioenergetics and mitochondrial function. Dig Liver Dis 49:697–704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2017.01.146
Waldhauer I, Steinle A (2008) NK cells and cancer immunosurveillance. Oncogene 27(45):5932–5943. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.267
Wang T, Sun F, Xie W, Tang M, He H, Jia X, Tian X, Wang M, Zhang J (2016) A bispecific protein rG7S-MICA recruits natural killer cells and enhances NKG2D-mediated immunosurveillance against hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 372(2):166–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.01.001
Wu JD, Higgins LM, Steinle A, Cosman D, Haugk K, Plymate SR (2004) Prevalent expression of the immunostimulatory MHC class I chain–related molecule is counteracted by shedding in prostate cancer. J Clin Investig 114(4):560–568. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI200422206
Wu JD, Atteridge CL, Wang X, Seya T, Plymate SR (2009) Obstructing shedding of the immune stimulatory micb prevents tumor formation: implication for targeted cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 15(2):632–640. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1305
Xie W, Liu F, Wang Y, Ren X, Wang T, Chen Z, Tang M, Sun F, Li Z, Wang M, Zhang J (2016) VEGFR2 targeted antibody fused with MICA stimulates NKG2D mediated immunosurveillance and exhibits potent anti-tumor activity against breast cancer. Oncotarget 7(13):16445–16461
Yang XR, Xu Y, Fan J et al (2009) CD24 is a novel predictor for poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after surgery. Clin Cancer Res 15(17):5518–5527. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0151
Ying T, Gong R, Ju TW, Prabakaran P, Dimitrov DS (2014) Engineered Fc based antibody domains and fragments as novel scaffolds. Biochim Et Biophys Acta 1844(11):1977–1982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.04.018
Zwirner NW, Fuertes MB, Girart MV, Domaica CI, Rossi LE (2007) Cytokine-driven regulation of NK cell functions in tumor immunity: role of the MICA-NKG2D system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 18(1):159–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2007.01.013
Acknowledgements
Thank Thomas A. Gavin, Professor Emeritus, Cornell University, for help with editing this paper.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC81473125) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20161459), Jiangsu Province Qinglan Project (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Ethical approval
All experimental procedures were conducted in conformity with institutional guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals in Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, and they conformed to the National Institutes of Regulations for the Administration of Affairs Concerning Experimental Animals.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Y., Sun, F., Zhang, X. et al. CD24 targeting bi-specific antibody that simultaneously stimulates NKG2D enhances the efficacy of cancer immunotherapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 145, 1179–1190 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02865-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02865-8