Abstract
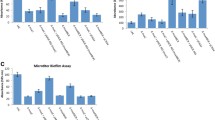
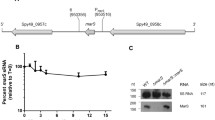
The pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus from local infection to systemic dissemination involves a range of virulence factors including structural and secreted products. Among various control mechanisms, small noncoding RNAs are involved in the regulation of multiple pathogenicity factors in S. aureus. The sRNA SprX which is encoded in the pathogenicity island of methicillin-susceptible S. aureus strain Newman and was shown to influence antibiotic resistance previously, upregulated the expression of virulence genes, especially the cell wall-associated clumping factor B (ClfB) and delta hemolysin (Hld). Bioinformatic analysis revealed several multiple mRNAs associated with pathogenicity as targets for SprX1, one of the three copies of sprX. Both overexpression and chromosomal disruption of sprX1 supported the scheme of upregulation of clfB and hld expression. Altered expression of SprX1 altered the levels of Hld and ClfB mRNAs, hemolysis, clumping of cells, biofilm formation by plate adhesion studies and confocal microscopic analysis as well as infection pathology of modified strains in mice models. ClfB and Hld mRNAs interacted directly with SprX1 in in vitro assays. Increased level of the regulatory RNA, namely RNAIII, that comprises Hld mRNA and also regulates the biofilm formation, indicates that SprX1 may also function through RNAIII for regulating virulence factors. An immunodominant protein, antigen A, was downregulated by SprX1 in two-dimensional electrophoresis. Taken together, these results signify the role of sRNA SprX in the pathogenicity of S. aureus Newman.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Foster TJ, Geoghegan JA, Ganesh VK, Hook M (2014) Adhesion, invasion and evasion: the many functions of the surface proteins of Staphylococcus aureus. Nat Rev Microbiol 12:49–62
Powers ME, Wardenburg JB (2014) Igniting the fire: Staphylococcus aureus virulence factors in the pathogenesis of sepsis. PLoS Pathog 10:e1003871
Waters LS, Storz G (2009) Regulatory RNAs in bacteria. Cell 136:615–628
Storz G, Altuvia S, Wassarman KM (2005) An abundance of RNA regulators. Annu Rev Biochem 74:199–217
Sassi M, Augagneur Y, Mauro T, Ivain L, Chabelskaya S, Hallier M et al (2015) SRD: a Staphylococcus regulatory RNA database. RNA 21:1005–1017
Boisset S, Geissmann T, Huntzinger E, Fechter P, Bendridi N, Possedko M et al (2007) Staphylococcus aureus RNAIII coordinately represses the synthesis of virulence factors and the transcriptional regulator Rot by an antisense mechanism. Genes Dev 21:1353–1366
Bohn C, Rigoulay C, Chabelskaya S, Sharma CM, Marchais A, Skorski P et al (2010) Experimental discovery of small RNAs in Staphylococcus aureus reveals a riboregulator of central metabolism. Nucleic Acids Res 38:6620–6636
Chabelskaya S, Gaillot O, Felden B (2010) A Staphylococcus aureus small RNA is required for bacterial virulence and regulates the expression of an immune evasion molecule. PLoS Pathog 6:e1000927
Sayed N, Jousselin A, Felden B (2011) A cis-antisense RNA acts in trans in Staphylococcus aureus to control translation of a human cytolytic peptide. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19:105–112
Morrison JM, Miller EW, Benson MA, Alonzo FIII, Yoong P, Torres VJ et al (2012) Characterization of SSR42, a novel virulence factor regulatory RNA that contributes to the pathogenesis of a Staphylococcus aureus USA300 representative. J Bacteriol 194:2924–2938
Eyraud A, Tattevin P, Chabelskaya S, Felden B (2014) A small RNA controls a protein regulator involved in antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Nucleic Acids Res 42:4892–4905
Romilly C, Lays C, Tomasini A, Caldelari I, Benito Y, Hammann P et al (2014) A noncoding RNA promotes bacterial persistence and decreases virulence by regulating a regulator in Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS Pathog 10:e1003979
Xue T, Zhang X, Sun H, Sun B (2014) ArtR, a novel sRNA of Staphylococcus aureus, regulates α-toxin expression by targeting the 5′ UTR of sarT mRNA. Med Microbiol Immunol 203:1–12
Pinel-Marie ML, Brielle R, Felden B (2014) Dual toxic peptide coding Staphylococcus aureus RNA under antisense regulation targets host cells and bacterial rivals unequally. Cell Rep 7:424–435
Le Pabic H, Germain-Amiot N, Bordeau V, Felden B (2015) A bacterial regulatory RNA attenuates virulence, spread and human host cell phagocytosis. Nucleic Acids Res 43:9232–9248
Blevins JS, Beenken KE, Elasri MO, Hurlburt BK, Smeltzer MS (2002) Strain dependent differences in the regulatory roles of sarA and agr in Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun 70:470–480
Bohn C, Rigoulay C, Bouloc P (2007) No detectable effect of RNA-binding protein Hfq absence in Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Microbiol 7:10
Huntzinger E, Boisset S, Saveanu C, Benito Y, Geissmann T, Namane A et al (2005) Staphylococcus aureus RNAIII and the endoribonuclease III coordinately regulate spa gene expression. EMBO J 24:824–835
Duthie ES, Lorenz LL (1952) Staphylococcal coagulase: mode of action and antigenicity. J Gen Microbiol 6:95–107
Pichon C, Felden B (2005) Small RNA genes expressed from Staphylococcus aureus genomic and pathogenicity islands with specific expression among pathogenic strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:14249–14254
Zuker M (2003) Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3406–3415
Tjaden B (2008) TargetRNA: a tool for predicting targets of small RNA action in bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res 36:109–113
Eggenhofer F, Tafer H, Stadler PF, Hofacker IL (2011) RNApredator: fast accessibility based prediction of sRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res 39:W149–W154
Muckstein U, Tafer H, Hackermuller J, Bernhart SH, Stadler PF, Hofacker IL (2006) Thermodynamics of RNA-RNA Binding. Bioinformatics 22:1177–1182
Busch A, Richter AS, Backofen R (2008) IntaRNA: efficient prediction of bacterial sRNA targets incorporating target site accessibility and seed regions. Bioinformatics 24:2849–2856
Monk IR, Shah IM, Xu M, Tan MW, Foster TJ (2012) Transforming the untransformable: application of direct transformation to manipulate genetically Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. mBio 3:e00277-11
Sambrook J, Russel DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Lab Press, New York
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (2006) The single step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate phenol chloroform extraction: twenty something years on. Nat Protoc 1:581–585
Zmantar T, Kouidhi B, Miladi H, Mahdouani K, Bakhrouf A (2010) A microtiter plate assay for Staphylococcus aureus biofilm quantification at various pH levels and hydrogen peroxide supplementation. New Microbiol 33:137–145
Hochbaum AI, Kolodkin-Gal I, Foulston L, Kolter R, Aizenber J, Losick R (2011) Inhibitory effects of d-amino acids on Staphylococcus aureus biofilm development. J Bacteriol 193:5616–5622
Ravi MS, Vijay R, Kumari S, Panchasara C (2013) Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of orthodontic adhesives on human lymphocyte—an in vitro study. Med Sci 2:820–829
Wiseman GM (1975) The hemolysins of Staphylococcus aureus. Bacteriol Rev 39:317–344
Kernodle DS, McGraw PA, Barg NL, Menzies BE, Voladri RK, Harshman S (1995) Growth of Staphylococcus aureus with nafcillin in vitro induces alpha-toxin production and increases the lethal activity of sterile broth filtrates in a murine model. J Infect Dis 172:410–419
Bayer AS, Ramos MD, Menzies BE, Yeaman MR, Shen AJ, Cheung AL (1997) Hyper production of alpha-toxin by Staphylococcus aureus results in paradoxically reduced virulence in experimental endocarditis: a host defense role for platelet microbicidal proteins. Infect Immun 65:4652–4660
Zhang L, Gray L, Novick RP, Ji G (2002) Transmembrane topology of AgrB, the protein involved in the post-translational modification of AgrD in Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem 277:34736–34742
Schmitz FJ, Veldkamp KE, Van Kessel KPM, Verhoef J, Van Strijp JA (1997) Delta toxin from Staphylococcus aureus as a costimulator of human neutrophil oxidative burst. J Infect Dis 176:1531–1537
Sakoulas G, Moellering RC Jr, Eliopoulos GM (2006) Adaptation of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the face of vancomycin therapy. Clin Infect Dis 42:S40–S50
Morfeldt E, Taylor D, von Gabain A, Arvidson S (1995) Activation of alpha-toxin translation in Staphylococcus aureus by the trans-encoded antisense RNA, RNAIII. EMBO J 14:4569–4577
Den Reijer PM, Haisma EM, Lemmens-den Toom NA, Willemse J, Koning RA et al (2016) Detection of alpha-toxin and other virulence factors in biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus on polystyrene and a human epidermal model. PLoS ONE 24:e0152544
Cheng AG, Kim HK, Burts ML, Krausz T, Schneewind O, Missiakas DM (2009) Genetic requirements for Staphylococcus aureus abscess formation and persistence in host tissues. FASEBJ 23:3393–3404
Wertheim HFL, Walsh E, Choudhurry R, Melles DC, Boelens HAM, Miajlovic H et al (2008) Key role for clumping factor B in Staphylococcus aureus nasal colonization of humans. PLoS Med 5:e17
Iyer VR, Sharma R, Pathania R, Navani NK (2012) Small RNAs of pathogenic bacteria: not small enough to be overlooked for therapeutics. Mol Cell Pharmacol 4:17–30
Benito Y, Kolb FA, Romby P, Lina G, Etienne J, Vandensch F (2000) Probing the structure of RNAIII, the Staphylococcus aureus agr regulatory RNA and identification of the RNA domain involved in repression of protein A expression. RNA 6:668–679
Archer NK, Mazaitis MJ, Costerton JW, Leid JG, Powers ME, Shirtliff ME (2011) Staphylococcus aureus biofilms properties, regulation and roles in human disease. Virulence 2:445–459
Chambers JR, Sauer K (2013) Small RNAs and their role in biofilm formation. Trends Microbiol 21:39–41
Coelho LR, Souza RR, Ferreira FA, Guimaraes MA, Ferreira-Carvalho BT, Figueiredo AM (2008) agr RNAIII divergently regulates glucose-induced biofilm formation in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiology 154:3480–3490
Le KY, Otto M (2015) Quorum sensing regulation in staphylococci- an overview. Front Microbiol 6:1174
Resch A, Rosenstein R, Nerz C, Gotz F (2005) Differential gene expression profiling of Staphylococcus aureus cultivated under biofilm and planktonic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2663–2676
Abraham NM, Jefferson KK (2012) Staphylococcus aureus clumping factor B mediates biofilm formation in the absence of calcium. Microbiology 158:1504–1512
Thurlow LR, Hanke ML, Fritz T, Angle A, Aldrich A, Williams SH et al (2011) Staphylococcus aureus biofilms prevent macrophage phagocytosis and attenuate inflammation in vivo. J Immunol 186:6585–6596
Lorenz U, Ohlsen K, Karch H, Hecker M, Thiede A, Hacker J (2000) Human antibody response during sepsis against targets expressed by methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 29:145–153
Stapleton MR, Horsburgh MJ, Hayhurst EJ, Wright L, Jonsson IM, Tarkowski A et al (2007) Characterization of IsaA and SceD, two putative lytic transglycosylases of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 189:7316–7325
Payne DE, Martin NR, Parzych KR, Rickard AH, Underwood A, Boles BR (2013) Tannic acid inhibits Staphylococcus aureus surface colonization in an IsaA-dependent manner. Infect Immun 81:496–504
Sakata N, Terakubo S, Mukai T (2005) Subcellular location of the soluble lytic transglycosylase homologue in Staphylococcus aureus. Curr Microbiol 50:47–51
Nair D, Memmi G, Hernandez D, Bard J, Beaume M, Gill S et al (2011) Whole genome sequencing of Staphylococcus aureus strain RN4220, a key laboratory strain used in virulence research, identifies mutations that affect not only virulence factors but also the fitness of the strain. J Bacteriol 193:2332–2335
Acknowledgments
We thank Professors Timothy Foster and Ian. R. Monk, Trinity College, Dublin, Abraham. L. Sonenshein, Tufts University, Boston, for providing shuttle plasmids, S. aureus and E. coli strains. The pCN40 vector was obtained through the Network on Antimicrobial Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus (NARSA) program supported under NIAD, NIH Contract No. HHSN272200700055C. MK was supported by a research fellowship (F.4-1/2006(BSR)/7-128/2007) by University Grant Commission, Government of India. The initial phase of this work was partially funded by a grant from the Department of Biotechnology, India (BT/PR/P0056/AGR/36/29/2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics statement
The study protocols for the experimental use of mice were carried out in strict accordance with and approved by Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision on Experiments on Animals (CPCSEA), Government of India (Approval number 938/PO/a/06/CPCSEA).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kathirvel, M., Buchad, H. & Nair, M. Enhancement of the pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus strain Newman by a small noncoding RNA SprX1. Med Microbiol Immunol 205, 563–574 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-016-0467-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-016-0467-9