Abstract
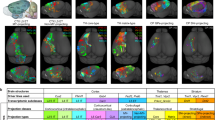
Quantifying the distribution of cells in every brain region is fundamental to attaining a comprehensive census of distinct neuronal and glial types. Until recently, estimating neuron numbers involved time-consuming procedures that were practically limited to stereological sampling. Progress in open-source image recognition software, growth in computing power, and unprecedented neuroinformatics developments now offer the potentially paradigm-shifting alternative of comprehensive cell-by-cell analysis in an entire brain region. The Allen Brain Atlas provides free digital access to complete series of raw Nissl-stained histological section images along with regional delineations. Automated cell segmentation of these data enables reliable and reproducible high-throughput quantification of regional variations in cell count, density, size, and shape at whole-system scale. While this strategy is directly applicable to any regions of the mouse brain, we first deploy it here on the closed-loop circuit of the hippocampal formation: the medial and lateral entorhinal cortices; dentate gyrus (DG); areas Cornu Ammonis 3 (CA3), CA2, and CA1; and dorsal and ventral subiculum. Using two independent image processing pipelines and the adult mouse reference atlas, we report the first cellular-level soma segmentation in every sub-region and non-principal layer of the left hippocampal formation through the full rostral-caudal extent. It is important to note that our techniques excluded the layers with the largest number of cells, DG granular and CA pyramidal, due to dense packing. The numerical estimates for the remaining layers are corroborated by traditional stereological sampling on a data subset and well match sparse published reports.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abercrombie M (1946) Estimation of nuclear population from microtome sections. Anat Rec 94:239–247. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.1090940210
Allen Data Production (2011) Allen mouse brain atlas technical white paper: in situ hybridization data production. http://help.brain-map.org/download/attachments/2818169/ABADataProductionProcesses.pdf. Accessed 15 Feb 2017
Amaral DG, Ishizuka N, Claiborne B (1990) Chapter 1 Chapter Neurons, numbers and the hippocampal network. Progress in brain research understanding the brain through the hippocampus the hippocampal region as a model for studying brain structure and function. pp 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0079-6123(08)61237-6
Andrade JP, Madeira M, Paula-Barbosa M (2000) Sexual dimorphism in the subiculum of the rat hippocampal formation. Brain Res 875:125–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(00)02605-6
Andrey P, Kiêu K, Kress C et al (2010) Statistical analysis of 3D images detects regular spatial distributions of centromeres and chromocenters in animal and plant nuclei. PLoS Comput Biol. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000853
Ascoli GA, Alonso-Nanclares L, Anderson S et al (2008) Petilla terminology: nomenclature of features of GABAergic interneurons of the cerebral cortex. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:557–568. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2402
Bahney J, Bartheld CS (2017) The cellular composition and glia-neuron ratio in the spinal cord of a human and a nonhuman primate: comparison with other species and brain regions. Anat Rec 301:697–710. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.23728
Baldwin SA, Gibson T, Callihan CT, Sullivan PG, Palmer E, Scheff SW (1997) Neuronal cell loss in the CA3 subfield of the hippocampus following cortical contusion utilizing the optical disector method for cell counting. J Neurotrauma 14:385–398. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.1997.14.385
Bayer S, Yackel J, Puri P (1982) Neurons in the rat dentate gyrus granular layer substantially increase during juvenile and adult life. Science 216:890–892. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7079742
Bezaire MJ, Raikov I, Burk K, Vyas D, Soltesz I (2016) Interneuronal mechanisms of hippocampal theta oscillations in a full-scale model of the rodent CA1 circuit. ELife. https://doi.org/10.7554/elife.18566
Bhanu B, Peng J (2000) Adaptive integrated image segmentation and object recognition. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part C (Appl Rev) 30:427–441. https://doi.org/10.1109/5326.897070
Boss BD, Peterson GM, Cowan WM (1985) On the number of neurons in the dentate gyrus of the rat. Brain Res 338:144–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(85)90257-4
Boyce RW, Gundersen HJ (2018) The automatic proportionator estimator is highly efficient for estimation of total number of sparse cell populations. Front Neuroanat. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2018.00019
Bray M, Vokes MS, Carpenter AE (2015) Using cell profiler for automatic identification and measurement of biological objects in images. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142727.mb1417s109
Brun VH, Solstad T, Kjelstrup KB, Fyhn M, Witter MP, Moser EI, Moser M (2008) Progressive increase in grid scale from dorsal to ventral medial entorhinal cortex. Hippocampus 18(12):1200–1212. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.20504
Calhoun ME, Kurth D, Phinney AL et al (1998) Hippocampal neuron and synaptophysin-positive bouton number in aging C57BL/6 mice. Neurobiol Aging 19:599–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0197-4580(98)00098-0
Canto CB, Wouterlood FG, Witter MP (2008) What does the anatomical organization of the entorhinal cortex tell us? Neural Plast 2008:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/381243
Erö C, Gewaltig M, Keller D, Markram H (2018) A cell atlas for the mouse brain. Front Neuroinform. https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2018.00084
Fitting S, Booze RM, Hasselrot U, Mactutus CF (2009) Dose-dependent long-term effects of Tat in the rat hippocampal formation: a design-based stereological study. Hippocampus. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.20648
García-Cabezas MÁ, John YJ, Barbas H, Zikopoulos B (2016) Distinction of neurons, glia and endothelial cells in the cerebral cortex: an algorithm based on cytological features. Front Neuroanat. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2016.00107
Giocomo LM, Hasselmo ME (2008) Time constants of h current in layer II stellate cells differ along the dorsal to ventral axis of medial entorhinal cortex. J Neurosci 28:9414–9425. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3196-08.2008
Goldenberg TM, Bakay RA, Ribak CE (1995) Electron microscopy of cell islands in layer II of the primate entorhinal cortex. J Comp Neurol 355:51–66. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.903550108
Gonzalez-Riano C, Tapia-González S, García A, Muñoz A, DeFelipe J, Barbas C (2017) Metabolomics and neuroanatomical evaluation of post-mortem changes in the hippocampus. Brain Struct Funct 222:2831–2853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-017-1375-5
Grady MS, Charleston JS, Maris D, Witgen BM, Lifshitz J (2003) Neuronal and glial cell number in the hippocampus after experimental traumatic brain injury: analysis by stereological estimation. J Neurotrauma 20:929–941. https://doi.org/10.1089/089771503770195786
Häder D (2001) Image analysis: methods and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Hasselmo ME, Stern CE (2015) Current questions on space and time encoding. Hippocampus 25:744–752. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.22454
Hedreen JC (1998a) Lost caps in histological counting methods. Anat Rec 250:366–372. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0185(199803)250:3%3c366:aid-ar11%3e3.3.co;2-v
Hedreen JC (1998b) What was wrong with the Abercrombie and empirical cell counting methods? A review. Anat Rec 250:373–380. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0185(199803)250:3%3c373:aid-ar12%3e3.0.co;2-l
Herculano-Houzel S, Lent R (2005) Isotropic fractionator: a simple, rapid method for the quantification of total cell and neuron numbers in the brain. J Neurosci 25:2518–2521. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.4526-04.2005
Herculano-Houzel S, Mota B, Lent R (2006) Cellular scaling rules for rodent brains. PNAS 103:12138–12143. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0604911103
Herculano-Houzel S, Ribeiro P, Campos L, Silva AV, Torres LB, Catania KC, Kaas JH (2011) Updated neuronal scaling rules for the brains of glires (rodents/lagomorphs). Brain Behav Evol 78:302–314. https://doi.org/10.1159/000330825
Herculano-Houzel S, Watson C, Paxinos G (2013) Distribution of neurons in functional areas of the mouse cerebral cortex reveals quantitatively different cortical zones. Front Neuroanat. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2013.00035
Hosseini-Sharifabad M, Nyengaard JR (2007) Design-based estimation of neuronal number and individual neuronal volume in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci Methods 162:206–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.01.009
Hu T, Xu Q, Lv W, Liu Q (2017) Touching soma segmentation based on the rayburst sampling algorithm. Neuroinformatics 15:383–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-017-9336-y
Insausti AM, Megı́as M, Crespo D et al (1998a) Hippocampal volume and neuronal number in Ts65Dn mice: a murine model of down syndrome. Neurosci Lett 253:175–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(98)00641-7
Insausti R, Herrero MT, Witter MP (1998b) Entorhinal cortex of the rat: cytoarchitectonic subdivisions and the origin and distribution of cortical efferents. Hippocampus 7(2):146–183. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1098-1063(1997)7:23.0.co;2-l
Insel TR, Landis SC, Collins FS (2013) The NIH brain initiative. Science 340:687–688. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1239276
Jinno S, Fleischer F, Eckel S, Schmidt V, Kosaka T (2007) Spatial arrangement of microglia in the mouse hippocampus: a stereological study in comparison with astrocytes. Glia 55(13):1334–1347. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.20552
Jones AR, Overly CC, Sunkin SM (2009) The Allen Brain Atlas: 5 years and beyond. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:821–828. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2722
Kaae SS, Chen F, Wegener G, Madsen TM, Nyengaard JR (2012) Quantitative hippocampal structural changes following electroconvulsive seizure treatment in a rat model of depression. Synapse 66:667–676. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.21553
Kandel ER (2004) The molecular biology of memory storage: a dialog between genes and synapses. Biosci Rep 24:475–522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10540-005-2742-7
Kandel ER, Markram H, Matthews PM, Yuste R, Koch C (2013) Neuroscience thinks big (and collaboratively). Nat Rev Neurosci 14:659–664. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3578
Kayasandik CB, Labate D (2016) Improved detection of soma location and morphology in fluorescence microscopy images of neurons. J Neurosci Methods 274:61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2016.09.007
Kim Y, Yang GR, Pradhan K et al (2017) Brain-wide maps reveal stereotyped cell-type-based cortical architecture and subcortical sexual dimorphism. Cell. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.020
Kitamura T, Pignatelli M, Suh J, Kohara K, Yoshiki A, Abe K, Tonegawa S (2014) Island cells control temporal association memory. Science 343(6173):896–901. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1244634
Lamprecht M, Sabatini D, Carpenter A (2007) Cell Profiler™: free, versatile software for automated biological image analysis. Biotechniques 42:71–75. https://doi.org/10.2144/000112257
Latorre A, Alonso-Nanclares L, Muelas S, Peña J, Defelipe J (2013) Segmentation of neuronal nuclei based on clump splitting and a two-step binarization of images. Expert Syst Appl 40:6521–6530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2013.06.010
Lau C, Ng L, Thompson C et al (2008) Exploration and visualization of gene expression with neuroanatomy in the adult mouse brain. BMC Bioinform 9:153. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-153
Lister JP, Tonkiss J, Blatt GJ, Kemper TL, Debassio WA, Galler JR, Rosene DL (2006) Asymmetry of neuron numbers in the hippocampal formation of prenatally malnourished and normally nourished rats: a stereological investigation. Hippocampus 16:946–958. https://doi.org/10.1002/hipo.20221
Long JM, Kalehua AN, Muth NJ et al (1998) Stereological analysis of astrocyte and microglia in aging mouse hippocampus. Neurobiol Aging 19:497–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0197-4580(98)00088-8
Luengo-Sanchez S, Bielza C, Benavides-Piccione R, Fernaud-Espinosa I, Defelipe J, Larrañaga P (2015) A univocal definition of the neuronal soma morphology using Gaussian mixture models. Front Neuroanat. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2015.00137
Maechler M (2016) Package ‘diptest’ (Tech.). Retrieved June 15, 2018, from https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/diptest/diptest.pdf. Accessed 15 June 2018
Malberg JE, Eisch AJ, Nestler EJ, Duman RS (2000) Chronic antidepressant treatment increases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 20:9104–9110
Meyer HS, Wimmer VC, Oberlaender M, Kock CP, Sakmann B, Helmstaedter M (2010) Number and laminar distribution of neurons in a thalamocortical projection column of rat vibrissal cortex. Cereb Cortex 20:2277–2286. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhq067
Miki T, Satriotomo I, Li H et al (2005) Application of the physical disector to the central nervous system: estimation of the total number of neurons in subdivisions of the rat hippocampus. Anat Sci Int 80:153–162. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1447-073x.2005.00121.x
Moser EI, Moser M, Mcnaughton BL (2017) Spatial representation in the hippocampal formation: a history. Nat Neurosci 20:1448–1464. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4653
Mulders W, West M, Slomianka L (1997) Neuron numbers in the presubiculum, parasubiculum, and entorhinal area of the rat. J Comp Neurol 385:83–94. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19970818)385:1%3c83:aid-cne5%3e3.0.co;2-8
Murakami TC, Mano T, Saikawa S et al (2018) A three-dimensional single-cell-resolution whole-brain atlas using CUBIC-X expansion microscopy and tissue clearing. Nat Neurosci 21:625–637. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0109-1
Nakatomi H, Kuriu T, Okabe S et al (2002) Regeneration of hippocampal pyramidal neurons after ischemic brain injury by recruitment of endogenous neural progenitors. Cell 110:429–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00862-0
Otsu N (1979) A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 9:62–66. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsmc.1979.4310076
Peng H, Roysam B, Ascoli GA (2013) Automated image computing reshapes computational neuroscience. BMC Bioinform 14:293. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-293
Quan T, Zheng T, Yang Z et al (2013) NeuroGPS: automated localization of neurons for brain circuits using L1 minimization model. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep01414
Rajkowska G (2000) Postmortem studies in mood disorders indicate altered numbers of neurons and glial cells. Biol Psychiatry 48:766–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-3223(00)00950-1
Rajkowska G, Clarke G, Mahajan G et al (2016) Differential effect of lithium on cell number in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex in adult mice: a stereological study. Bipolar Disord 18:41–51. https://doi.org/10.1111/bdi.12364
Ramsden M, Berchtold NC, Kesslak JP, Cotman CW, Pike CJ (2003) Exercise increases the vulnerability of rat hippocampal neurons to kainate lesion. Brain Res 971:239–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(03)02365-5
Rapp PR, Gallagher M (1996) Preserved neuron number in the hippocampus of aged rats with spatial learning deficits. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93:9926–9930. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.18.9926
Rasmussen T, Schliemann T, Sørensen JC, Zimmer J, West MJ (1996) Memory impaired aged rats: no loss of principal hippocampal and subicular neurons. Neurobiol Aging 17:143–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/0197-4580(95)02032-2
Ray S, Brecht M (2016) Structural development and dorsoventral maturation of the medial entorhinal cortex. ELife. https://doi.org/10.7554/elife.13343
Ropireddy D, Bachus S, Ascoli G (2012) Non-homogeneous stereological properties of the rat hippocampus from high-resolution 3D serial reconstruction of thin histological sections. Neuroscience 205:91–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.12.055
Sankur B (2004) Survey over image thresholding techniques and quantitative performance evaluation. J Electron Imaging 13:146. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.1631315
Schindelin J, Rueden CT, Hiner MC, Eliceiri KW (2015) The ImageJ ecosystem: an open platform for biomedical image analysis. Mol Reprod Dev 82:518–529. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrd.22489
Schmitz C, Hof P (2005) Design-based stereology in neuroscience. Neuroscience 130:813–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.08.050
Schmitz C, Eastwood BS, Tappan SJ et al (2014) Current automated 3D cell detection methods are not a suitable replacement for manual stereologic cell counting. Front Neuroanat. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnana.2014.00027
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2089
Sherwood CC, Stimpson CD, Raghanti MA et al (2006) Evolution of increased glia-neuron ratios in the human frontal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:13606–13611. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0605843103
Sousa N, Madeira MD, Paula-Barbosa MM (1998) Effects of corticosterone treatment and rehabilitation on the hippocampal formation of neonatal and adult rats. An unbiased stereological study. Brain Res 794:199–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(98)00218-2
Sun C, Kitamura T, Yamamoto J et al (2015) Distinct speed dependence of entorhinal island and ocean cells, including respective grid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112:9466–9471. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1511668112
Sunkin SM, Ng L, Lau C et al (2012) Allen Brain Atlas: an integrated spatio-temporal portal for exploring the central nervous system. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1042
Tapias V, Greenamyre JT (2014) A rapid and sensitive automated image-based approach for in vitro and in vivo characterization of cell morphology and quantification of cell number and neurite architecture. Curr Protoc Cytom. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142956.cy1233s68
Vinet J, Lemieux P, Tamburri A, Tiesinga P, Scafidi J, Gallo V, Sík A (2010) Subclasses of oligodendrocytes populate the mouse hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 31(3):425–438. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07082.x
West MJ, Slomianka L, Gundersen HJ (1991) Unbiased stereological estimation of the total number of neurons in the subdivisions of the rat hippocampus using the optical fractionator. Anat Rec 231:482–497. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.1092310411
Wheeler DW, White CM, Rees CL, Komendantov AO, Hamilton DJ, Ascoli GA (2015) Hippocampome.org: a knowledge base of neuron types in the rodent hippocampus. ELife. https://doi.org/10.7554/elife.09960
Witter M (2011) Entorhinal cortex. Scholarpedia 6:4380
Wu H, Rassoulpour A, Goodman JH, Scharfman HE, Bertram EH, Schwarcz R (2005) Kynurenate and 7-chlorokynurenate formation in chronically epileptic rats. Epilepsia 46:1010–1016. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2005.67404.x
Zhang D, Liu S, Song Y, Feng D, Peng H, Cai W (2018) Automated 3D soma segmentation with morphological surface evolution for neuron reconstruction. Neuroinformatics 16:153–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-017-9353-x
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Drs. Diek W. Wheeler (from the authors’ lab) and Christopher L. Rees (Harvard University) for critical discussions, and to Dr. Lydia Ng (Allen Institute for Brain Science) for sharing technical details about image scaling and resolution in the Allen Reference Atlas. This work was supported in part by grants R01 NS39600 and U01 MH114829 from the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attili, S.M., Silva, M.F.M., Nguyen, Tv. et al. Cell numbers, distribution, shape, and regional variation throughout the murine hippocampal formation from the adult brain Allen Reference Atlas. Brain Struct Funct 224, 2883–2897 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01940-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-019-01940-7