Abstract
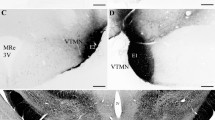
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) has a critical role in the central regulation of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary, and subsequently, thyroid hormone secretion from the thyroid gland. In addition to its role in the regulation of HPT axis, TRH is a potent regulator of prolactin (PRL) secretion by stimulating PRL secretion either directly from lactotrophs or indirectly via its action on the tuberoinfundibular dopamine (TIDA) neurons. In rodents, the TRH neurons which regulate TSH and thyroid hormone secretion, called hypophysiotropic TRH neurons, are in the medial subdivision of the parvicellular paraventricular nucleus (PVN). In humans, the PVN also contains a large population of TRH neurons, especially in its medial part, but the location of hypophysiotropic TRH neurons is not yet known. In addition to regulating TSH and PRL secretion, TRH also functions as a neurotransmitter/neuromodulator. In rodents and teleosts, TRH axons densely innervate TIDA neurons to inhibit tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) biosynthesis, neuronal firing, and dopamine turnover which may contribute to increasing PRL secretion. No such connections have been reported in humans, although dopaminergic neurons express TRH receptors and TRH also regulates PRL secretion. The objectives of this study were to map TRH-IR and TH-IR structures in the human hypothalamus with single-label light microscopic immunocytochemistry and study their interaction with double-label light microscopic immunocytochemistry. We show that TRH-IR nerve terminals densely surround TH-IR neurons (perikarya and dendrites) in the infundibulum of the human hypothalamus. The micrographs illustrating these juxtapositions were taken by Olympus BX45 microscope equipped with a digital camera and with 100X oil immersion objective. Composite images were created from the consecutive micrographs if the neurons were larger than the frame of the camera, using Adobe Photoshop software. As no gaps between TRH-IR and TH-IR elements were seen, these contacts may be functional synapses by which TRH regulates the activity of dopaminergic neurons and subsequently TSH and PRL secretion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albanese A, Altavista MC, Rossi P (1986) Organization of central nervous system dopaminergic pathways. J Neural Transm Suppl 22:3–17
Ansari MS, Almalki MH (2016) Primary hypothyroidism with markedly high prolactin. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 7:35
Bjorklund A, Nobin A (1973) Fluorescence histochemical and microspectrofluorometric mapping of dopamine and noradrenaline cell groups in the rat diencephalon. Brain Res 51:193–205
Boler J, Enzmann F, Folkers K, Bowers CY, Schally AV (1969) The identity of chemical and hormonal properties of the thyrotropin releasing hormone and pyroglutamyl-histidyl-proline amide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 37:705–710
Burgus R, Dunn TF, Desiderio D, Guillemin R (1969) Molecular structure of the hypothalamic hypophysiotropic TRF factor of ovine origin: mass spectrometry demonstration of the PCA-His-Pro-NH2 sequence. C R Acad Hebd Seances Acad Sci D 269:1870–1873
Dudas B (2013) Anatomy of the human hypothalamus, the human hypothalamus: anatomy, functions and disorders, edited by B. Nova Scientific Publishers, Dudas
Dudas B, Baker M, Rotoli G, Grignol G, Bohn MC, Merchenthaler I (2010) Distribution and morphology of the catecholaminergic neural elements in the human hypothalamus. Neuroscience 171:187–195
Dudas B, Merchenthaler I (2001) Catecholaminergic axons innervate LH-releasing hormone immunoreactive neurons of the human diencephalon. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:5620–5626
Dudas B, Merchenthaler I (2006) Three-dimensional representation of the neurotransmitter systems of the human hypothalamus: inputs of the gonadotrophin hormone-releasing hormone neuronal system. J Neuroendocrinol 18:79–95
Erlanger BF, Borek F, Beiser SM, Lieberman S (1957) Steroid-protein conjugates. I. Preparation and characterization of conjugates of bovine serum albumin with testosterone and with cortisone. J Biol Chem 228:713–727
Felten DL (1976) Catecholamine neurons in the squirrel monkey hypothalamus. J Neural Transm 39:269–280
Felten DL, Laties AM, Carpenter MB (1974) Monoamine-containing cell bodies in the squirrel monkey brain. Am J Anat 139:153–165
Felten DL, Sladek JR Jr (1983) Monoamine distribution in primate brain V. Monoaminergic nuclei: anatomy, pathways and local organization. Brain Res Bull 10:171–284
Fliers E, Noppen NW, Wiersinga WM, Visser TJ, Swaab DF (1994) Distribution of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)-containing cells and fibers in the human hypothalamus. J Comp Neurol 350:311–323
Foster GA, Hokfelt T, Coyle JT, Goldstein M (1985) Immunohistochemical evidence for phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase-positive/tyrosine hydroxylase-negative neurones in the retina and the posterior hypothalamus of the rat. Brain Res 330:183–188
Freeman ME, Kanyicska B, Lerant A, Nagy G (2000) Prolactin: structure, function, and regulation of secretion. Physiol Rev 80:1523–1631
Frohlich E, Wahl R (2019) The forgotten effects of thyrotropin-releasing hormone:metabolic functions and medical applications. Front Neuroendocrinol 52:29–43
Galas L, Raoult E, Tonon MC, Okada R, Jenks BG, Castano JP, Kikuyama S, Malagon M, Roubos EW, Vaudry H (2009) TRH acts as a multifunctional hypophysiotropic factor in vertebrates. Gen Comp Endocrinol 164:40–50
Gallyas F, Gorcs T, Merchenthaler I (1982) High-grade intensification of the end-product of the diaminobenzidine reaction for peroxidase histochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem 30:183–184
Gallyas F, Merchenthaler I (1988) Copper-H2O2 oxidation strikingly improves silver intensification of the nickel-diaminobenzidine (Ni-DAB) end-product of the peroxidase reaction. J Histochem Cytochem 36:807–810
Goldstein J, Perello M, Nillni EA (2007) PreproThyrotropin-releasing hormone 178–199 affects tyrosine hydroxylase biosynthesis in hypothalamic neurons: a possible role for pituitary prolactin regulation. J Mol Neurosci 31:69–82
Grattan DR (2015) 60 years of neuroendocrinology: the hypothalamo-prolactin axis. J Endocrinol 226:T101–T122
Hokfelt T, Fuxe K, Johansson O, Jeffcoate S, White N (1975a) Distribution of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) in the central nervous system as revealed with immunohistochemistry. Eur J Pharmacol 34:389–392
Hokfelt T, Fuxe K, Johansson O, Jeffcoate S, White N (1975b) Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH)-containing nerve terminals in certain brain stem nuclei and in the spinal cord. Neurosci Lett 1:133–139
Hokfelt T, Johansson O, Ljungdahl A, Lundberg JM, Schultzberg M (1980) Peptidergic neurones. Nature 284:515–521
Honbo KS, van Herle AJ, Kellett KA (1978) Serum prolactin levels in untreated primary hypothyroidism. Am J Med 64:782–787
Ishikawa K, Taniguchi Y, Inoue K, Kurosumi K, Suzuki M (1988) Immunocytochemical delineation of thyrotrophic area: origin of thyrotropin-releasing hormone in the median eminence. Neuroendocrinology 47:384–388
Jackson IM (1980) TRH in the rat nervous system: identity with synthetic TRH on high performance liquid chromatography following affinity chromatography. Brain Res 201:245–248
Jackson IM, Reichlin S (1974) Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH): distribution in hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic brain tissues of mammalian and submammalian chordates. Endocrinology 95:854–862
Jacobs LS, Snyder PJ, Wilber JF, Utiger RD, Daughaday WH (1971) Increased serum prolactin after administration of synthetic thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 33:996–998
Jokic D, Wang X (2011) Primary hypothyroidism associated with hyperprolactinemia and pituitary macroadenoma. Thyroid Sci 6:1–4
Joseph-Bravo P, Jaimes-Hoy L, Uribe RM, Charli JL (2015) 60 YEARS OF NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY: TRH, the first hypophysiotropic releasing hormone isolated: control of the pituitary-thyroid axis. J Endocrinol 227:X3
Kadar A, Sanchez E, Wittmann G, Singru PS, Fuzesi T, Marsili A, Larsen PR, Liposits Z, Lechan RM, Fekete C (2010) Distribution of hypophysiotropic thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)-synthesizing neurons in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of the mouse. J Comp Neurol 518:3948–3961
Kawano H, Tsuruo Y, Bando H, Daikoku S (1991) Hypophysiotropic TRH-producing neurons identified by combining immunohistochemistry for pro-TRH and retrograde tracing. J Comp Neurol 307:531–538
Koller KJ, Wolff RS, Warden MK, Zoeller RT (1987) Thyroid hormones regulate levels of thyrotropin-releasing-hormone mRNA in the paraventricular nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:7329–7333
Kubek MJ, Lorincz MA, Wilber JF (1977) The identification of thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) in hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic loci of the human nervous system. Brain Res 126:196–200
Landgraf R, Neumann ID (2004) Vasopressin and oxytocin release within the brain: a dynamic concept of multiple and variable modes of neuropeptide communication. Front Neuroendocrinol 25:150–176
Lechan RM, Fekete C (2006) The TRH neuron: a hypothalamic integrator of energy metabolism. Prog Brain Res 153:209–235
Lechan RM, Hollenberg A, Fekete C (2009) Hypothalamic-pituitarythyroid axis: organization, neural/endocrine control of TRH. In: Squire LR (ed) Encyclopedia of neuroscience. Academic Press, Oxford, UK, pp 75–87
Lechan RM, Segerson TP (1989) Pro-TRH gene expression and precursor peptides in rat brain. Observations by hybridization analysis and immunocytochemistry. Ann N Y Acad Sci 553:29–59
Lyons DJ, Horjales-Araujo E, Broberger C (2010) Synchronized network oscillations in rat tuberoinfundibular dopamine neurons: switch to tonic discharge by thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Neuron 65:217–229
Manaker S, Eichen A, Winokur A, Rhodes CH, Rainbow TC (1986) Autoradiographic localization of thyrotropin releasing hormone receptors in human brain. Neurology 36:641–646
Mantyh PW, Hunt SP (1985) Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) receptors. Localization by light microscopic autoradiography in rat brain using [3H][3-Me-His2]TRH as the radioligand. J Neurosci 5:551–561
Mefford IN (1988) Epinephrine in mammalian brain. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 12:365–388
Merchenthaler I, Csernus V, Csontos C, Petrusz P, Mess B (1988) New data on the immunocytochemical localization of thyrotropin-releasing hormone in the rat central nervous system. Am J Anat 181:359–376
Merchenthaler I, Liposits Z (1994) Mapping of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) neuronal systems of rat forebrain projecting to the median eminence and the OVLT. Immunocytochemistry combined with retrograde labeling at the light and electron microscopic levels. Acta Biol Hung 45:361–374
Metcalf G, Dettmar PW (1981) Is thyrotropin releasing hormone an endogenous ergotropic substance in the brain? Lancet 1:586–589
Mihaly E, Fekete C, Legradi G, Lechan RM (2001) Hypothalamic dorsomedial nucleus neurons innervate thyrotropin-releasing hormone-synthesizing neurons in the paraventricular nucleus. Brain Res 891:20–31
Nieuwenhuys R (1985) Chemoarchitecture of the brain. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg
Okon E, Koch Y (1976) Localisation of gonadotropin-releasing and thyrotropin-releasing hormones in human brain by radioimmunoassay. Nature 263:345–347
Parker CR Jr, Porter JC (1983) Regional localization and subcellular compartmentalization of thyrotropin-releasing hormone in adult human brain. J Neurochem 41:1614–1622
Ruggiero DA, Ross CA, Anwar M, Park DH, Joh TH, Reis DJ (1985) Distribution of neurons containing phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase in medulla and hypothalamus of rat. J Comp Neurol 239:127–154
Russell JA (2018) Fifty Years of Advances in Neuroendocrinology. Brain Neurosci Adv 2:2398212818812014
Sharif NA, Burt DR (1983) Receptors for thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) in rabbit spinal cord. Brain Res 270:259–263
Singh O, Pradhan DR, Nagalakshmi B, Kumar S, Mitra S, Sagarkar S, Sakharkar AJ, Lechan RM, Singru PS (2019) Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) in the brain and pituitary of the teleost, Clarias batrachus and its role in regulation of hypophysiotropic dopamine neurons. J Comp Neurol 527:1070–1101
Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE (1980) Paraventricular nucleus: a site for the integration of neuroendocrine and autonomic mechanisms. Neuroendocrinology 31:410–417
Tashjian AH Jr, Barowsky NJ, Jensen DK (1971) Thyrotropin releasing hormone: direct evidence for stimulation of prolactin production by pituitary cells in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 43:516–523
Tillet Y (1994) Catecholaminergic neuronal systems in the diencephalon of mammals. In: Smeets WJ, Reinwer A (eds) Phylogeny and development of catecholamine systems in the CNS of vertebrates. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 207–246
Ungerstedt U (1971) Stereotaxic mapping of the monoamine pathways in the rat brain. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 367:1–48
van Vulpen EH, Yang CR, Nissen R, Renaud LP (1999) Hypothalamic A14 and A15 catecholamine cells provide the dopaminergic innervation to the supraoptic nucleus in rat: a combined retrograde tracer and immunohistochemical study. Neuroscience 93:675–680
Vogel RA, Cooper BR, Barlow TS, Prange AJ Jr, Mueller RA, Breese GR (1979) Effects of thyrotropin-releasing hormone on locomotor activity, operant performance and ingestive behavior. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 208:161–168
Wittmann G, Fuzesi T, Singru PS, Liposits Z, Lechan RM, Fekete C (2009) Efferent projections of thyrotropin-releasing hormone-synthesizing neurons residing in the anterior parvocellular subdivision of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. J Comp Neurol 515:313–330
Yen PM (2001) Physiological and molecular basis of thyroid hormone action. Physiol Rev 81:1097–1142
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have nothing to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dudas, B., Merchenthaler, I. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone axonal varicosities appear to innervate dopaminergic neurons in the human hypothalamus. Brain Struct Funct 225, 2193–2201 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-020-02120-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-020-02120-8