Abstract
Purpose
Multiple studies have attempted to demonstrate the interest of the cell adhesion marker, E cadherin, as a diagnostic and prognosis marker in colorectal cancer (CRC). However, it was considered non specific.
Materials and methods
Studies were carried out with CRC cell lines and patients’ cohort operated for CRC. The expression of E cadherin was studied after 5 fluorouracil (5FU) treatment and correlated to CRC relapse, chemo-resistance and survival.
Results
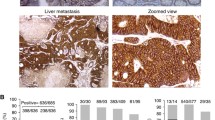
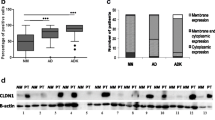
In CRC cell lines derived from high tumor stages, extracellular domain of E cadherin expression decreased after 5FU treatment whereas it increased in supernatants. Interestingly, only specific cleaved forms at 55 kDa of E cadherin were detected in supernatants. In CRC surgical patients, more importantly concerning extracellular E cadherin domain, a decreased expression was observed in tissues in function of CRC stages whereas an increased expression was found in sera. Moreover, there is an increasing trend of survival with weak serum E cadherin secretion, reinforcing the implication of this protein in CRC evolution.
Discussion
The extracellular domain can be defined as a 5FU resistance marker and allow CRC monitoring.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed D, Eide PW, Eilertsen IA et al (2013) Epigenetic and genetic features of 24 colon cancer cell lines. Oncogenesis 2(9):e71
Canel M, Serrels A, Frame MC et al (2013) E-cadherin–integrin crosstalk in cancer invasion and metastasis. J Cell Sci 126(2):393–401
Chan AOO, Lam SK, Chu KM et al (2001) Soluble E-cadherin is a valid prognostic marker in gastric carcinoma. Gut 48(6):808–811
David JM, Rajasekaran AK (2012) Dishonorable discharge: the oncogenic roles of cleaved E-cadherin fragments. Cancer Res 72(12):2917–2923
Eche N (2004) Marqueurs des cancers digestifs: côlon–rectum, pancréas, foie. Immuno-Anal Biol Spéc 19(5):279–285
Efstathiou JA, Liu D, Wheeler JMD et al (1999) Mutated epithelial cadherin is associated with increased tumorigenicity and loss of adhesion and of responsiveness to the motogenic trefoil factor 2 in colon carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96(5):2316–2321
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M et al (2013) GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase. International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon
Grieve AG, Rabouille C (2014) Extracellular cleavage of E-cadherin promotes epithelial cell extrusion. J Cell Sci 127(15):3331–3346
Hayashido Y, Hamana T, Yoshioka Y et al (2005) Plasminogen activator/plasmin system suppresses cell–cell adhesion of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via proteolysis of E-cadherin. Int J Oncol 27(3):693–698
Johnson SK, Ramani VC, Hennings L et al (2007) Kallikrein 7 enhances pancreatic cancer cell invasion by shedding E-cadherin. Cancer 109(9):1811–1820
Karapetis C, Khambata-Ford S, Jonker D et al (2008) K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. N Eng J Med 359:1757–1765
Katayama M, Hirai S, Kamihagi K et al (1994) Soluble E-cadherin fragments increased in circulation of cancer patients. Br J Cancer 69(3):580–585
Kokura S, Yoshida N, Imamoto E et al (2004) Anoxia/reoxygenation down-regulates the expression of E-cadherin in human colon cancer cell lines. Cancer Lett 211(1):79–87
Labianca R, Nordlinger B, Beretta GD et al (2013) Early colon cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 24(suppl 6):vi64–vi72
Maretzky T, Reiss K, Ludwig A et al (2005) ADAM10 mediates E-cadherin shedding and regulates epithelial cell–cell adhesion, migration, and β-catenin translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(26):9182–9187
Mélin C, Perraud A, Akil H et al (2012) Cancer stem cell sorting from colorectal cancer cell lines by sedimentation field flow fractionation. Anal Chem 84:1549–1556
Mélin C, Perraud A, Christou N et al (2015) New ex-ovo colorectal-cancer models from different SdFFF-sorted tumor-initiating cells. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:8433–8443
Noe V, Fingleton B, Jacobs K et al (2001) Release of an invasion promoter E-cadherin fragment by matrilysin and stromelysin-1. J Cell Sci 114(1):111–1118
Okugawa Y, Toiyama Y, Inoue Y et al (2012) Clinical significance of serum soluble E-cadherin in colorectal carcinoma. J Surg Res 175(2):e67–e73
Rios-Doria J, Day KC, Kuefer R et al (2003) The role of calpain in the proteolytic cleavage of E-cadherin in prostate and mammary epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 278(2):1372–1379
Shen Y, Hirsch DS, Sasiela CA et al (2008) Cdc42 regulates E-cadherin ubiquitination and degradation through an epidermal growth factor receptor to Src-mediated pathway. J Biol Chem 283(8):5127–5137
Steinhusen U, Weiske J, Badock V et al (2001) Cleavage and shedding of E-cadherin after induction of apoptosis. J Biol Chem 276(7):4972–4980
Vaiopoulos AG, Kostakis ID, Koutsilieris M et al (2012) Colorectal cancer stem cells. Stem Cells 30(3):363–371
Van Roya F, Berxb G (2008) The cell–cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin. CMLS Cell Mol Life Sci 65:3756–3788
Wever OD, Derycke L, Hendrix A et al (2007) Soluble cadherins as cancer biomarkers. Clin Exp Metastasis 24(8):685–697
Wilmanns C, Grossmann J, Steinhauer S et al (2004) Soluble serum E-cadherin as a marker of tumour progression in colorectal cancer patients. Clin Exp Metastasis 21(1):75–78
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the Anatomo-pathology department who made the immunohistochemical experiments. All this work was supported by a grant from CHU de Limoges [CORC Comité d’Orientation Recherche en Cancer Limousin, 2013], sponsored by Conseil Régional and ARS Limousin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christou, N., Perraud, A., Blondy, S. et al. The extracellular domain of E cadherin linked to invasiveness in colorectal cancer: a new resistance and relapses monitoring serum-bio marker?. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 143, 1177–1190 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2382-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2382-x