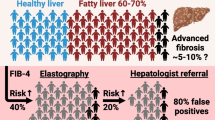
Abstract
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which can manifest as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) or severe fibrosis, is the most prevalent chronic liver disease in children and adolescents. However, there is no proven cure for it so far. This study was conducted to determine whether adolescents with NAFLD would improve with treatment intervention with orlistat. This study is a randomized controlled trial (RCT). Fifty-three adolescents with overweight/obese as well as with NAFLD randomly allocated to receive orlistat (n = 27) or placebo as control (n = 26) for 12 weeks. In addition, NAFLD activity score, anthropometric factors, biochemical parameters including serum levels of lipid profiles, liver enzyme, and glucose metabolism taken from subjects at baseline and end of the study were investigated. The findings of our article indicated that orlistat improves liver enzymes (alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase) (P = < 0.001), steatosis score (P = 0.001), NAFLD activity score (P = < 0.001), weight (P = < 0.001), body mass index (BMI) (P = < 0.001), waist circumferences (WC) (P = < 0.001), BMI-Z score (P = < 0.001), glucose metabolism (P = 0.001), total cholesterol (TC) (P = 0.009), low density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL) (P = < 0.001), and high density lipoprotein-cholesterol HDL levels (P = 0.014) compared to the control group after adjusting for possible confounders for 12 weeks. However, no significant changes were observed on triglyceride (TG) following intake of orlistat compared to placebo after adjusting for confounders.
Conclusion: The findings of our study reported that orlistat improved NAFLD-related factors and metabolic syndrome-related factors compared to placebo for 12 weeks.
Trial Registration: (Clinical trial registry number: IRCT20220409054467N2, with a registration date of 2022–05-13).
What is Known: • Among the interventions of interest for the management of pediatric NAFLD, we can mention lifestyle and pharmaceutical measures. | |
What is New: • This study was conducted to determine whether adolescents with NAFLD would improve with treatment intervention with orlistat. • The findings of our study reported that orlistat improved NAFLD-related factors and metabolic syndrome-related factors compared to placebo for 12 weeks. |

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data available on request due to privacy/ethical restrictions.
References
Anderson EL, Howe LD, Jones HE, Higgins JP, Lawlor DA, Fraser A (2015) The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 10:e0140908
Temple JL, Cordero P, Li J, Nguyen V, Oben JA (2016) A guide to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in childhood and adolescence. Int J Mol Sci 17:947
Li J, Ha A, Rui F, Zou B, Yang H, Xue Q, Hu X, Xu Y, Henry L, Barakat M (2022) Meta-analysis: global prevalence, trend and forecasting of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents, 2000–2021. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 56:396–406
Ma J, Wang Z, Song Y, Hu P, Zhang B (2010) BMI percentile curves for Chinese children aged 7–18 years, in comparison with the WHO and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention references. Public Health Nutr 13(12):1990–1996
Friesen CS, Hosey-Cojocari C, Chan SS, Csanaky IL, Wagner JB, Sweeney BR, Friesen A, Fraser JD, Shakhnovich V (2021) Efficacy of weight reduction on pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: opportunities to improve treatment outcomes through pharmacotherapy. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 12:663351
Harrison S, Fincke C, Helinski D, Torgerson S, Hayashi P (2004) A pilot study of orlistat treatment in obese, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 20:623–628
Ye J, Wu Y, Li F, Wu T, Shao C, Lin Y, Wang W, Feng S, Zhong B (2019) Effect of orlistat on liver fat content in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with obesity: assessment using magnetic resonance imaging-derived proton density fat fraction. Ther Adv Gastroenterol 12:1756284819879047
Ali Khan R, Kapur P, Jain A, Farah F, Bhandari U (2017) Effect of orlistat on periostin, adiponectin, inflammatory markers and ultrasound grades of fatty liver in obese NAFLD patients. Therap Clin Risk Manag 139–149
Harrison SA, Fecht W, Brunt EM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA (2009) Orlistat for overweight subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized, prospective trial. Hepatology 49:80–86
Hussein O, Grosovski M, Schlesinger S, Szvalb S, Assy N (2007) Orlistat reverse fatty infiltration and improves hepatic fibrosis in obese patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Dig Dis Sci 52:2512–2519
Sabuncu T, Nazligul Y, Karaoglanoglu M, Ucar E, Kilic FB (2003) The effects of sibutramine and orlistat on the ultrasonographic findings, insulin resistance and liver enzyme levels in obese patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Rom J Gastroenterol 12:189–192
Liyanagedera S, Williams RP, Veraldi S, Nobili V, Mann JP (2017) The pharmacological management of NAFLD in children and adolescents. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 10:1225–1237
McDuffie JR, Calis KA, Uwaifo GI, Sebring NG, Fallon EM, Hubbard VS, Yanovski JA (2002) Three-month tolerability of orlistat in adolescents with obesity-related comorbid conditions. Obes Res 10:642–650
Chanoine J-P, Hampl S, Jensen C, Boldrin M, Hauptman J (2005) Effect of orlistat on weight and body composition in obese adolescents: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 293:2873–2883
Halpern B, Halpern A (2015) Safety assessment of FDA-approved (orlistat and lorcaserin) anti-obesity medications. Expert Opin Drug Saf 14:305–315
Baranowski T, Taveras EM (2018) Childhood obesity prevention: changing the focus. Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. 140 Huguenot Street, 3rd Floor New Rochelle, NY 10801 USA, pp 1–3
Hallal PC, Victora CG (2004) Reliability and validity of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ). Med Sci Sports Exerc 36:556
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS (1972) Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 18:499–502
Nobili V, Manco M, Devito R, Di Ciommo V, Comparcola D, Sartorelli MR, Piemonte F, Marcellini M, Angulo P (2008) Lifestyle intervention and antioxidant therapy in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, controlled trial. Hepatology 48:119–128
Louthan MV, Theriot JA, Zimmerman E, Stutts JT, McClain CJ (2005) Decreased prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in black obese children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 41:426–429
Seth A, Orkin S, Yodoshi T, Liu C, Fei L, Hardy J, Trout AT, Arce Clachar AC, Bramlage K, Xanthakos S (2020) Severe obesity is associated with liver disease severity in pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Pediatr Obes 15:e12581
Wald AB, Uli NK (2009) Pharmacotherapy in pediatric obesity: current agents and future directions. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 10:205–214
Yu CC, Li AM, Chan KO, Chook P, Kam JT, Au CT, So RC, Sung RY, McManus AM (2013) Orlistat improves endothelial function in obese adolescents: a randomised trial. J Paediatr Child Health 49:969–975
Maahs D, De Serna DG, Kolotkin RL, Ralston S, Sandate J, Qualls C, Schade DS (2006) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of orlistat for weight loss in adolescents. Endocr Pract 12:18–28
Wang C, Pai AK, Putra J (2022) Paediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an approach to pathological evaluation. J Clin Pathol 75:443–451
Zakaria Z, Othman ZA, Bagi Suleiman J, Jalil NAC, Ghazali WSW, Mohamed M (2021) Protective and therapeutic effects of orlistat on metabolic syndrome and oxidative stress in high-fat diet-induced metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) in rats: role on Nrf2 activation. Veterinary sciences 8:274
Esmail VAW, Mohammed MO, Al-Nimer MS (2021) Short-term orlistat therapy improves fatty infiltration indices and liver fibrosis scores in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome. Arab Journal of Gastroenterology 22:1–5
Bush H, Golabi P, Younossi ZM (2017) Pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Children 4:48
Al-Tahami BAM, Ab AA-SI, Sanip Z, Yusoff Z, Shihabudin TMT, Singh TSP, Rasool AHG (2017) Metabolic and inflammatory changes with orlistat and sibutramine treatment in obese Malaysian subjects. J Nippon Med Sch 84:125–132
Combs TP, Berg AH, Obici S, Scherer PE, Rossetti L (2001) Endogenous glucose production is inhibited by the adipose-derived protein Acrp30. J Clin Investig 108:1875–1881
Ke J, An Y, Cao B, Lang J, Wu N, Zhao D (2020) Orlistat-induced gut microbiota modification in obese mice. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine (eCAM)
Nikniaz Z, Nikniaz L, Farhangi MA, Mehralizadeh H, Salekzamani S (2023) Effect of Orlistat on anthropometrics and metabolic indices in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Endocr Disord 23:142
Sahin M, Tanaci N, Yucel M, Tutuncu NB, Guvener N (2007) The effect of single-dose orlistat on postprandial serum glucose, insulin and glucagon-like peptide-1 levels in nondiabetic obese patients. Clin Endocrinol 67:346–350
Nielsen S, Guo Z, Johnson CM, Hensrud DD, Jensen MD (2004) Splanchnic lipolysis in human obesity. J Clin Investig 113:1582–1588
Parks EJ, Krauss RM, Christiansen MP, Neese RA, Hellerstein MK (1999) Effects of a low-fat, high-carbohydrate diet on VLDL-triglyceride assembly, production, and clearance. J Clin Investig 104:1087–1096
Kim DW, Park C, Yoon HM, Jung AY, Lee JS, Jung SC, Cho YA (2019) Technical performance of shear wave elastography for measuring liver stiffness in pediatric and adolescent patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 29:2560–2572
Nobili V, Alisi A, Grimaldi C, Liccardo D, Francalanci P, Monti L, Castellano A, de Ville de Goyet J (2014) Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma in a 7-year-old obese boy: coincidence or comorbidity? Pediatr Obes 9:e99–e102
Stefan N, Kantartzis K, Häring H-U (2008) Causes and metabolic consequences of fatty liver. Endocr Rev 29:939–960
Morino K, Petersen KF, Shulman GI (2006) Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance in humans and their potential links with mitochondrial dysfunction. Diabetes 55:S9–S15
Shoelson SE, Lee J, Goldfine AB (2006) Inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Investig 116:1793–1801
Doycheva I, Watt KD, Alkhouri N (2017) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adolescents and young adults: the next frontier in the epidemic. Hepatology 65:2100–2109
Kotnik P, Posovszky PF, Wabitsch M (2015) Endocrine and metabolic effects of adipose tissue in children and adolescents/Endokrina in presnovna funkcija maščobnega tkiva pri otrocih in mladostnikih. Slovenian Journal of Public Health 54:131–138
Kiortsis D, Filippatos T, Elisaf M (2005) The effects of orlistat on metabolic parameters and other cardiovascular risk factors. Diabetes Metab 31:15–22
Acknowledgements
We express our appreciation to the participants of this study. This study is taken from the Obesity registry program in children at Tehran University of Medical Sciences (IR.TUMS.CHMC.REC.1401.016). We are thankful to Dr Mohammad Hassan Sohouli and Dr Afshin Ostovar, head of the obesity registry at Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.R and Mh.S contributed in conception, design, and statistical analysis. A.Z., S.S, P.R, and MH.S contributed in data collection and manuscript drafting. P.R and MH.S supervised the study. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the research council and ethics committee Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran (no: IR.TUMS.CHMC.REC.1401.016). The study has been registered in IRCT (IRCT20220409054467N2, with a registration date of 2022–05-13).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Peter de Winter
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zahmatkesh, A., Sohouli, M.H., Shojaie, S. et al. The effect of orlistat in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver in adolescents with overweight and obese. Eur J Pediatr 183, 1173–1182 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-023-05369-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-023-05369-3