Abstract
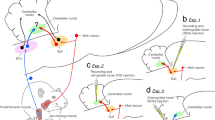
The supratrigeminal nucleus (Su5) is a key structure for controlling jaw movements; it receives proprioceptive sensation from jaw-closing muscle spindles (JCMSs) and sends projections to the trigeminal motor nucleus (Mo5). However, the central projections and regulation of JCMS proprioceptive sensation are not yet fully understood. Therefore, we aimed to reveal the efferent and afferent connections of the Su5 using neuronal tract tracings. Anterograde tracer injections into the Su5 revealed that the Su5 sends contralateral projections (or bilateral projections with a contralateral predominance) to the Su5, basilar pontine nuclei, pontine reticular nucleus, deep mesencephalic nucleus, superior colliculus, caudo-ventromedial edge of the ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus, parafascicular thalamic nucleus, zona incerta, and lateral hypothalamus, and ipsilateral projections (or bilateral projections with an ipsilateral predominance) to the intertrigeminal region, trigeminal oral subnucleus, dorsal medullary reticular formation, and hypoglossal nucleus as well as the Mo5. Retrograde tracer injections into the Su5 demonstrated that the Su5 receives bilateral projections with a contralateral predominance (or contralateral projections) from the primary and secondary somatosensory cortices, granular insular cortex, and Su5, and ipsilateral projections (or bilateral projections with an ipsilateral predominance) from the dorsal peduncular cortex, bed nuclei of stria terminalis, central amygdaloid nucleus, lateral hypothalamus, parasubthalamic nucleus, trigeminal mesencephalic nucleus, parabrachial nucleus, juxtatrigeminal region, trigeminal oral and caudal subnuclei, and dorsal medullary reticular formation. These findings suggest that the Su5, which receives JCMS proprioception, has efferent and afferent connections with multiple brain regions that are involved in emotional and autonomic functions as well as orofacial motor functions.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data and materials are available upon request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- 3:
-
Oculomotor nucleus
- 5C:
-
Caudal subnucleus of the trigeminal spinal nucleus
- 5I:
-
Interpolar subnucleus of the trigeminal spinal nucleus
- 5O:
-
Oral subnucleus of the trigeminal spinal nucleus
- 5Or:
-
Rostro-dorsomedial part of the 5O
- 7n:
-
Facial nerve
- 10:
-
Dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
- ac:
-
Anterior commissure
- Acb:
-
Accumbens nucleus
- ACg:
-
Anterior cingulate cortex
- AD:
-
Anterodorsal thalamic nucleus
- Agl:
-
Lateral agranular cortex
- Agm:
-
Medial agranular cortex
- AI:
-
Agranular insular cortex
- Amb:
-
Ambiguus nucleus
- AmBl:
-
Basolateral amygdaloid nucleus
- AmC:
-
Central amygdaloid nucleus
- AmL:
-
Lateral amygdaloid nucleus
- AP:
-
Area postrema
- Aq:
-
Aqueduct
- Au:
-
Auditory cortex
- AV:
-
Anteroventral thalamic nucleus
- BDA:
-
Biotinylated dextranamine
- BPn:
-
Basilar pontine nuclei
- BST:
-
Bed nucleus of stria terminalis
- BSTl:
-
Lateral division of the BST
- BSTm:
-
Medial division of the BST
- CC:
-
Central canal
- cc:
-
Corpus callosum
- CL:
-
Centrolateral thalamic nucleus
- Cl:
-
Claustrum
- CM:
-
Central medial thalamic nucleus
- CPu:
-
Caudate putamen
- CTb:
-
Cholera toxin B subunit
- Cu:
-
Cuneate nucleus
- cu:
-
Cuneate fasciculus
- dGIrvs2:
-
Dorsal part of the GI rostroventrally adjacent to the rostralmost part of the S2
- DI:
-
Dysgranular insular cortex
- dmRf:
-
Dorsal medullary reticular formation
- DP:
-
Dorsal peduncular cortex
- DpMe:
-
Deep mesencephalic nucleus
- DR:
-
Dorsal raphe nucleus
- DTg:
-
Dorsal tegmental nucleus
- Ect:
-
Ectorhinal cortex
- ECu:
-
External cuneate nucleus
- f:
-
Fornix
- fr:
-
Fasciculus retroflexus
- GI:
-
Granular insular cortex
- Gr:
-
Gracile nucleus
- I5:
-
Intertrigeminal region
- IC:
-
Inferior colliculus
- ic:
-
Internal capsule
- IL:
-
Infralimbic cortex
- IO:
-
Inferior olive
- IPAC:
-
Interstitial nucleus of the posterior limb of the anterior commissure
- J5:
-
Juxtatrigeminal region
- JCm:
-
Jaw-closing motor nucleus
- JCMS:
-
Jaw-closing muscle spindle
- JOm:
-
Jaw-opening motor nucleus
- KF:
-
Kölliker-Fuse nucleus
- LEnt:
-
Lateral entorhinal cortex
- lf:
-
Longitudinal fasciculus
- LGP:
-
Lateral globus pallidus
- LH:
-
Lateral hypothalamus
- LO:
-
Lateral orbital cortex
- MD:
-
Mediodorsal thalamic nucleus
- Me5:
-
Trigeminal mesencephalic nucleus
- MGP:
-
Medial globus pallidus
- ml:
-
Medial lemniscus
- MO:
-
Medial orbital cortex
- Mo5:
-
Trigeminal motor nucleus
- OPC:
-
Oval paracentral thalamic nucleus
- ox:
-
Optic chiasm
- PA:
-
Parietal association cortex
- Pa5:
-
Paratrigeminal nucleus
- PAG:
-
Periaqueductal gray
- PB:
-
Phosphate buffer
- Pb:
-
Parabrachial nucleus
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PC:
-
Paracentral thalamic nucleus
- Pf:
-
Parafascicular thalamic nucleus
- PnR:
-
Pontine reticular nucleus
- Po:
-
Posterior thalamic nucleus
- Pr:
-
Prepositus nucleus
- Pr5:
-
Trigeminal principal nucleus
- PRh:
-
Perirhinal cortex
- PrL:
-
Prelimbic cortex
- Psth:
-
Parasubthalamic nucleus
- PvH:
-
Paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus
- py:
-
Pyramidal tract
- pyx:
-
Pyramidal decussation
- R:
-
Red nucleus
- Rfvm:
-
Reticular formation ventral to the Mo5
- RRF:
-
Retrorubral field
- Rt:
-
Reticular thalamic nucleus
- RtTg:
-
Reticulotegmental nucleus
- S1:
-
Primary somatosensory cortex
- S2:
-
Secondary somatosensory cortex
- SC:
-
Superior colliculus
- scp:
-
Superior cerebellar peduncle
- Sm:
-
Submedial thalamic nucleus
- SNc:
-
Substantia nigra pars compacta
- SNr:
-
Substantia nigra pars reticulata
- Sol:
-
Solitary tract nucleus
- sp5:
-
Spinal trigeminal tract
- st:
-
Stria terminalis
- Sth:
-
Subthalamic nucleus
- Su5:
-
Supratrigeminal nucleus
- TA:
-
Temporal association cortex
- tth:
-
Trigeminothalamic tract
- VA:
-
Ventral anterior thalamic nucleus
- Ve:
-
Vestibular nucleus
- VII:
-
Facial nucleus
- VL:
-
Ventrolateral thalamic nucleus
- VM:
-
Ventromedial thalamic nucleus
- VO:
-
Ventral orbital cortex
- VPL:
-
Ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus
- VPM:
-
Ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus
- VPMcvm:
-
Caudo-ventromedial edge of the VPM
- VPPC:
-
Parvicellular part of the ventral posterior thalamic nucleus
- XII:
-
Hypoglossal nucleus
- ZI:
-
Zona incerta
References
Akhter F, Haque T, Sato F, Kato T, Ohara H, Fujio T, Tsutsumi K, Uchino K, Sessle BJ, Yoshida A (2014) Projections from the dorsal peduncular cortex to the trigeminal subnucleus caudalis (medullary dorsal horn) and other lower brainstem areas in rats. Neuroscience 266:23–37
Alden M, Besson JM, Bernard JF (1994) Organization of the efferent projections from the pontine parabrachial area to the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and neighboring regions: a PHA-L study in the rat. J Comp Neurol 341:289–314
Altschuler SM, Bao XM, Bieger D, Hopkins DA, Miselis RR (1989) Viscerotopic representation of the upper alimentary tract in the rat: sensory ganglia and nuclei of the solitary and spinal trigeminal tracts. J Comp Neurol 283:248–268
Arts MPM, Bemelmans FFJ, Cools AR (1998) Role of the retrorubral nucleus in striatally elicited orofacial dyskinesia in cats: effects of muscimol and bicuculline. Psychopharmacol 140:150–156
Åström KE (1953) On the central course of afferent fibres in the trigeminal, facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagal nerves and their nuclei in the mouse. Acta Physiol Scand 39(Suppl 106):209–320
Augustine JR (1985) The insular lobe in primates including humans. Neurol Res 7:2–10
Augustine JR (1996) Circuitry and functional aspects of the insular lobe in primates including humans. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 22:229–244
Avivi-Arber L, Lee JC, Sessle BJ (2010) Effects of incisor extraction on jaw and tongue motor representations within face sensorimotor cortex of adult rats. J Comp Neurol 518:1030–1045
Berendse HW, Groenewegen HJ (1991) Restricted cortical termination fields of the midline and intralaminar thalamic nuclei in the rat. Neuroscience 42:73–102
Bickford ME, Hall WC (1992) The nigral projection to predorsal bundle cells in the superior colliculus of the rat. J Comp Neurol 319:11–33
Bienkowski MS, Rinaman L (2013) Common and distinct neural inputs to the medial central nucleus of the amygdala and anterior ventrolateral bed nucleus of stria terminalis in rats. Brain Struct Funct 218:187–208
Brodal P (1982) The cerebropontocerebellar pathway: Salient features of its organization. Exp Brain Res [suppl] 6:108–133
Campbell SK, Parker TD, Welker W (1974) Somatotopic organization of the external cuneate nucleus in albino rats. Brain Res 77:1–23
Chang Z, Haque T, Iida C, Seki S, Sato F, Kato T, Uchino K, Ono T, Nakamura M, Bae YC, Yoshida A (2009) Distribution of premotoneurons for jaw-closing and jaw-opening motor nucleus receiving contacts from axon terminals of primary somatosensory cortical neurons in rats. Brain Res 1275:43–53
Coote JH (2005) A role for the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in the autonomic control of heart and kidney. Exp Physiol 90:169–173
Cunningham ET Jr, Sawchenko PE (2000) Dorsal medullary pathways subserving oromotor reflexes in the rat: implications for the central neural control of swallowing. J Comp Neurol 417:448–466
de No ́RL (1922) Contribucio ́na1conocimientodelnervio trige ́mino. Libro en honor de Dn. S. Ramo ́n y Cajal. Madrid, Mo ́ya 2:13
de No ́RL (1933) Vestibulo-ocular reflex arc. Arch Neurol Psychiat 30:245–291
Dong HW, Swanson LW (2003) Projections from the rhomboid nucleus of the bed nuclei of the stria terminalis: implications for cerebral hemisphere regulation of ingestive behaviors. J Comp Neurol 463:434–472
Donga R, Lund JP, Veilleux D (1990) An electrophysiological study of trigeminal commissural interneurons in the anaesthetized rabbit. Brain Res 515:351–354
Donoghue JP, Parham C (1983) Afferent connections of the lateral agranular field of the rat motor cortex. J Comp Neurol 217:390–404
Donoghue JP, Wise SP (1982) The motor cortex of the rat: cytoarchitecture and microstimulation mapping. J Comp Neurol 212:76–88
Dubner R, Sessle BJ, Storey AT (1978) The Neural Basis of Oral and Facial Function. Plenum Press, New York
Fujio T, Sato F, Tachibana Y, Kato T, Tomita A, Higashiyama K, Ono T, Maeda Y, Yoshida A (2016) Revisiting the supratrigeminal nucleus in the rat. Neuroscience 324:307–320
Gauriau C, Bernard JF (2004) Posterior triangular thalamic neurons convey nociceptive messages to the secondary somatosensory and insular cortices in the rat. J Neurosci 24:752–761
Goldberg LJ, Nakamura Y (1968) Lingually induced inhibition of masseteric motoneurones. Experientia 24:371–373
Goto M, Swanson LW (2004) Axonal projections from the parasubthalamic nucleus. J Comp Neurol 469:581–607
Graeff FG, Guimarães FS, De Andrade TG, Deakin JF (1996) Role of 5-HT in stress, anxiety, and depression. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 54:129–141
Hanamori T, Kunitake T, Kato K, Kannan H (1998a) Neurons in the posterior insular cortex are responsive to gustatory stimulation of the pharyngolarynx, baroreceptor and chemoreceptor stimulation, and tail pinch in rats. Brain Res 785:97–106
Hanamori T, Kunitake T, Kato K, Kannan H (1998b) Responses of neurons in the insular cortex to gustatory, visceral, and nociceptive stimuli in rats. J Neurophysiol 79:2535–2545
Haque T, Akhter F, Kato T, Sato F, Takeda R, Higashiyama K, Moritani M, Bae YC, Sessle BJ, Yoshida A (2012) Somatotopic direct projections from orofacial areas of secondary somatosensory cortex to trigeminal sensory nuclear complex in rats. Neuroscience 219:214–233
Hattox AM, Priest CA, Keller A (2002) Functional circuitry involved in the regulation of whisker movements. J Comp Neurol 442:266–276
Herman JP, Cullinan WE (1997) Neurocircuitry of stress: central control of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. Trends Neurosci 20:78–84
Hicks RR, Huerta MF (1991) Differential thalamic connectivity of rostral and caudal parts of cortical area Fr2 in rats. Brain Res 568:325–329
Huerta MF, Harting JK (1984) Connectional organization of the superior colliculus. Trends Neurosci 7:286–289
Ikenoue E, Akhter F, Tsutsumi Y, Sato F, Ohara H, Uchino K, Furuta T, Tachibana Y, Yoshida A (2018) Transcortical descending pathways through granular insular cortex conveying orofacial proprioception. Brain Res 1687:11–19
Ito S (1992) Multiple projection of vagal non-myelinated afferents to the anterior insular cortex in rats. Neurosci Lett 148:151–154
Ito H, Yanase M, Yamashita A, Kitabatake C, Hamada A, Suhara Y, Narita M, Ikegami D, Sakai H, Yamazaki M, Narita M (2013) Analysis of sleep disorders under pain using an optogenetic tool: possible involvement of the activation of dorsal raphe nucleus-serotonergic neurons. Mol Brain 6:59. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-6606-6-59
Jerge CR (1963) The function of the nucleus supratrigeminalis. J Neurophysiol 26:393–402
Kawamura Y, Tsukamoto S (1960) Analysis of jaw movements from the cortical jaw motor area and amygdala. Jpn J Physiol 10:471–488
Kidokoro Y, Kubota K, Shuto S, Sumino R (1968) Possible interneurons responsible for reflex inhibition of motoneurons of jaw-closing muscles from the inferior dental nerve. J Neurophysiol 31:709–716
Kosinski RJ, Neafsey EJ, Castro AJ (1986) A comparative topographical analysis of dorsal column nuclear and cerebral cortical projections to the basilar pontine gray in rats. J Comp Neurol 244:163–173
Landgren S, Olsson KA (1980) The effect of electrical stimulation in the hypothalamus on the monosynaptic jaw closing and the disynaptic jaw opening reflexes in the cat. Exp Brain Res 39:389–400
Li YQ, Takada M, Kaneko T, Mizuno N (1995) Premotor neurons for trigeminal motor nucleus neurons innervating the jaw-closing and jaw-opening muscles: differential distribution in the lower brainstem of the rat. J Comp Neurol 356:563–579
Luo P, Wong R, Dessem D (1995) Projection of jaw-muscle spindle afferents to the caudal brainstem in rats demonstrated using intracellular biotinamide. J Comp Neurol 358:63–78
Luo P, Moritani M, Dessem D (2001) Jaw-muscle spindle afferent pathways to the trigeminal motor nucleus in the rat. J Comp Neurol 435:341–353
Ma WL, Zhang WB, Xiong KH, Guo F (2007) Visceral and orofacial somatic afferent fiber terminals converge onto the same neuron in paratrigeminal nucleus: An electron microscopic study in rats. Auton Neurosci 131:45–49
Malick A, Burstein R (1998) Cells of origin of the trigeminohypothalamic tract in the rat. J Comp Neurol 400:125–144
Malick A, Strassman RM, Burstein R (2000) Trigeminohypothalamic and reticulohypothalamic tract neurons in the upper cervical spinal cord and caudal medulla of the rat. J Neurophysiol 84:2078–2112
Mascaro MB, Prosdocimi FC, Bittencourt JC, Elias CF (2009) Forebrain projections to brainstem nuclei involved in the control of mandibular movements in rats. Eur J Oral Sci 117:676–684
Mesulam MM, Mufson EJ (1982) Insula of the old world monkey. III: efferent cortical output and comments on function. J Comp Neurol 212:38–52
Mihailoff GA, Kosinski RJ, Azizi SA, Border BG (1989) Survey of noncortical afferent projections to the basilar pontine nuclei: a retrograde tracing study in the rat. J Comp Neurol 282:617–643
Mitrofanis J (2005) Some certainty for the “zone of uncertainty”? Exploring the function of the zona incerta. Neuroscience 130:1–15
Miyazaki R, Luschei ES (1987) Responses of neurons in nucleus supratrigeminalis to sinusoidal jaw movements in the cat. Exp Neurol 96:145–157
Mizuno N (1970) Projection fibers from the main sensory trigeminal nucleus and the supratrigeminal region. J Comp Neurol 139:457–471
Nakamura Y, Kubo Y (1978) Masticatory rhythm in intracellular potential of trigeminal motoneurons induced by stimulation of orbital cortex and amygdala in cats. Brain Res 14:504–509
Nakamura S, Inoue T, Nakajima K, Moritani M, Nakayama K, Tokita K, Yoshida A, Maki K (2008) Synaptic transmission from the supratrigeminal region to jaw-closing and jaw-opening motoneurons in developing rats. J Neurophysiol 100:1885–1896
Nonaka M, Nishimura A, Nakamura S, Nakayama K, Mochizuki A, Iijima T, Inoue T (2012) Convergent pre-motoneuronal inputs to single trigeminal motoneurons. J Dent Res 91:888–893
Notsu K, Tsumori T, Yokota S, Sekine J, Yasui Y (2008) Posterior lateral hypothalamic axon terminals are in contact with trigeminal premotor neurons in the parvicellular reticular formation of the rat medulla oblongata. Brain Res 1244:71–81
Ogawa H, Wang XD (2002) Neurons in the cortical taste area receive nociceptive inputs from the whole body as well as the oral cavity in the rat. Neurosci Lett 322:87–90
Ohta M, Moriyama Y (1986) Supratrigeminal neurons mediate the shortest, disynaptic pathway from the central amygdaloid nucleus to the contralateral trigeminal motoneurons in the rat. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol 83:633–641
Oka A, Yamamoto M, Takeda R, Ohara H, Sato F, Akhter F, Haque T, Kato T, Sessle BJ, Takada K, Yoshida A (2013) Jaw-opening and -closing premotoneurons in the nucleus of the solitary tract making contacts with laryngeal and pharyngeal afferent terminals in rats. Brain Res 1540:48–63
Paik SK, Lee HJ, Choi MK, Cho YS, Park MJ, Moritani M, Yoshida A, Kim YS, Bae YC (2009) Ultrastructural analysis of glutamate-, GABA-, and glycine-immunopositive boutons from supratrigeminal premotoneurons in the rat trigeminal motor nucleus. J Neurosci Res 87:1115–1122
Papp RS, Palkovits M (2014) Brainstem projections of neurons located in various subdivisions of the dorsolateral hypothalamic area-an anterograde tract-tracing study. Front Neuroanat 8:34. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2014.00034
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press, Sydney
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 4th edn. Academic Press, Sydney
Paxinos G, Watson C (2014) The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 7th edn. Academic Press, Sydney
Peters J, Kalivas PW, Quirk GJ (2009) Extinction circuits for fear and addiction overlap in prefrontal cortex. Learn Mem 16:279–288
Phelan KD, Falls WM (1989) The interstitial system of the spinal trigeminal tract in the rat: anatomical evidence for morphological and functional heterogeneity. Somatosens Mot Res 6:367–399
Porter JD, Donaldson IM (1991) The anatomical substrate for cat extraocular muscle proprioception. Neuroscience 43:473–483
Rokx JT, van Willigen JD, Jüch PJ (1986) Bilateral brainstem connections of the rat supratrigeminal region. Acta Anat (basel) 127:16–21
Rosén I, Sjölund B (1973) Organization of group I activated cells in the main and external cuneate nuclei of the cat: identification of muscle receptors. Exp Brain Res 16:221–237
Sanders KH, Klein CE, Mayor TE, Heym C, Handwerker HO (1980) Differential effects of noxious and non-noxious input on neurones according to location in ventral periaqueductal grey or dorsal raphe nucleus. Brain Res 186:83–97
Sasamoto K, Ohta M (1982) Amygdaloid-induced jaw opening and facilitation or inhibition of the trigeminal motoneurons in the rat. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol 73:349–354
Sasamoto K, Zhang G, Iwasaki M (1990) Two types of rhythmical jaw movements evoked by stimulation of the rat cortex. Jpn J Oral Biol 32:57–68
Sato F, Akhter F, Haque T, Kato T, Takeda R, Nagase Y, Sessle BJ, Yoshida A (2013) Projections from the insular cortex to pain- receptive trigeminal caudal subnucleus (medullary dorsal horn) and other lower brainstem areas in rats. Neuroscience 233:9–27
Sato F, Uemura Y, Kanno C, Tsutsumi Y, Tomita A, Oka A, Kato T, Uchino K, Murakami J, Haque T, Tachibana Y, Yoshida A (2017) Thalamo-insular pathway conveying orofacial muscle proprioception in the rat. Neuroscience 365:158–178
Sato F, Kado S, Tsutsumi Y, Tachibana Y, Ikenoue E, Furuta T, Uchino K, Bae YC, Uzawa N, Yoshida A (2020) Ascending projection of jaw-closing muscle-proprioception to the intralaminar thalamic nuclei in rats. Brain Res 1739:146830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2020.146830
Satoh Y, Ishizuka K, Murakami T (2007) Changes in cortically induced rhythmic jaw movements after lesioning of the red nucleus in rats. Brain Res 1165:60–70
Sawchenko PE, Brown ER, Chan RK, Ericsson A, Li HY, Roland BL, Kovacs KJ (1996) The paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and the functional neuroanatomy of visceromotor responses to stress. Prog Brain Res 107:201–222
Shammah-Lagnado SJ, Alheid GF, Heimer L (2001) Striatal and central extended amygdala parts of the interstitial nucleus of the posterior limb of the anterior commissure: evidence from tract-tracing techniques in the rat. J Comp Neurol 439:104–126
Shigenaga Y, Mitsuhiro Y, Yoshida A, Cao CQ, Tsuru H (1988a) Morphology of single mesencephalic trigeminal neurons innervating masseter muscle of the cat. Brain Res 445:392–399
Shigenaga Y, Sera M, Nishimori T, Suemune S, Nishimura M, Yoshida A, Tsuru K (1988b) The central projection of masticatory afferent fibers to the trigeminal sensory nuclear complex and upper cervical spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 268:489–507
Shigenaga Y, Doe K, Suemune S, Mitsuhiro Y, Tsuru K, Otani K, Shirana Y, Hosoi M, Yoshida A, Kagawa K (1989) Physiological and morphological characteristics of periodontal mesencephalic trigeminal neurons in the cat –intra-axonal staining with HRP. Brain Res 505:91–110
Shigenaga Y, Mitsuhiro Y, Shirana Y, Tsuru H (1990) Two types of jaw-muscle spindle afferents in the cat as demonstrated by intra-axonal staining with HRP. Brain Res 514:219–237
Shimizu K, Asano M, Kitagawa J, Ogiso B, Ren K, Oki H, Matsumoto M, Iwata K (2006) Phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in medullary and upper cervical cord neurons following noxious tooth pulp stimulation. Brain Res 1072:99–109
Stanek IV E, Cheng S, Takatoh J, Han BX, Wang F (2014) Monosynaptic premotor circuit tracing reveals neural substrates for oro-motor coordination. eLife 3:e02511. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02511
Swanson LW (2004) Brain maps: Structure of the rat brain. A laboratory guide with printed and electronic templates for data, models and schematics (3rd ed.). Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Swenson RS, Kosinski RJ, Castro AJ (1984) Topography of spinal, dorsal column nuclear, and spinal trigeminal projections to the pontine gray in rats. J Comp Neurol 222:301–311
Takata M, Kawamura Y (1970) Neurophysiologic properties of the supratrigeminal nucleus. Jap J Physiol 20:1–11
Takemura M, Sugimoto T, Shigenaga Y (1991) Difference in central projection of primary afferents innervating facial and intraoral structures in the rat. Exp Neurol 111:324–331
Taylor A (1990) Neurophysiology of the Jaws and Teeth. Macmillan Press, London
Ter Horst GJ, Copray JC, Liem RS, Van Willigen JD (1991) Projections from the rostral parvocellular reticular formation to pontine and medullary nuclei in the rat: involvement in autonomic regulation and orofacial motor control. Neuroscience 40:735–758
Thompson RH, Swanson LW (2003) Structural characterization of a hypothalamic visceromotor pattern generator network. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 41:153–202
Tomita A, Kato T, Sato F, Haque T, Oka A, Yamamoto M, Ono T, Bae YC, Maeda Y, Sessle BJ, Yoshida A (2012) Somatotopic direct projections from orofacial areas of primary somatosensory cortex to pons and medulla, especially to trigeminal sensory nuclear complex, in rats. Neuroscience 200:166–185
Torvik A (1956) Afferent connections to the sensory trigeminal nuclei, the nucleus of the solitary tract and adjacent structures. J Comp Neurol 106:51–141
Travers JB, Norgren R (1983) Afferent projections to the oral motor nuclei in the rat. J Comp Neurol 220:280–298
Tsutsumi Y, Mizuno Y, Haque H, Sato F, Furuta T, Oka A, Moritani M, Bae YC, Yamashiro T, Tachibana Y, Yoshida A (2021) Widespread corticopetal projections from the oval paracentral nucleus of the intralaminar thalamic nuclei conveying orofacial proprioception in rats. Brain Struct Funct 226:1115–1133
Uchida T, Adachi K, Fujita S, Lee J, Gionhaku N, Cools AR, Koshikawa N (2005) Role of GABAA receptors in the retrorubral filed and ventral pallidum in rat jaw movements elicited by dopaminergic stimulation of the nucleus accumbens shell. Eur J Pharmacol 510:39–47
Uchino K, Higashiyama K, Kato T, Haque T, Sato F, Tomita A, Tsutsumi K, Moritani M, Yamamura K, Yoshida A (2015) Jaw movement-related primary somatosensory cortical area in the rat. Brain Res 284:55–64
Uemura Y, Haque T, Sato F, Tsutsumi Y, Ohara H, Oka A, Furuta T, Bae YC, Yamashiro T, Tachibana Y, Yoshida A (2020) Proprioceptive thalamus receiving forelimb and neck muscle spindle inputs via the external cuneate nucleus in the rat. Brain Struct Funct 225:2177–2192
Valverde F (1962) Reticular formation of the albino rat’s brain stem cytoarchitecture and corticofugal connections. J Comp Neurol 119:25–53
Van Eden CG, Lamme VA, Uylings HB (1992) Heterotopic cortical afferents to the medial prefrontal cortex in the rat. A combined retrograde and anterograde tracer study. Eur J Neurosci 4:77–97
VanderWerf F, Aramideh M, Ongerboer de Visser BW, Baljet B, Speelman JD, Otto AJ (1997) A retrograde double fluorescent tracing study of the levator palpebrae superioris muscle in the cynomolgus monkey. Exp Brain Res 113:174–179
Vidal-Gonzalez I, Vidal-Gonzalez B, Rauch SL, Quirk GJ (2006) Microstimulation reveals opposing influences of prelimbic and infralimbic cortex on the expression of conditioned fear. Learn Mem 13:728–733
Weiner S, Shaikh MB, Siegel A (1993) Electromyographic activity in the masseter muscle resulting from stimulation of hypothalamic behavioral sites in the cat. J Orofac Pain 7:370–377
Wiesendanger R, Wiesendanger M (1982) The corticopontine system in the rat. II. The Projection Pattern J Comp Neurol 208:227–238
Yamamoto T, Yuyama N, Kawamura Y (1981) Cortical neurons responding to tactile, thermal and taste stimulations of the rat’s tongue. Brain Res 221:202–206
Yamamoto T, Matsuo R, Kiyomitsu Y, Kitamura R (1988) Sensory inputs from the oral region to the cerebral cortex in behaving rats: an analysis of unit responses in cortical somatosensory and taste areas during ingestive behavior. J Neurophysiol 60:1303–1321
Yamamoto T, Matsuo R, Kiyomitsu Y, Kitamura R (1989) Sensory and motor responses of trigeminal and reticular neurons during ingestive behavior in rats. Exp Brain Res 76:386–400
Yamamoto M, Moritani M, Chang Z, Taki I, Tomita A, Ono T, Bae YC, Shigenaga Y, Yoshida A (2007) The somatotopic organization of trigeminal premotoneurons in the cat brainstem. Brain Res 1149:111–117
Yasui Y, Kayahara T, Shiroyama T, Nakano K (1993) Neurons in the intertrigeminal region of the rat send projection fibers to the superior colliculus. Neurosci Lett 159:39–42
Yasui Y, Tsumori T, Ando A, Domoto T, Kayahara T, Nakano K (1994) Descending projections from the superior colliculus to the reticular formation around the motor trigeminal nucleus and the parvicellular reticular formation of the medulla oblongata in the rat. Brain Res 656:420–426
Yasui Y, Tsumori T, Ando A, Domoto T (1995) Demonstration of axon collateral projections from the substantia nigra pars reticulata to the superior colliculus and the parvicellular reticular formation in the rat. Brain Res 674:122–126
Yoshida A, Taki I, Chang Z, Iida C, Haque T, Tomita A, Seki S, Yamamoto S, Masuda Y, Moritani M, Shigenaga Y (2009) Corticofugal projections to trigeminal motoneurons innervating antagonistic jaw muscles in rats as demonstrated by anterograde and retrograde tract tracing. J Comp Neurol 514:368–386
Yoshida A, Fujio T, Sato F, Ali MS, Haque T, Ohara H, Moritani M, Kato T, Dostrovsky JO, Tachibana Y (2017) Orofacial proprioceptive thalamus of the rat. Brain Struct Funct 222:2655–2669
Zhang GX, Sasamoto K (1990) Projections of two separate cortical areas for rhythmical jaw movements in the rat. Brain Res Bull 24:221–230
Zhou Q, Imbe H, Dubner R, Ren K (1999) Persistent Fos protein expression after orofacial deep or cutaneous tissue inflammation in rats: implications for persistent orofacial pain. J Comp Neurol 412:276–291
Funding
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (18K19641 and 18KK0259 to A.Y., and 17K11608 and 20K09888 to F.S.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors read and approved the final manuscript. AY and YTa conceptualized the hypothesis, designed and supervised the experiments and directed the data analysis. MI, FS, YM and YTs, carried out the experiments and data analysis. TF and KU helped with the experiments and data analysis. AY, MI, FA, YCB, YTa and TI finalized the figures and text.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no financial or other relationships to report that might lead to a conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Detailed protocols for the care and use of laboratory animals were approved by the animal ethics committees of the Osaka University Graduate School of Dentistry.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, A., Inoue, M., Sato, F. et al. Efferent and afferent connections of supratrigeminal neurons conveying orofacial muscle proprioception in rats. Brain Struct Funct 227, 111–129 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-021-02391-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-021-02391-9